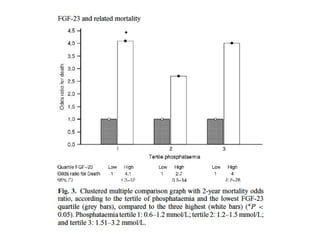
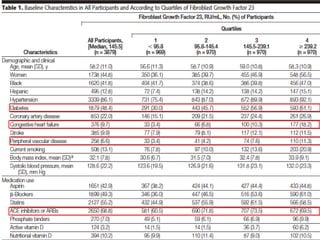
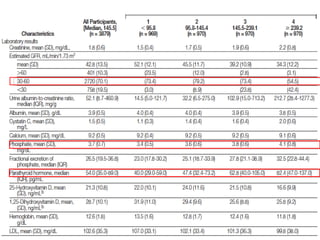
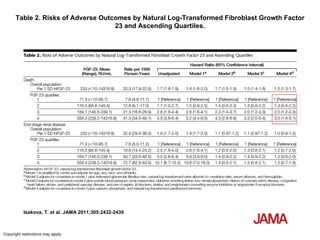
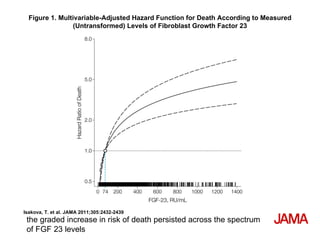
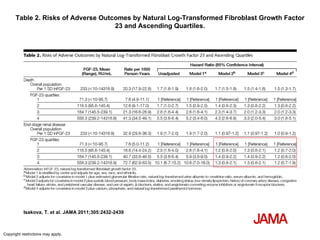
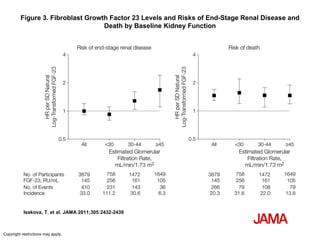
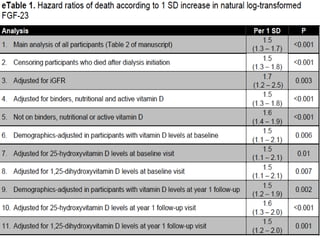
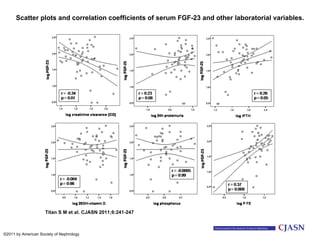
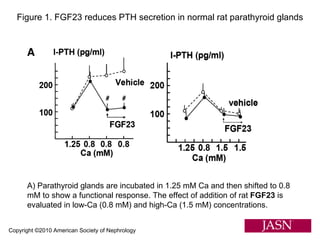
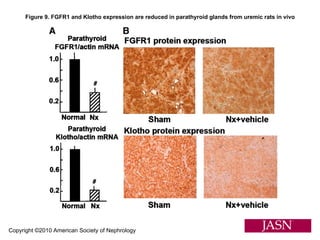
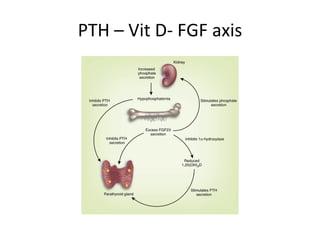
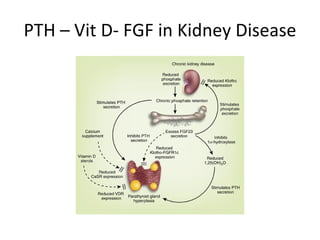
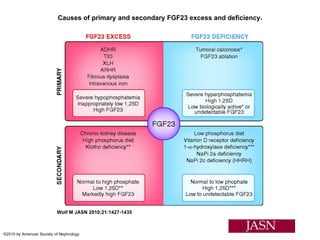
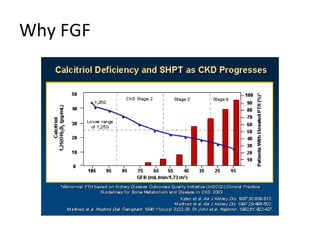
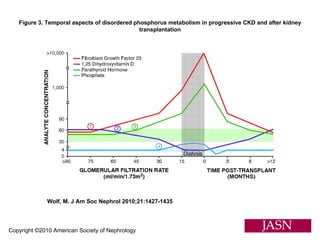
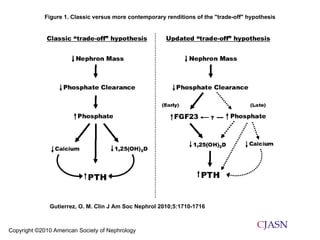
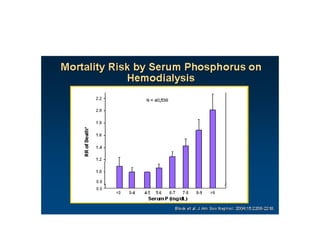
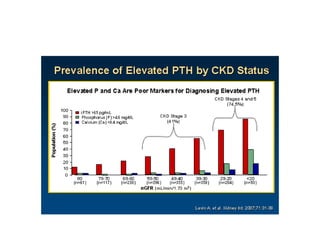
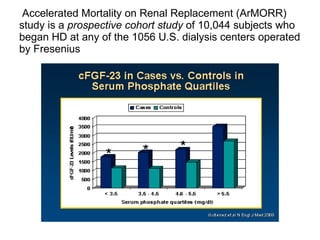
This document summarizes several studies on Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 (FGF23) and its relationship to outcomes in kidney disease. Elevated FGF23 levels were found to independently predict mortality and progression of chronic kidney disease. A prospective study of over 3,800 patients with stages 2-4 CKD found that higher FGF23 levels correlated with worse kidney function and were a strong independent risk factor for death, even after adjusting for other risk factors. However, elevated FGF23 predicted end-stage renal disease only before adjusting for estimated GFR and other kidney risk factors.

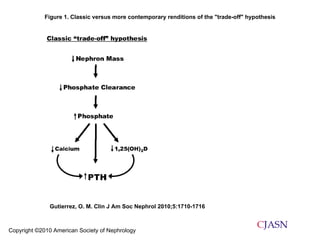



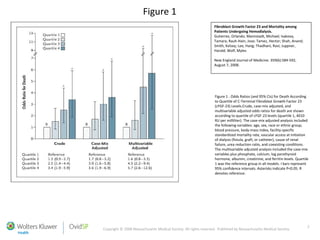

![Two-year survival curve (Cox proportional hazard), according to the serum FGF-23 quartile, adjusted for age, gender, diabetes, tobacco use, alfacalcidol use, dialysis vintage, serum albumin, tertile of phosphataemia, calcaemia and PTH values. Jean G et al. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2009;24:2792-2796 © The Author [2009]. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of ERA-EDTA. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oxfordjournals.org](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fgf-110921211024-phpapp01/85/Fgf-23-and-mortality-risk-in-CKD-17-320.jpg)