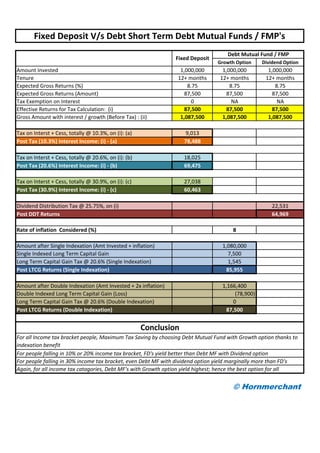
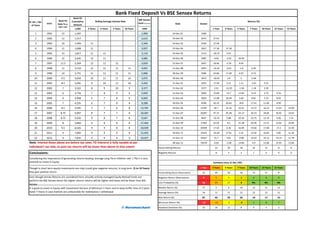
The document discusses investment strategies, emphasizing the performance and allocation of funds between debt-oriented hybrid funds and fixed deposits, along with the potential returns under various equity market scenarios. It highlights that capital protection funds outperform fixed deposits when equity returns are high, while also preserving capital during negative equity performance. Additionally, it compares tax-efficient returns of these investments, suggesting better post-tax outcomes through hybrid funds compared to traditional fixed deposit investments.