This document provides an overview of special education laws and strategies for supporting students with disabilities in general education classrooms. It discusses the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) and its requirements regarding identifying students with disabilities, providing a free and appropriate public education (FAPE), and educating students in the least restrictive environment (LRE). It also compares and contrasts different disability categories, provides examples of classroom accommodations and modifications, and offers inclusion tips.




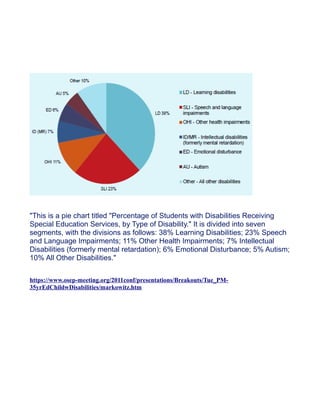






![References:
Crain Danielle,Thirty five years of Educating Students with Disabilities
https://www.osep-meeting.org/2011conf/presentations/Breakouts/Tue_PM-
35yrEdChildwDisabilities/markowitz.htm
Developmental Disabilities Increasing in US (2011)
http://www.cdc.gov/
ERIC Clearinghouse on Disabilities and Gifted Education. (1992). Legal foundations 1: Section 504 of
the Rehabilitation Act and the Americans with Disabilities Act. Reston, VA
Henderson,Kelly ,(2010) Overview of ADA, IDEA, and Section 504
Least Restrictive Environment [LRE] Law & Legal Definition
http://definitions.uslegal.com/l/least-restrictive-environment-lre/
MacLean, Kate ,(2001). Inclusive Teaching Guide
Overview of the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act OF 1997
(http://www.wrightslaw.com/bks/lawbk/ch4.idea.overview.pdf)
Overview of ADA, IDEA, and Section 504 Contents of the IEP (2010)
http://nichcy.org/schoolage/iep/iepcontents
Turnbull, Turnbull, & Wehmeyer, (2010), Exceptional Lives: Special Education in Today’s Schools, 6th
edition, Upper Saddle River, New Jersey](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalprojectese631-121014191233-phpapp01/85/Final-project-ese-631-12-320.jpg)