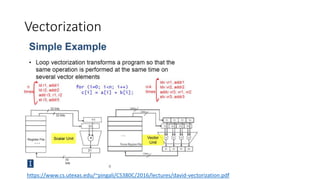
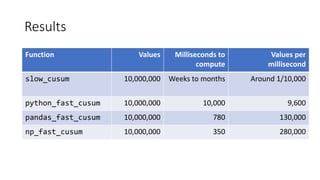
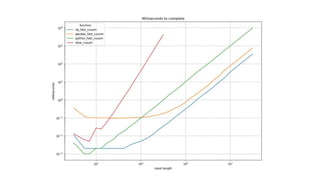
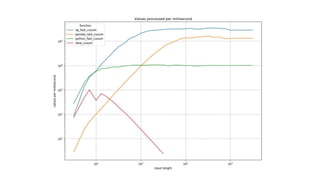
The presentation by Chris Conlan highlights methods to speed up Python code, suggesting techniques such as optimization, exploration of alternatives, compilation, and distribution. It emphasizes the importance of reducing unnecessary operations, experimenting with libraries, using compiled code, and leveraging multi-threading for efficiency. Practical examples show the performance differences between various approaches for computing cumulative sums, with resources provided for further exploration and learning.