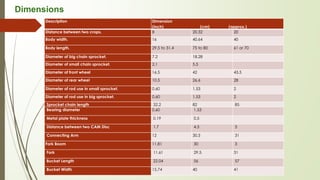
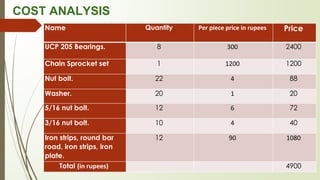
The document is a report submitted by nine students on a manual rice planting machine project under the supervision of an assistant professor. It provides background on rice cultivation in India and the need for mechanization. It then details the students' literature review on rice transplanting, describes the basic stages of rice cultivation, and presents production data for different countries. The report outlines the aims and plan of work for the project, including developing a prototype that is mechanical, easy to use, affordable and environmentally friendly. It provides the prototype's specifications and dimensions, description of how it works, advantages, limitations, cost analysis, and conclusions from the project with need for further improvements.