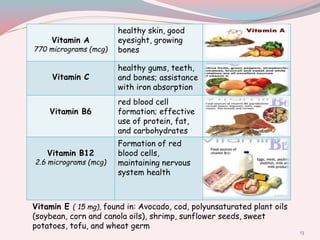
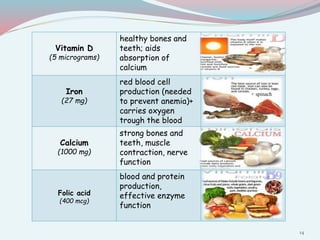
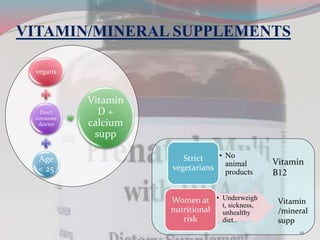
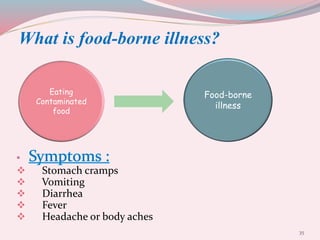
The document summarizes nutrition guidelines for pregnant women presented by nutrition students. It provides recommendations for a balanced diet including recommended daily intakes of proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients. It also discusses healthy weight gain during pregnancy, benefits of physical activity, common pregnancy issues like morning sickness and heartburn, and food safety risks. The key messages are that a balanced diet and moderate exercise are important for supporting the health of the mother and developing fetus, while avoiding foods with risks of foodborne illness like listeria, mercury, and toxoplasmosis.