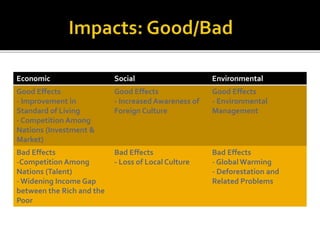
The document discusses several aspects of globalization including increased interconnectedness through transportation and communication technologies. It provides examples of how people from different parts of the world interact through trade, travel, and shared media. Globalization has positive economic impacts like improved standards of living but also cultural impacts like increased awareness of foreign cultures and loss of local culture. It also notes environmental impacts both positive and negative from factors like resource use and climate change.