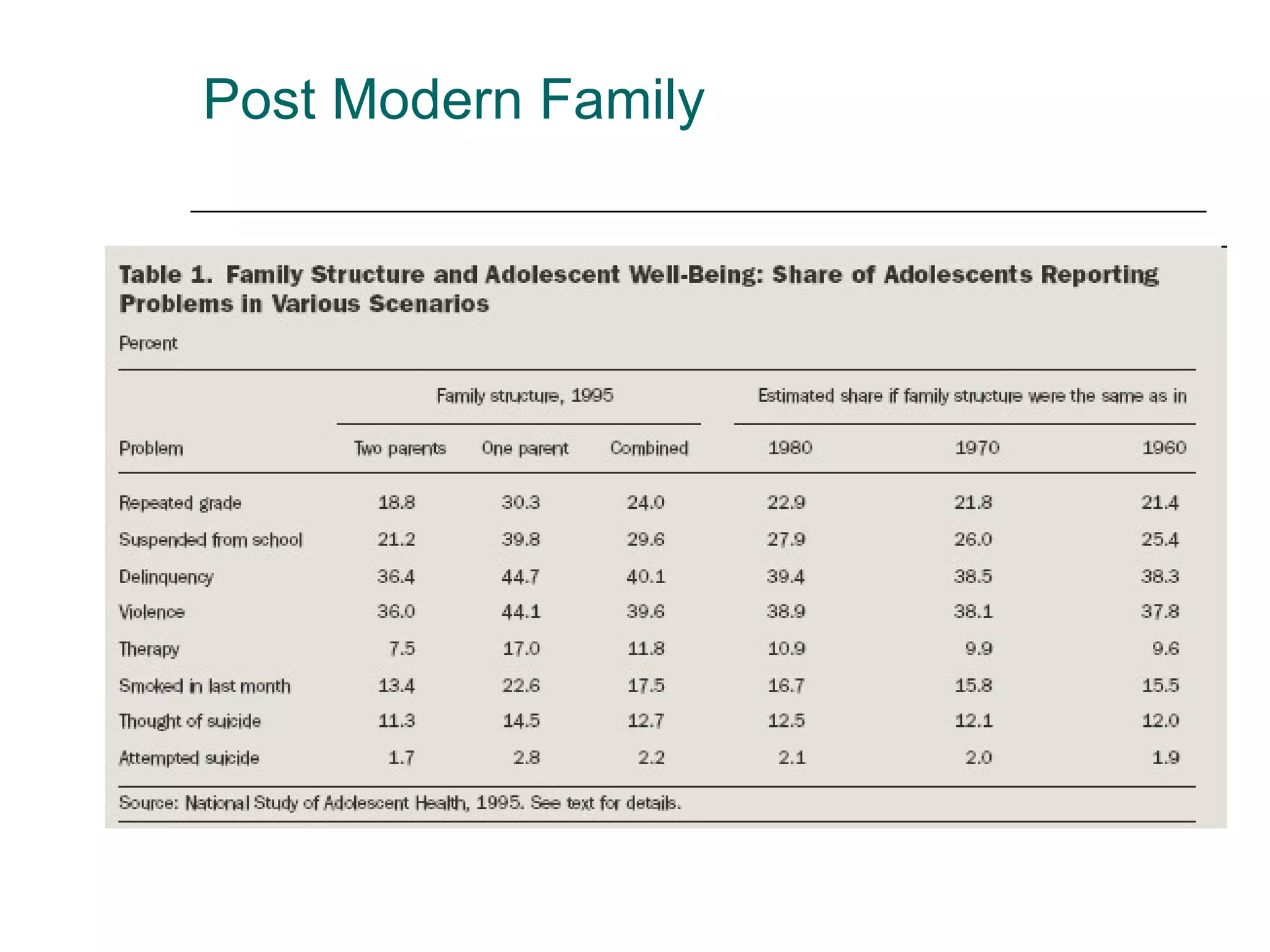
The document discusses the social context of curriculum and how various social forces influence education. It notes that students come from diverse backgrounds and schools have become more diverse. It also discusses the changing nature of families and society. Goals for education are outlined but statistics show many students still face challenges. Reform efforts at different levels are mentioned as well as different approaches to charter schools. Traditional schooling is compared to more modern approaches.