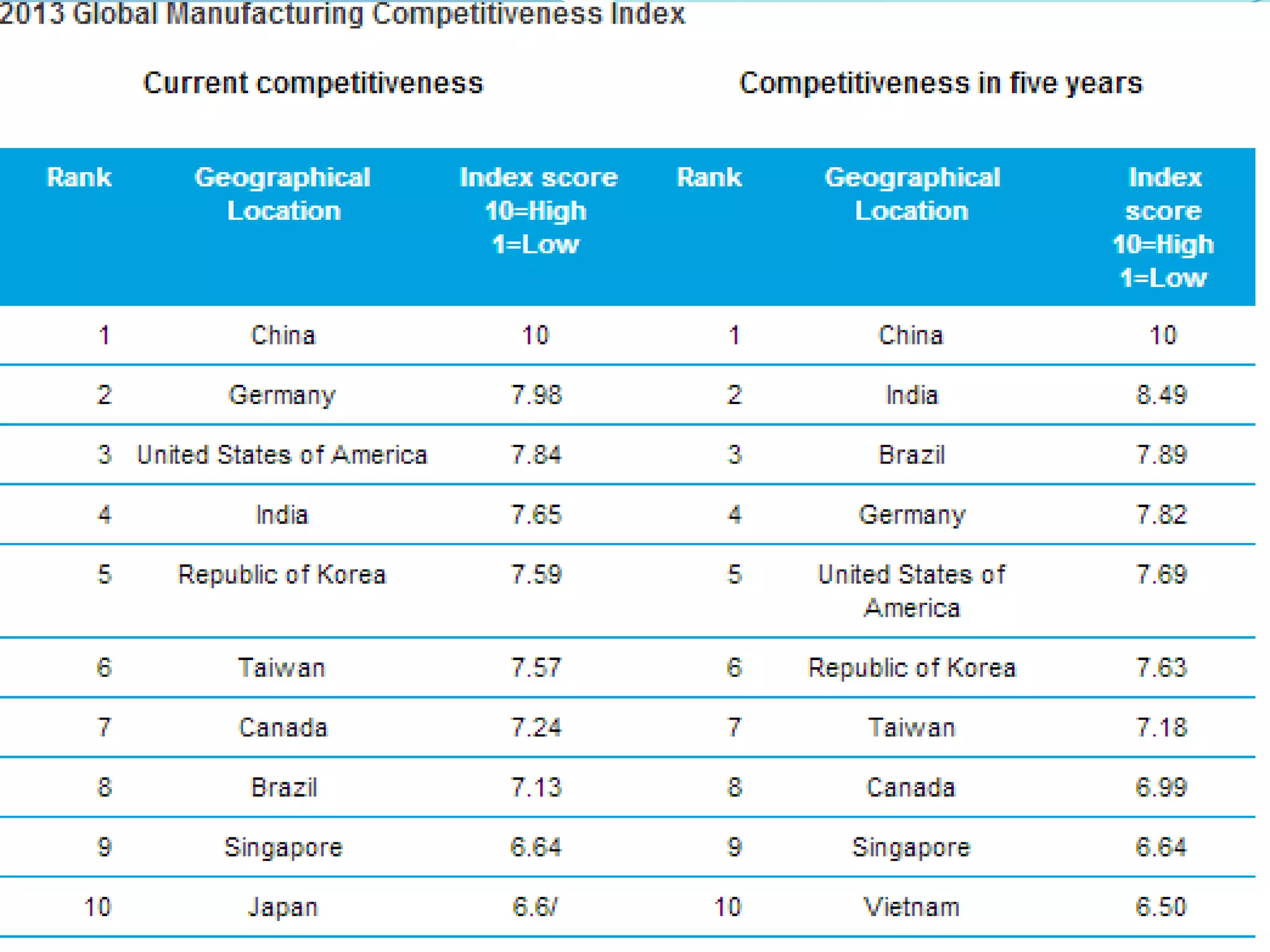
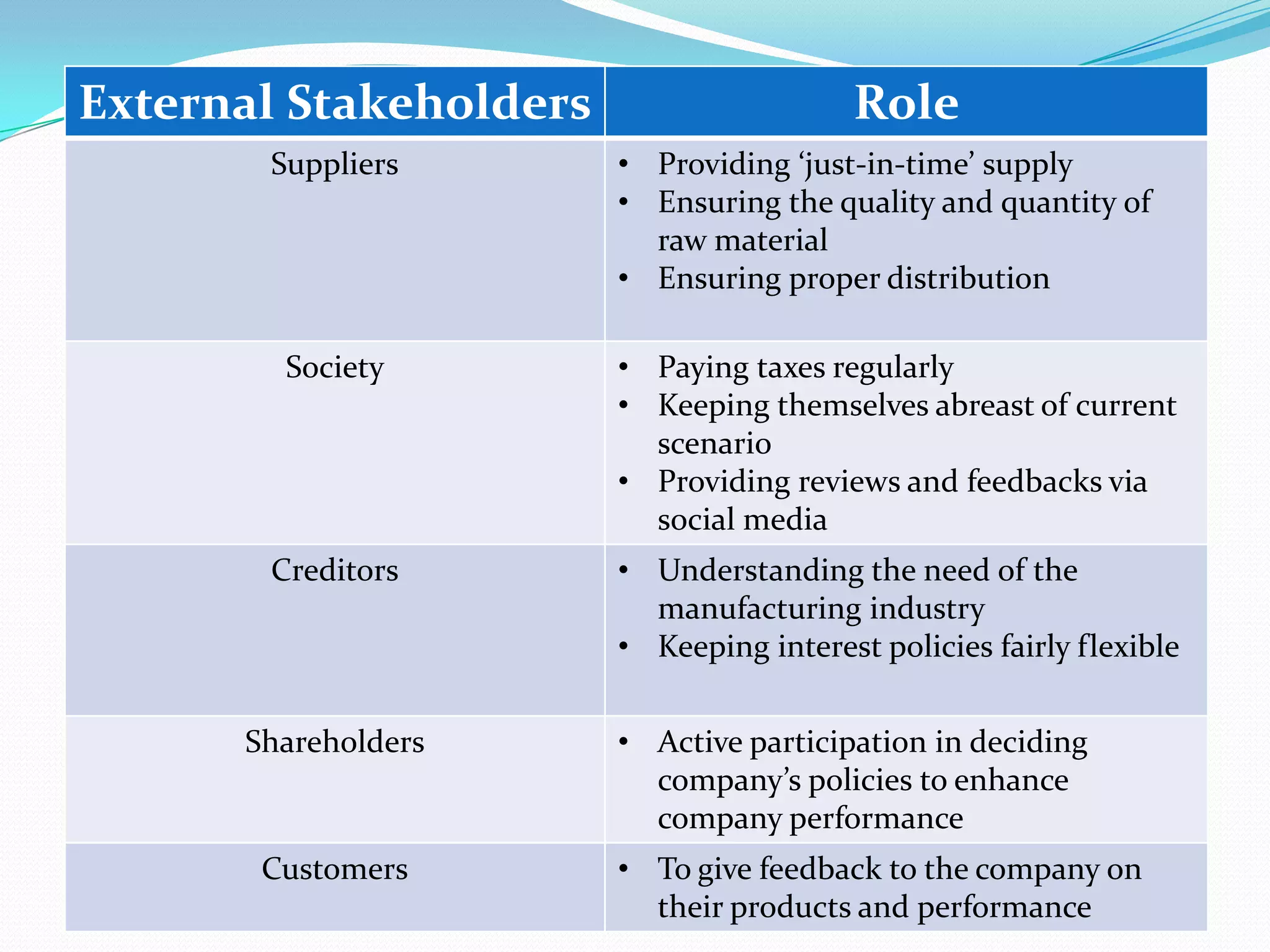
The document discusses a group project on making India a global manufacturing hub. It lists the group members and their professor mentor. It then discusses what defines a manufacturing hub and what factors like policy environment, infrastructure, education, and automation help make a country a manufacturing leader. It analyzes India's major manufacturing industries like textiles, chemicals, food processing, and steel and the role of stakeholders in supporting these sectors. For example, the government supports the textile industry through R&D, training, and financial assistance. Weaknesses in India's manufacturing include infrastructure gaps and rigid labor laws compared to countries like China. The document also discusses the Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor policy to strengthen infrastructure.