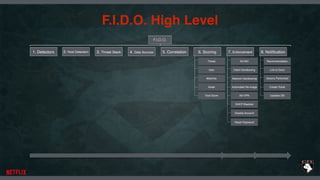
The document discusses the F.I.D.O. (Fully Integrated Defense Operation) framework aimed at addressing human and technical challenges in cybersecurity. It highlights the overwhelming nature of security alerts, the inefficiency of current practices, and proposes a solution through orchestration that improves response times and reduces false positives. The document emphasizes the need for improved machine-learning applications, data integration, and automated processes to enhance security operations.


























![Correlation Initiatives
• More data, different data, more data points
• Move past 1000 vectors
• More indicators
• Move laterally across data (detector, threat feed, whatever)
• Drill in multiple layers deep
• Better data enrichment algorithms for higher quality associations, thresholds,
increments
• Independent processes for correlation ( micro services ]
• Continue to evaluate ML for correlation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fido-public-161213051221/85/Fully-Integrated-Defense-Operation-28-320.jpg)