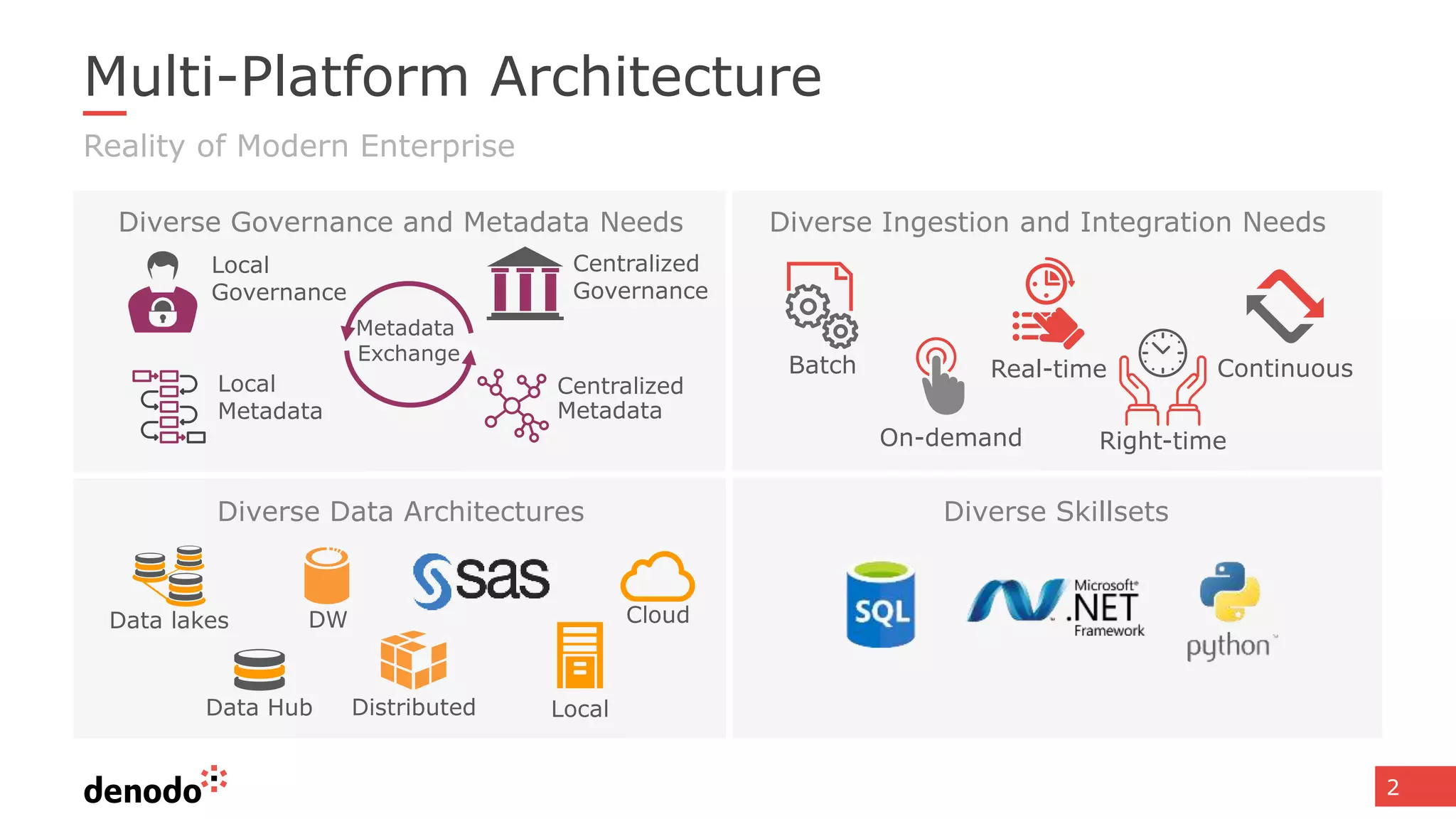
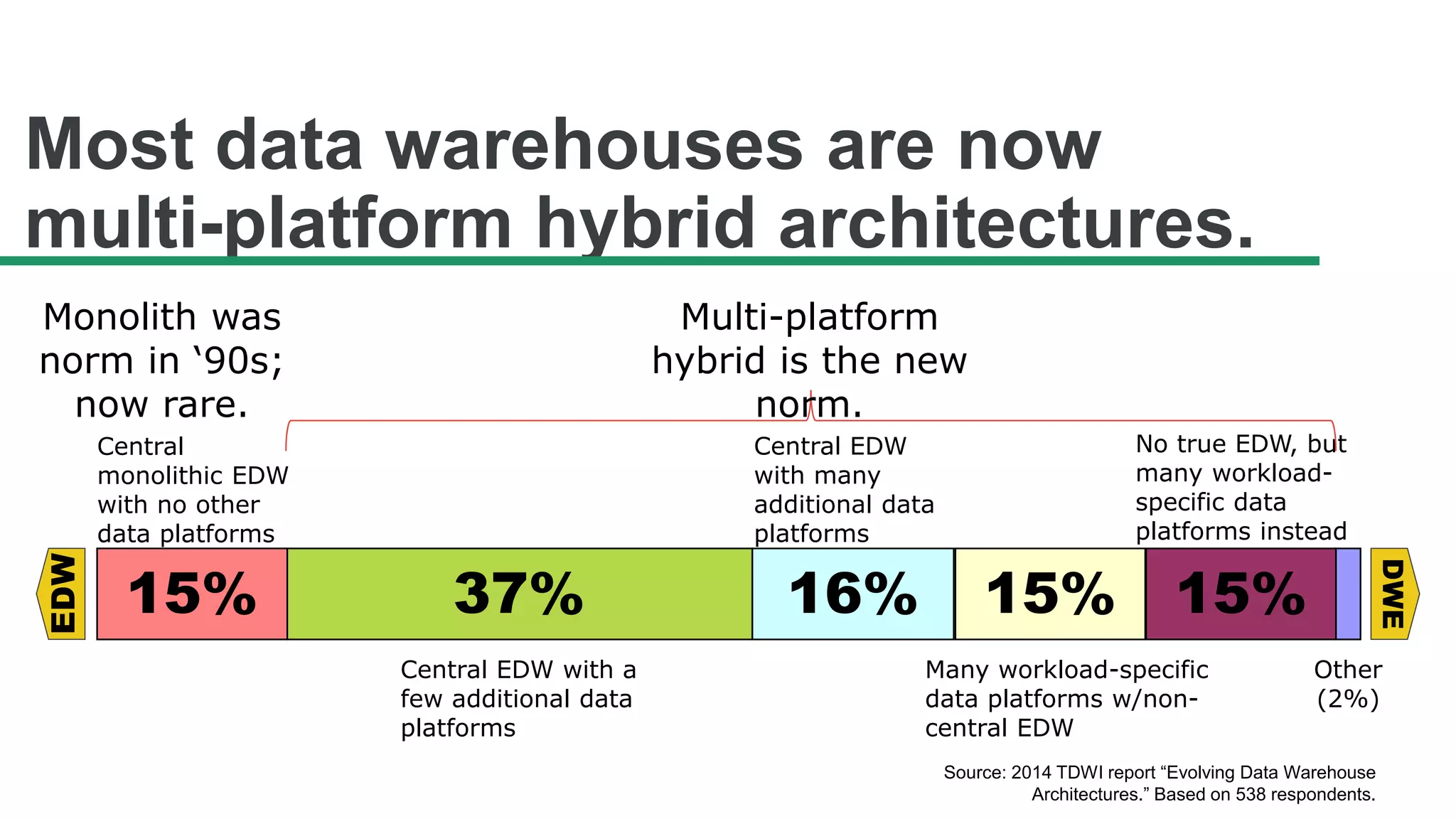
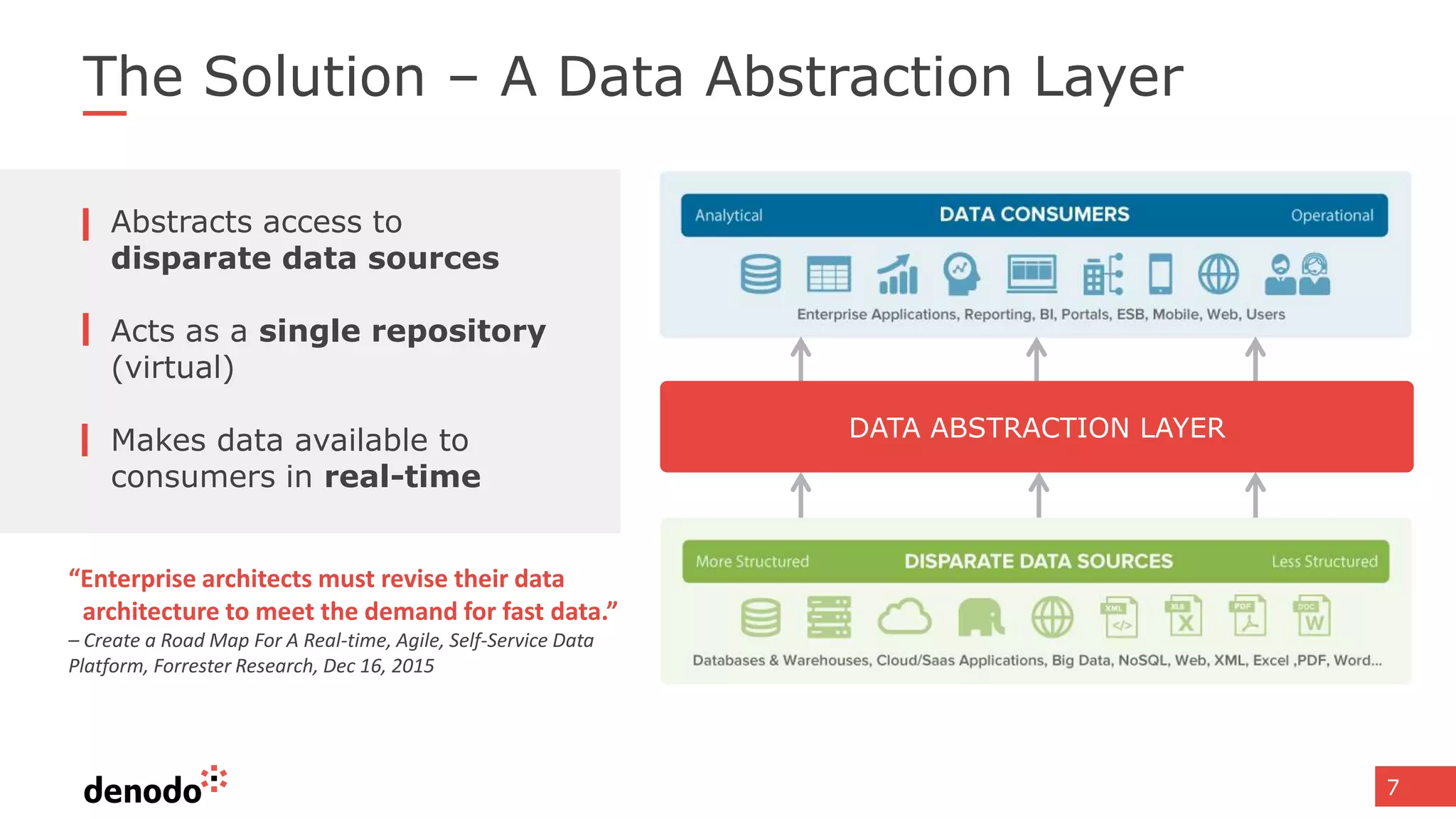
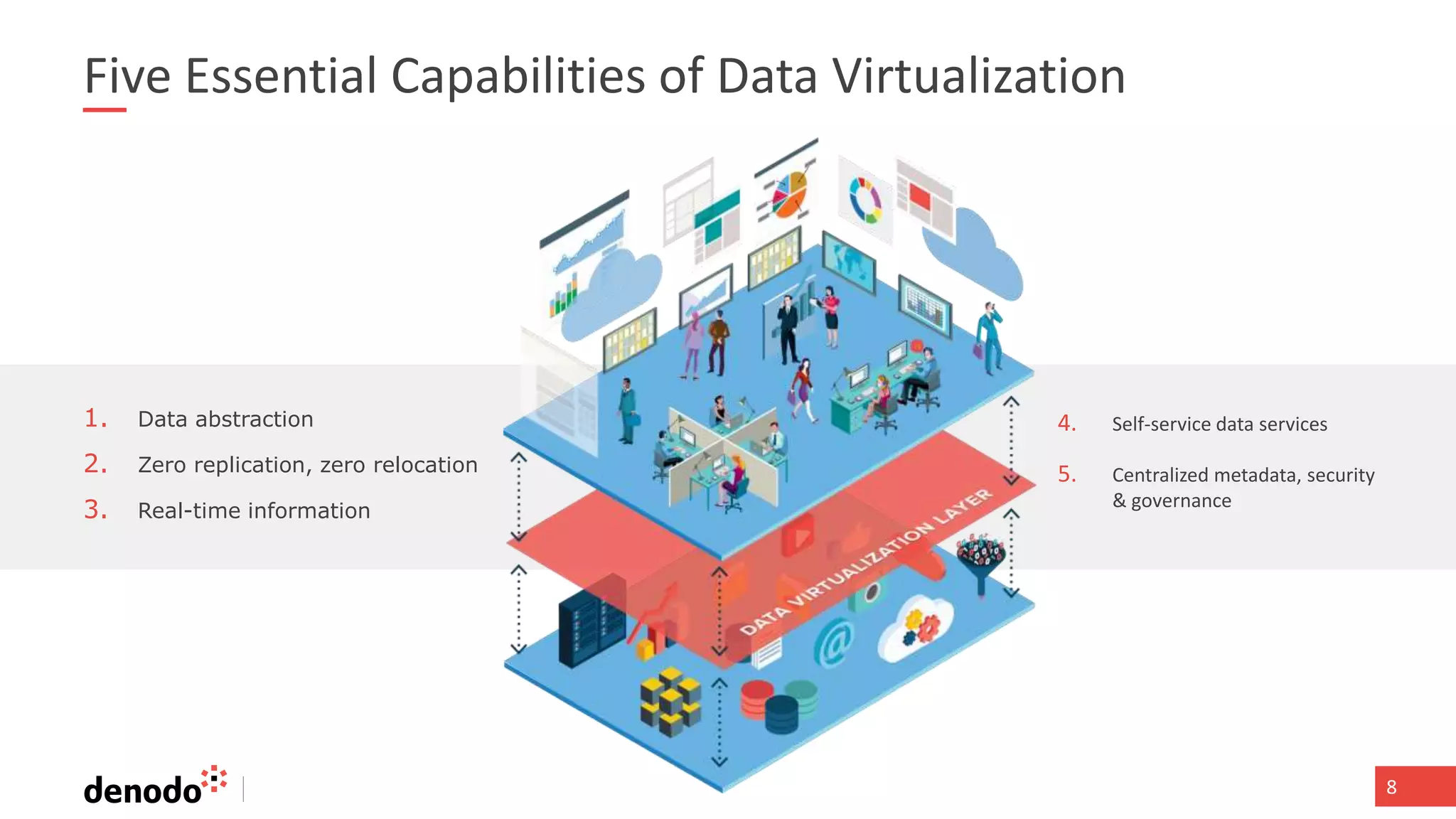
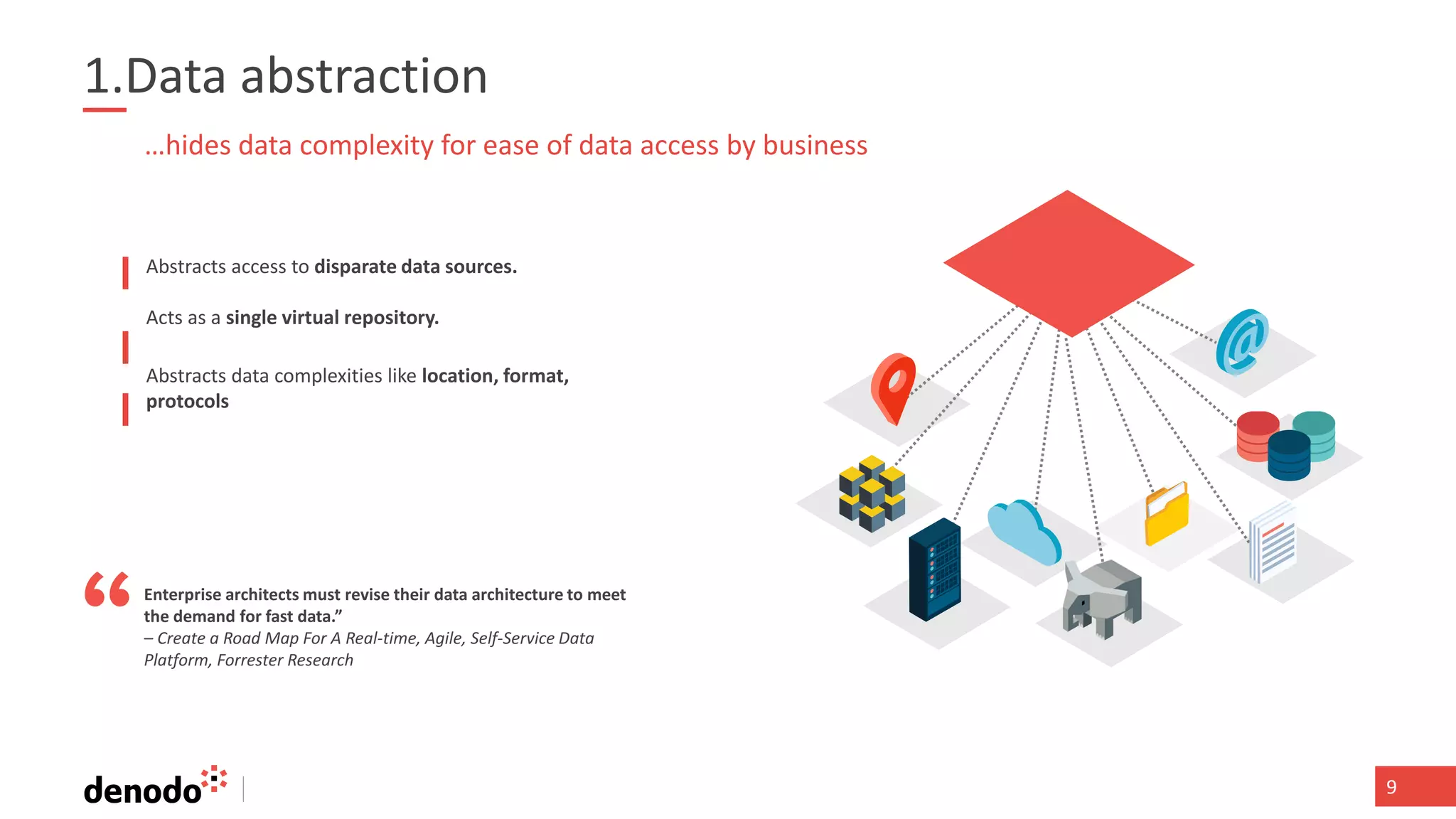
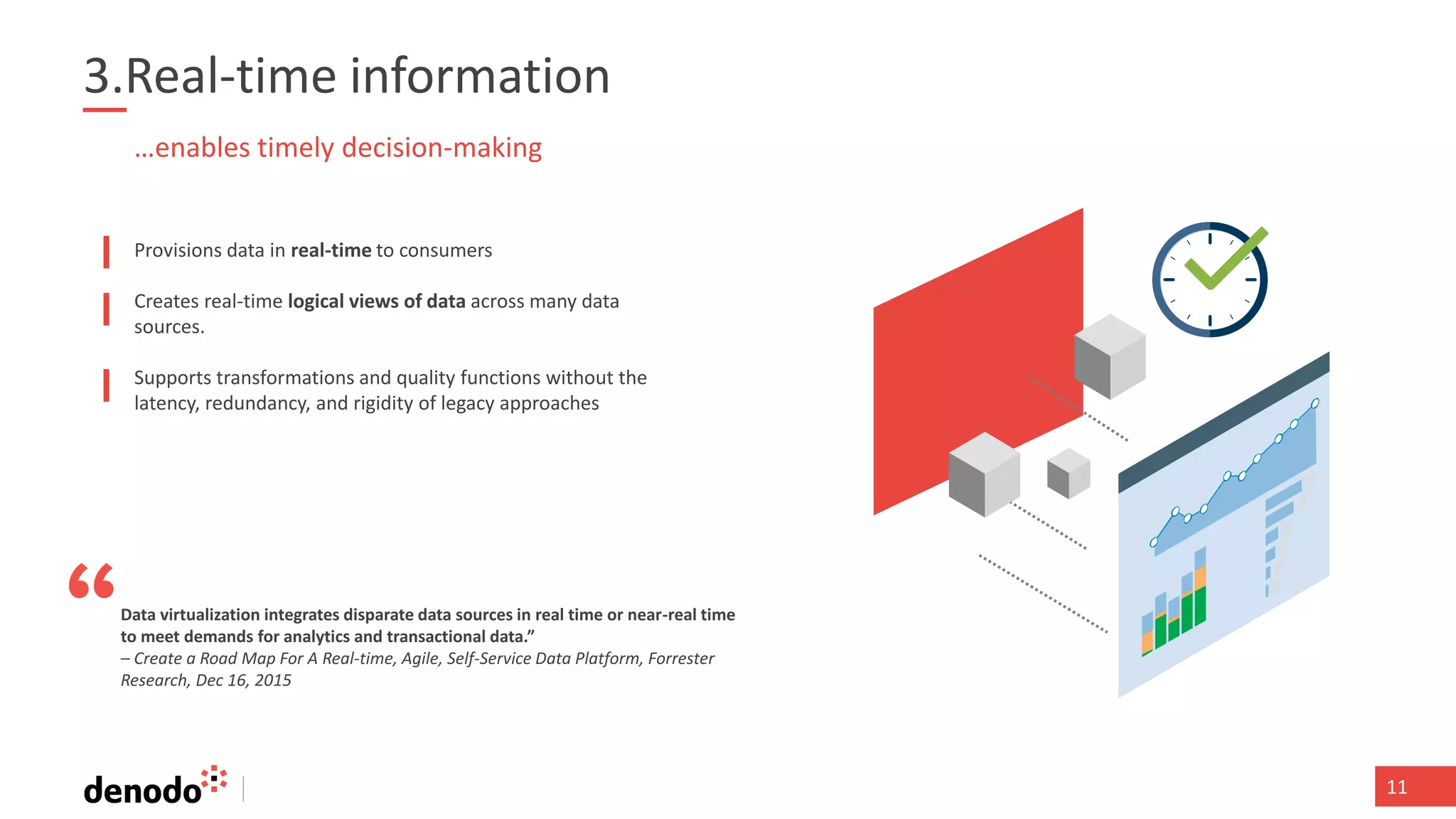
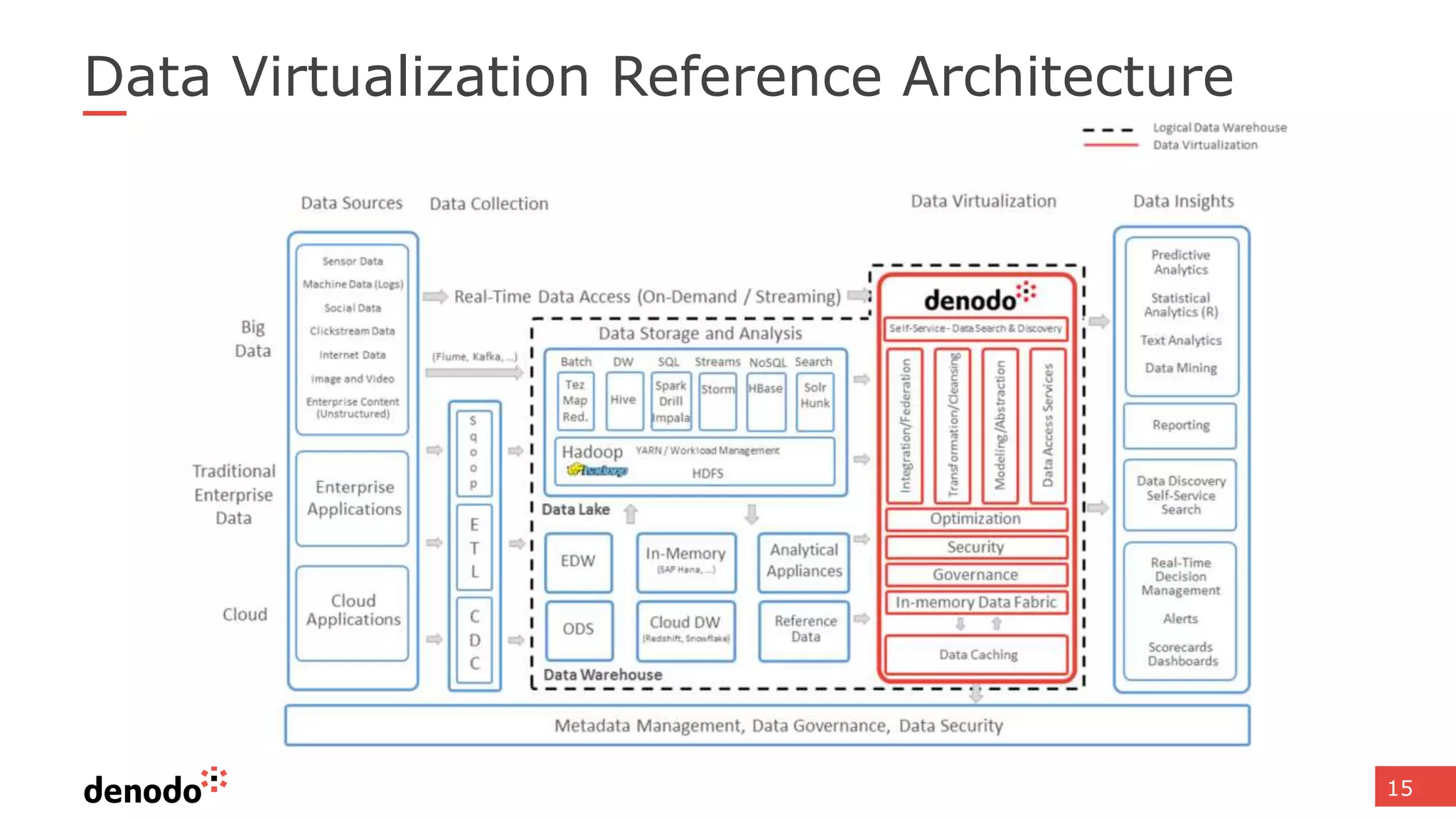
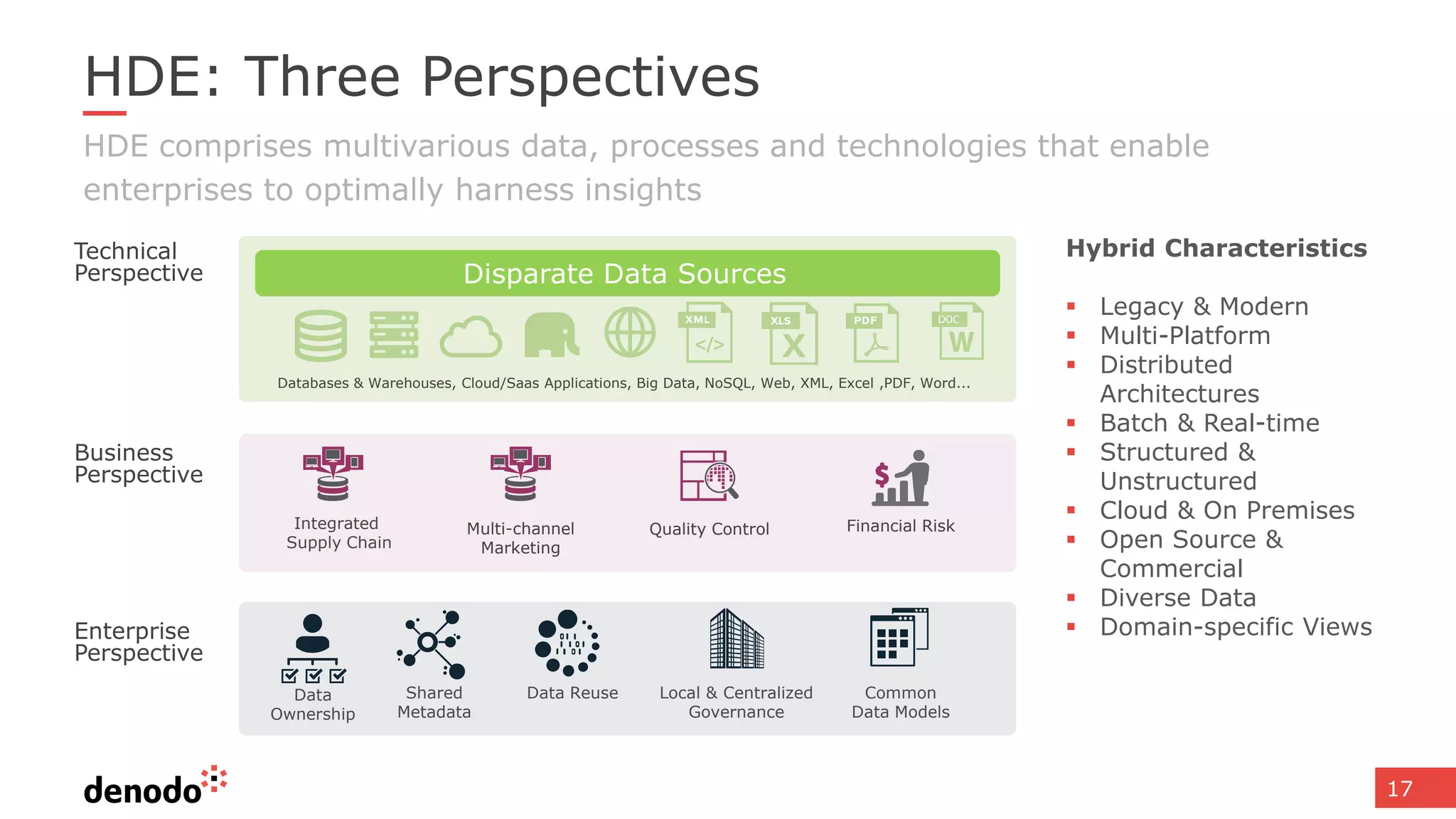
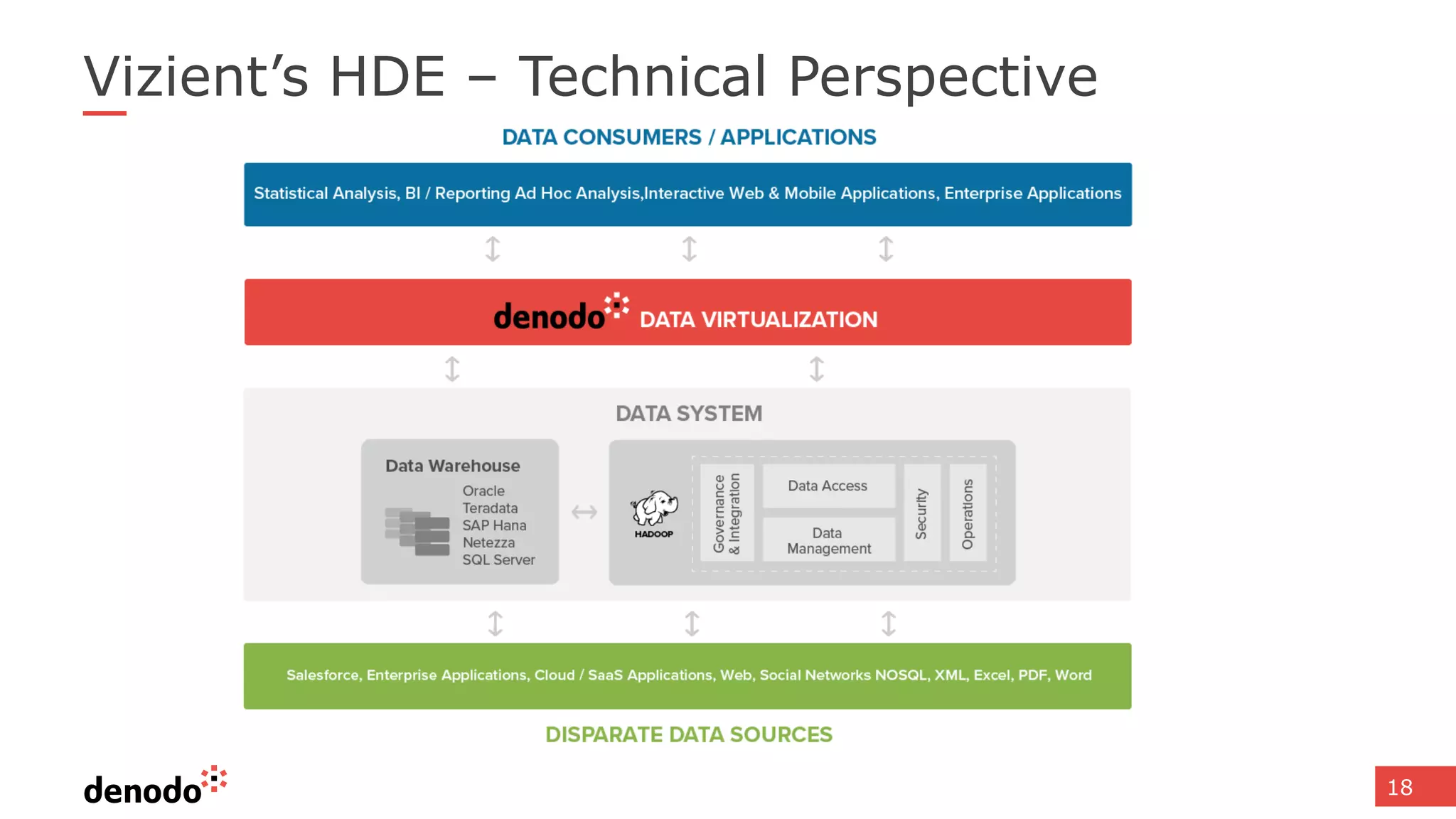
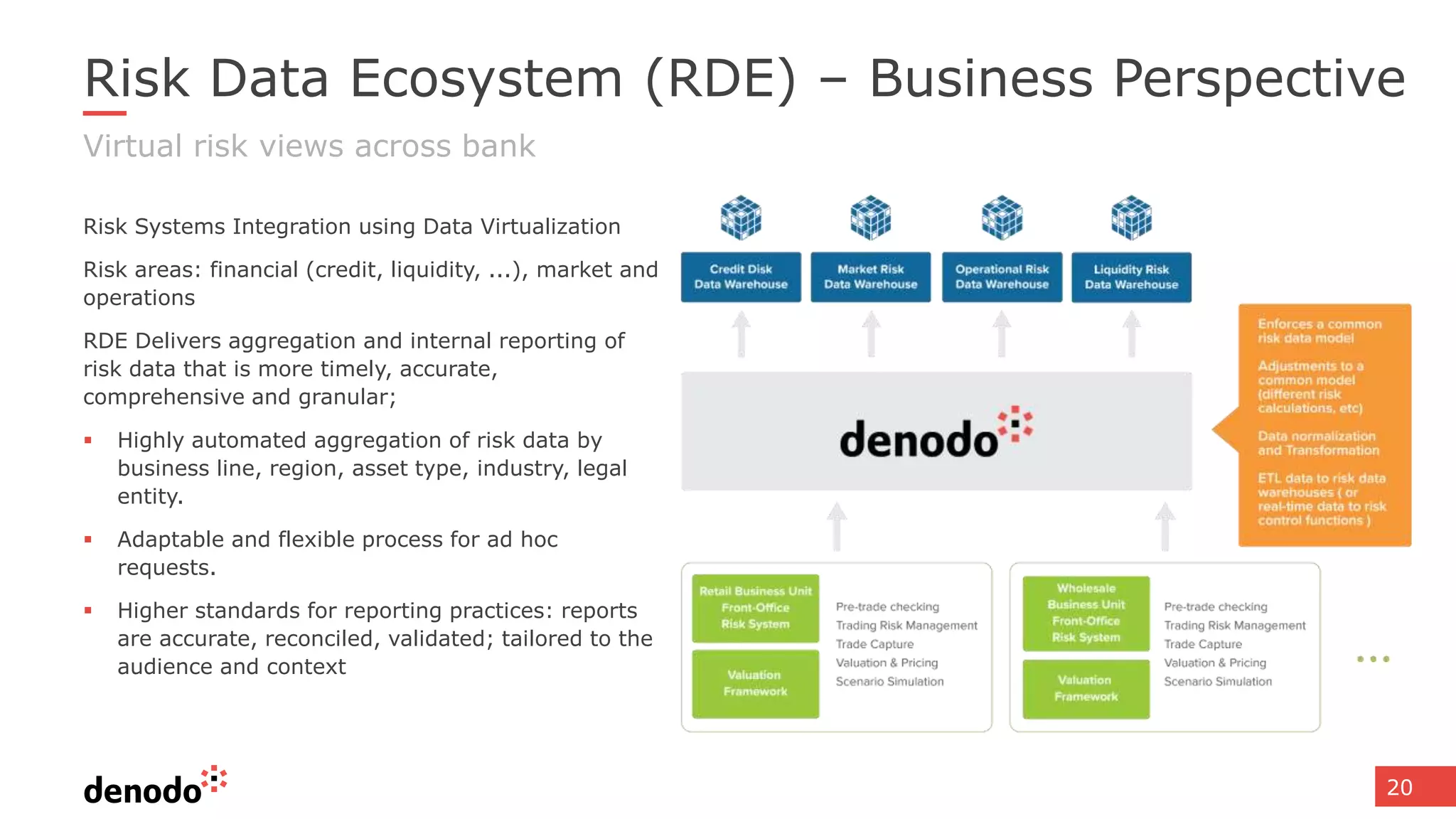
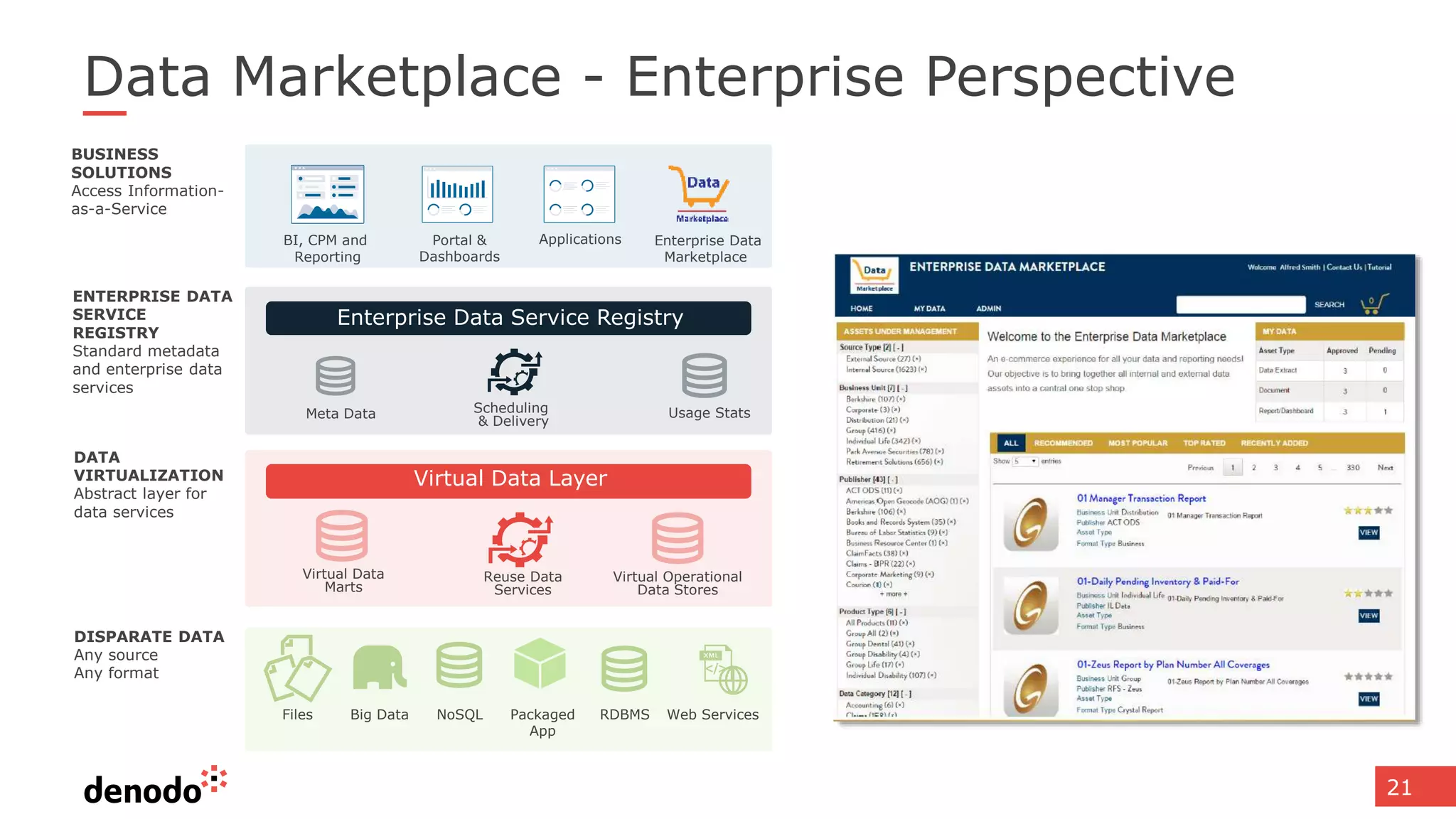
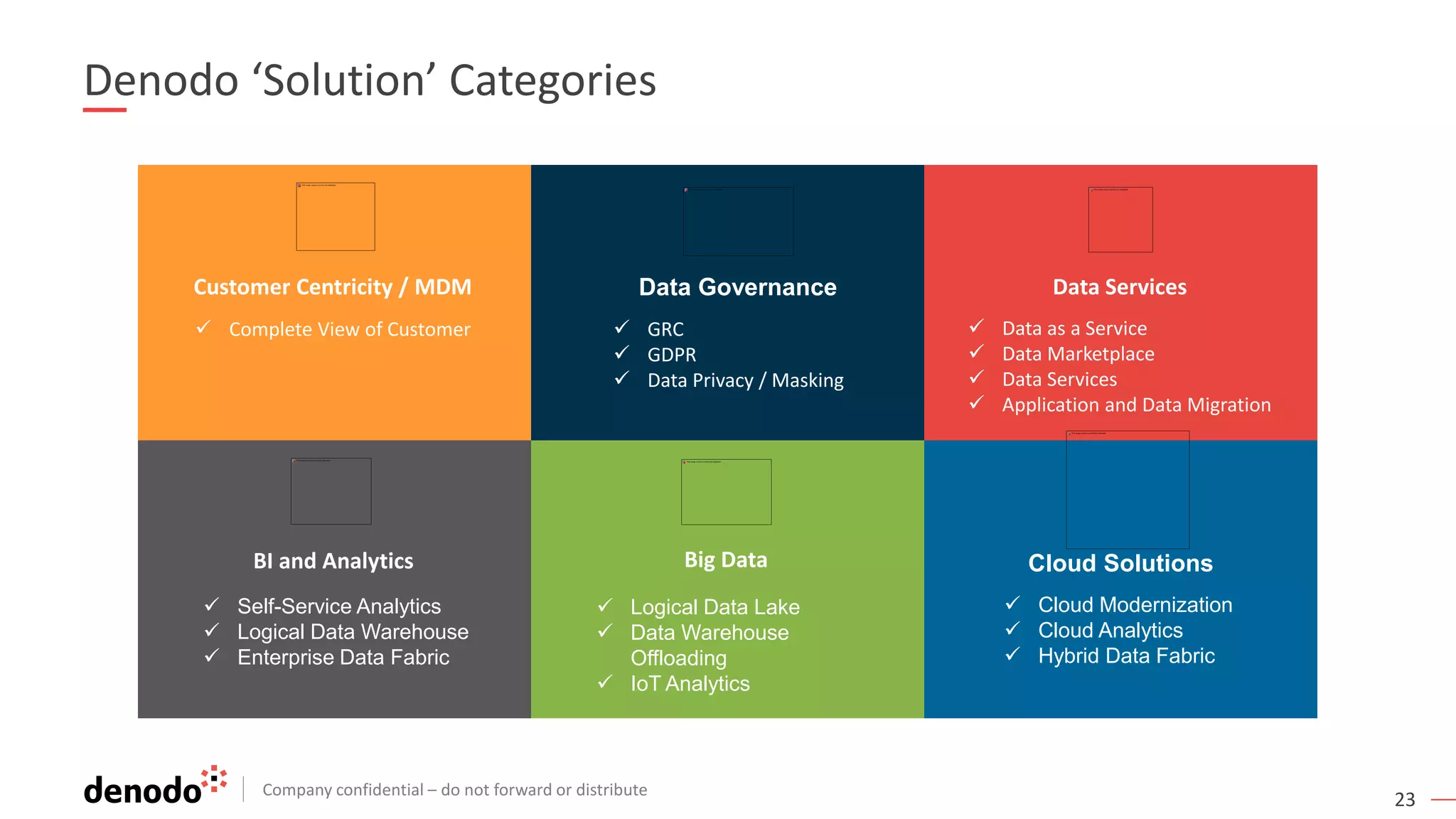
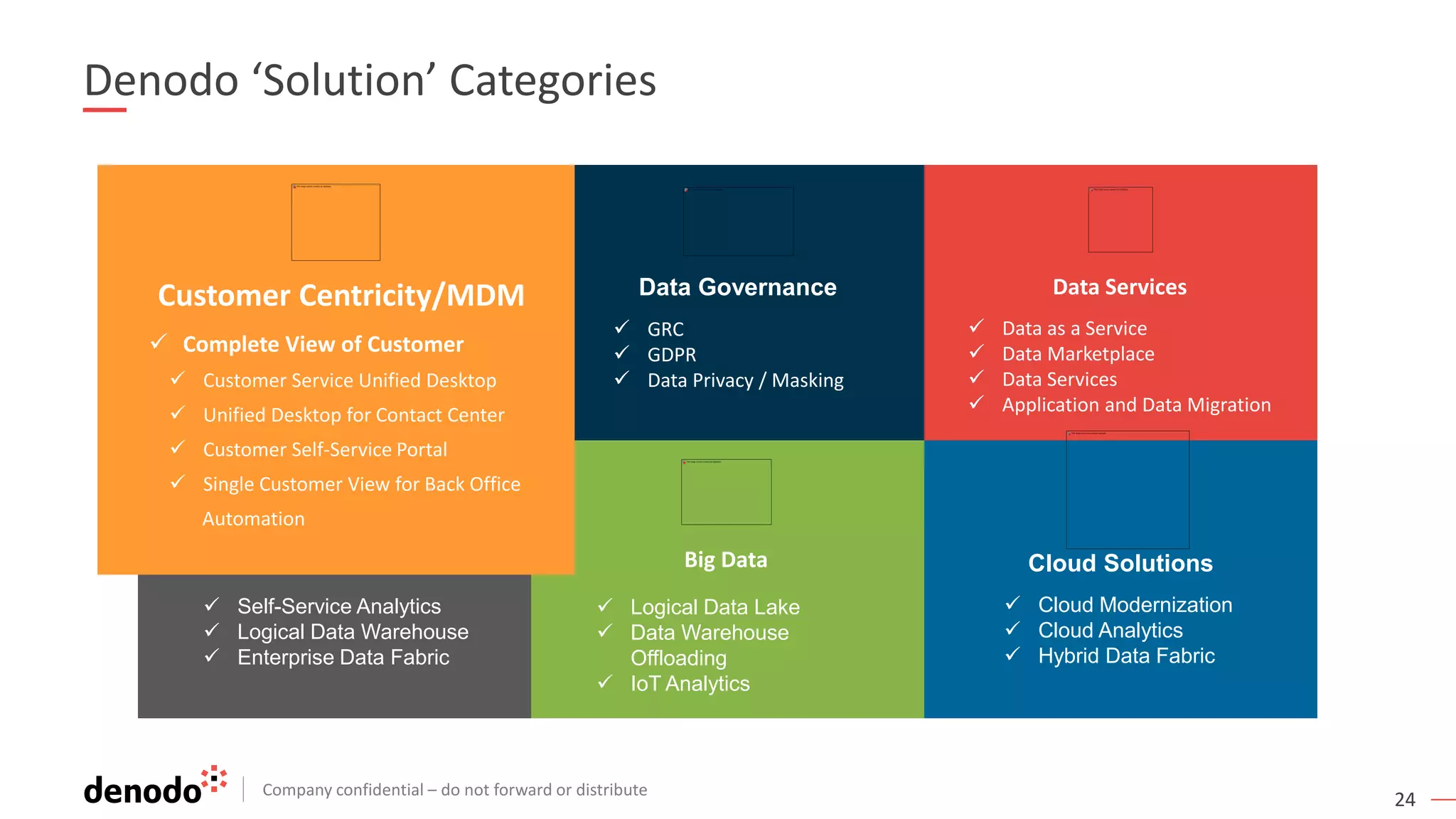
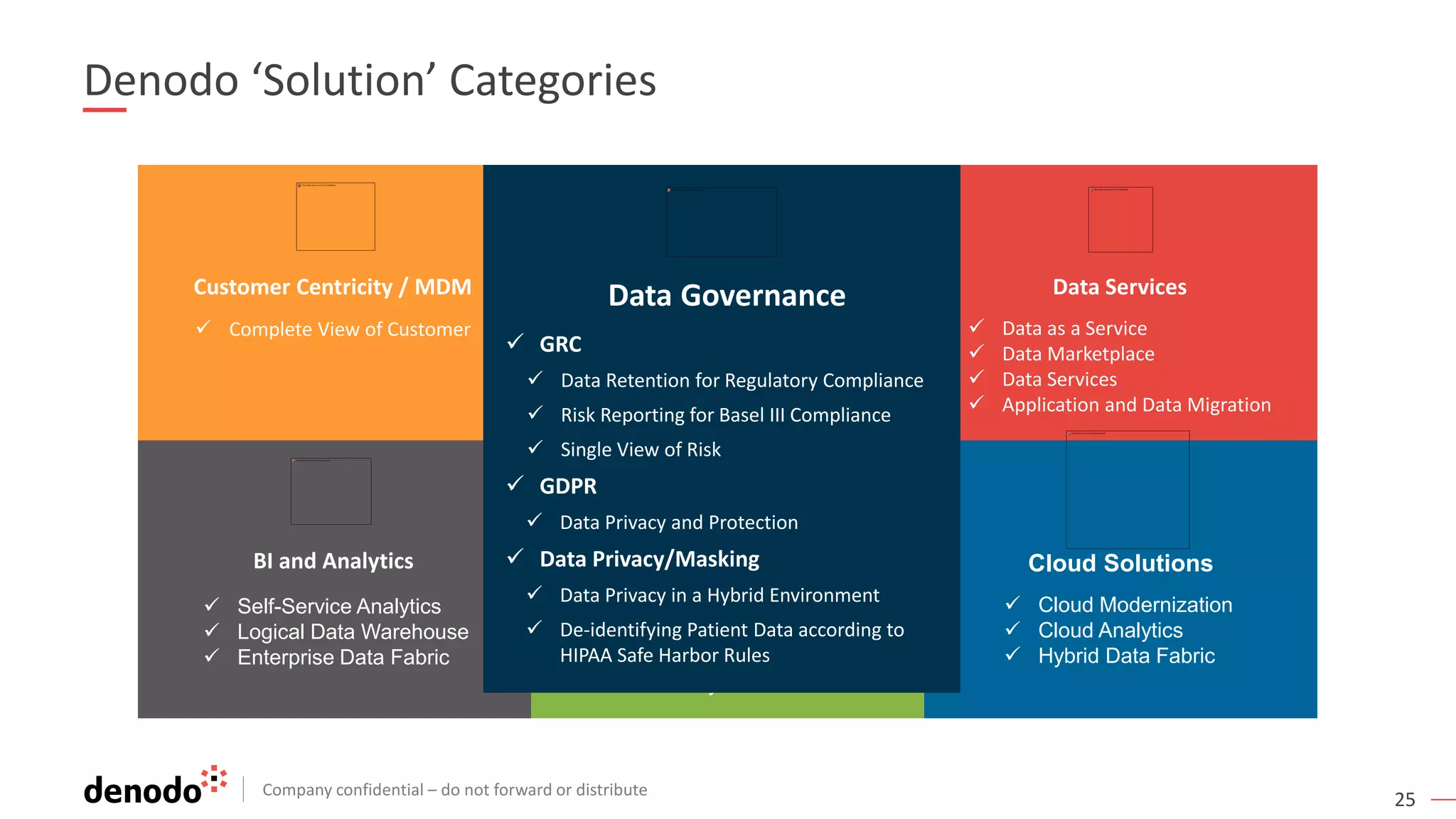
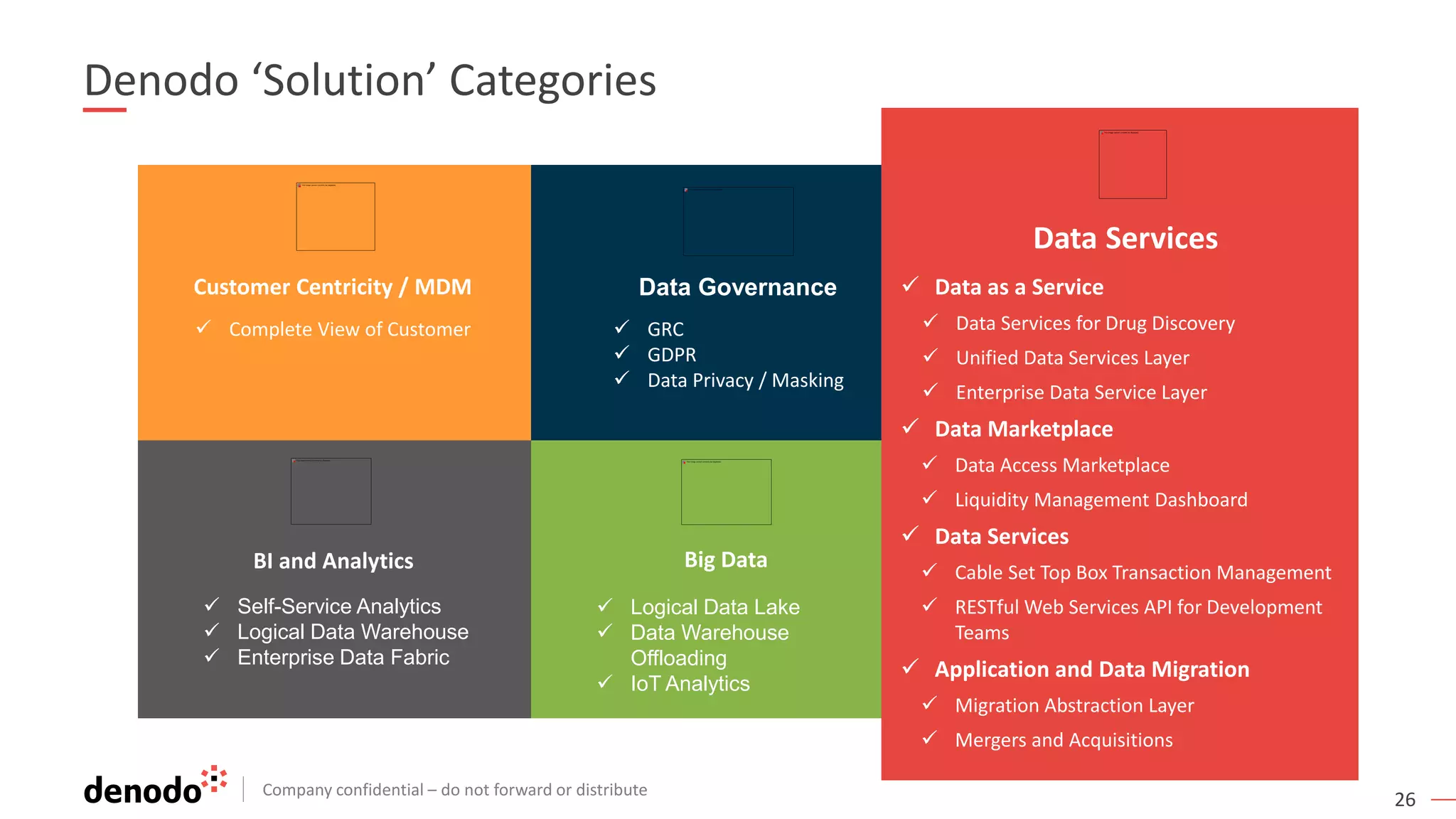
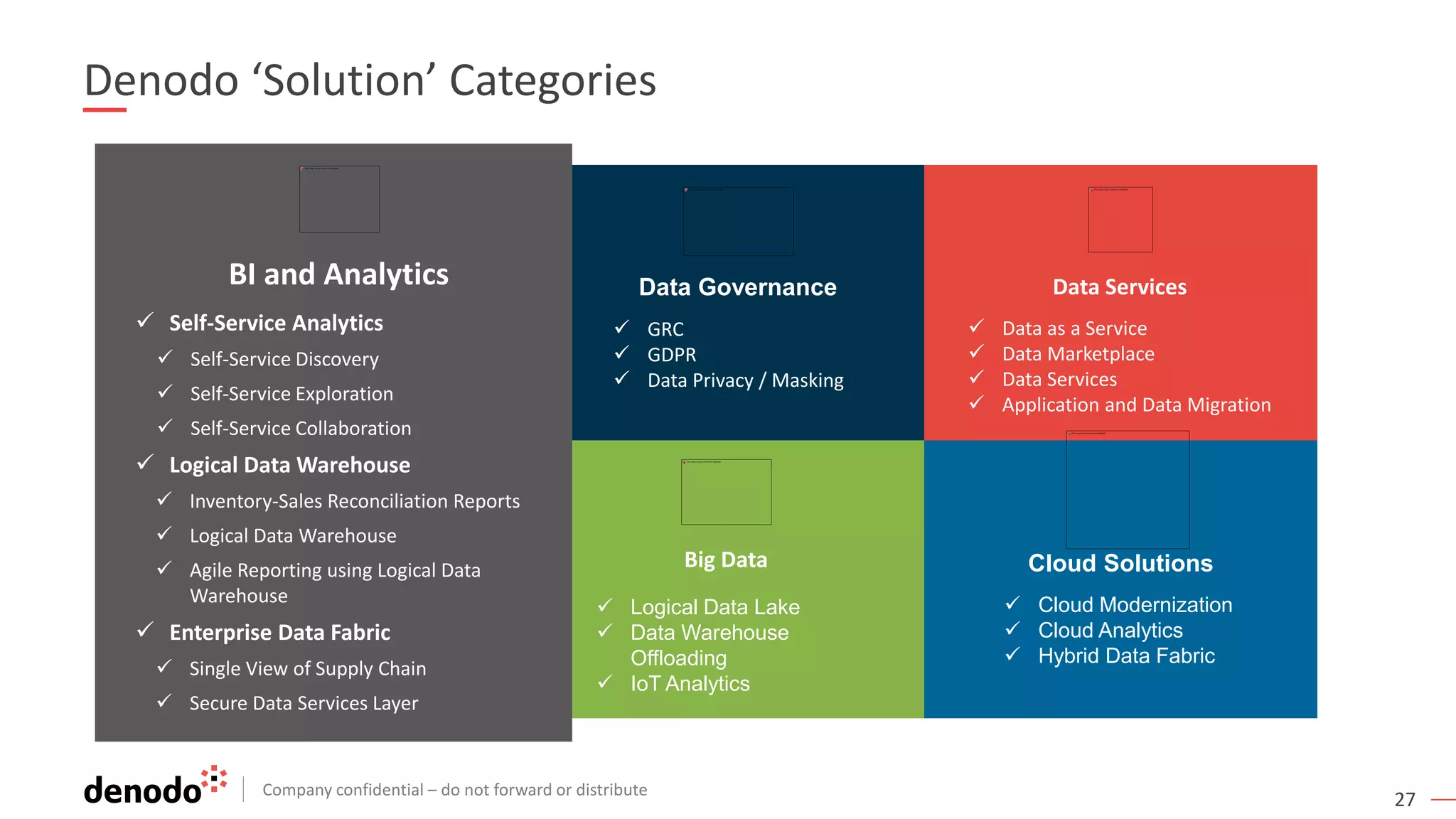
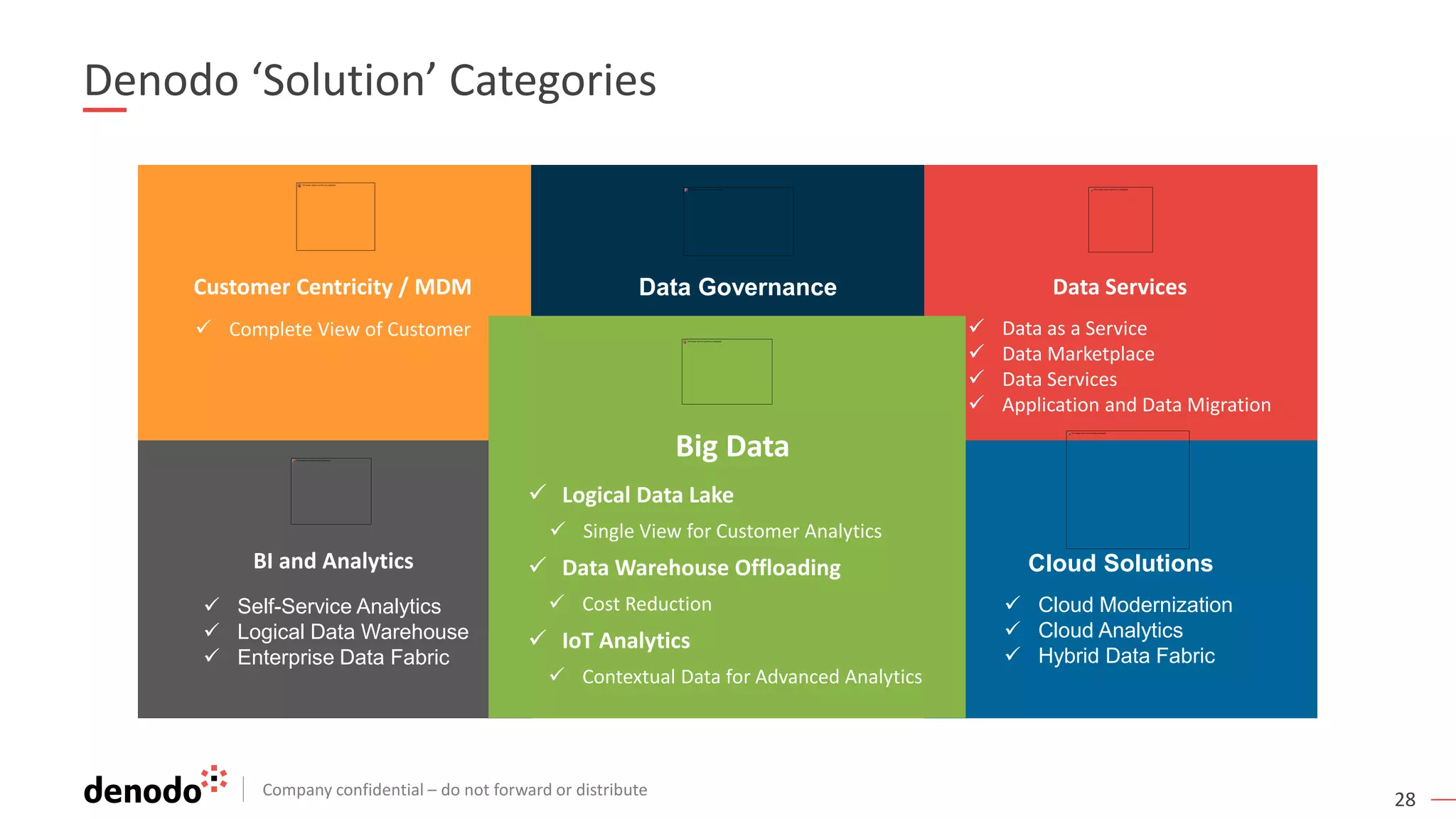
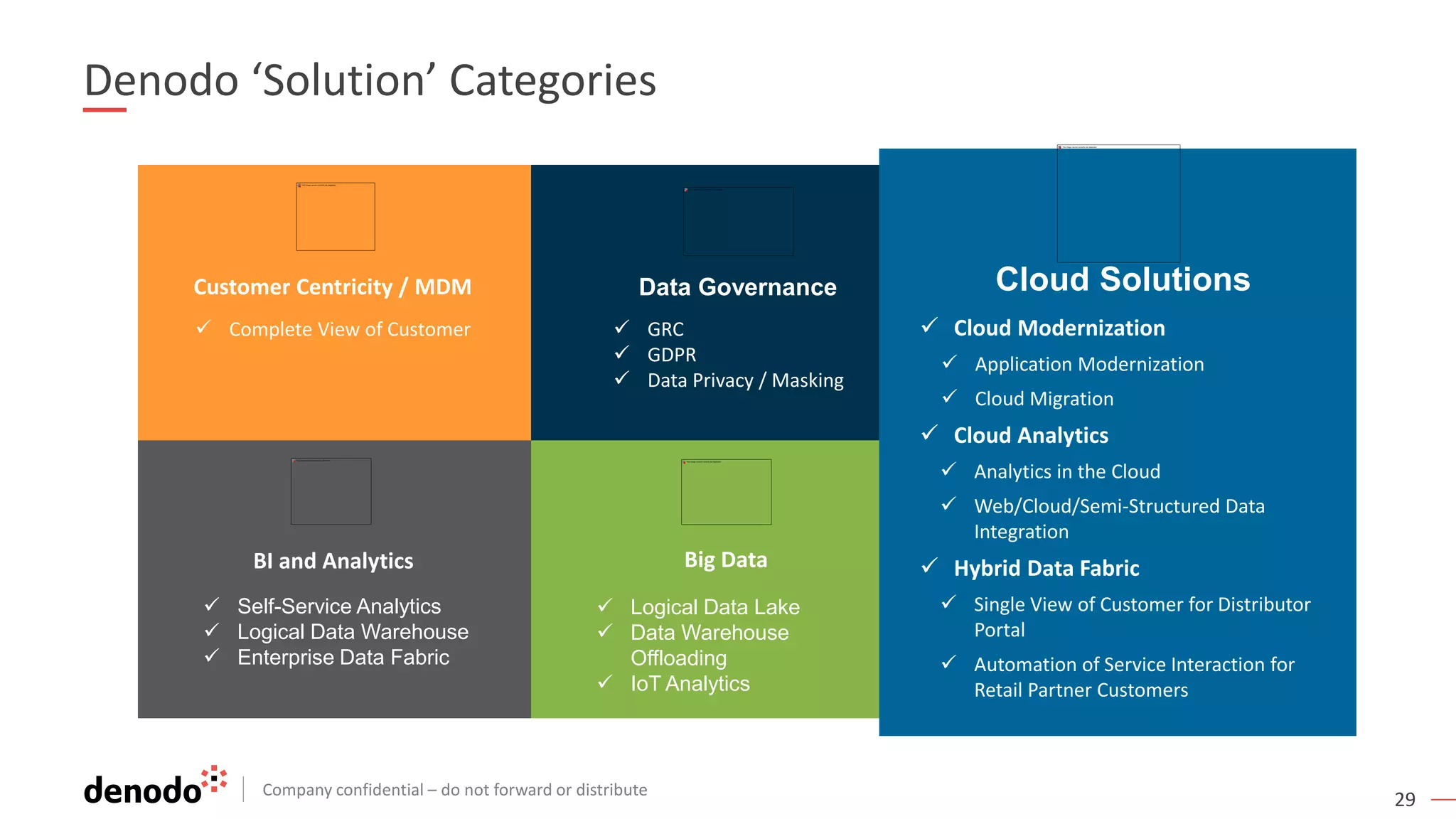
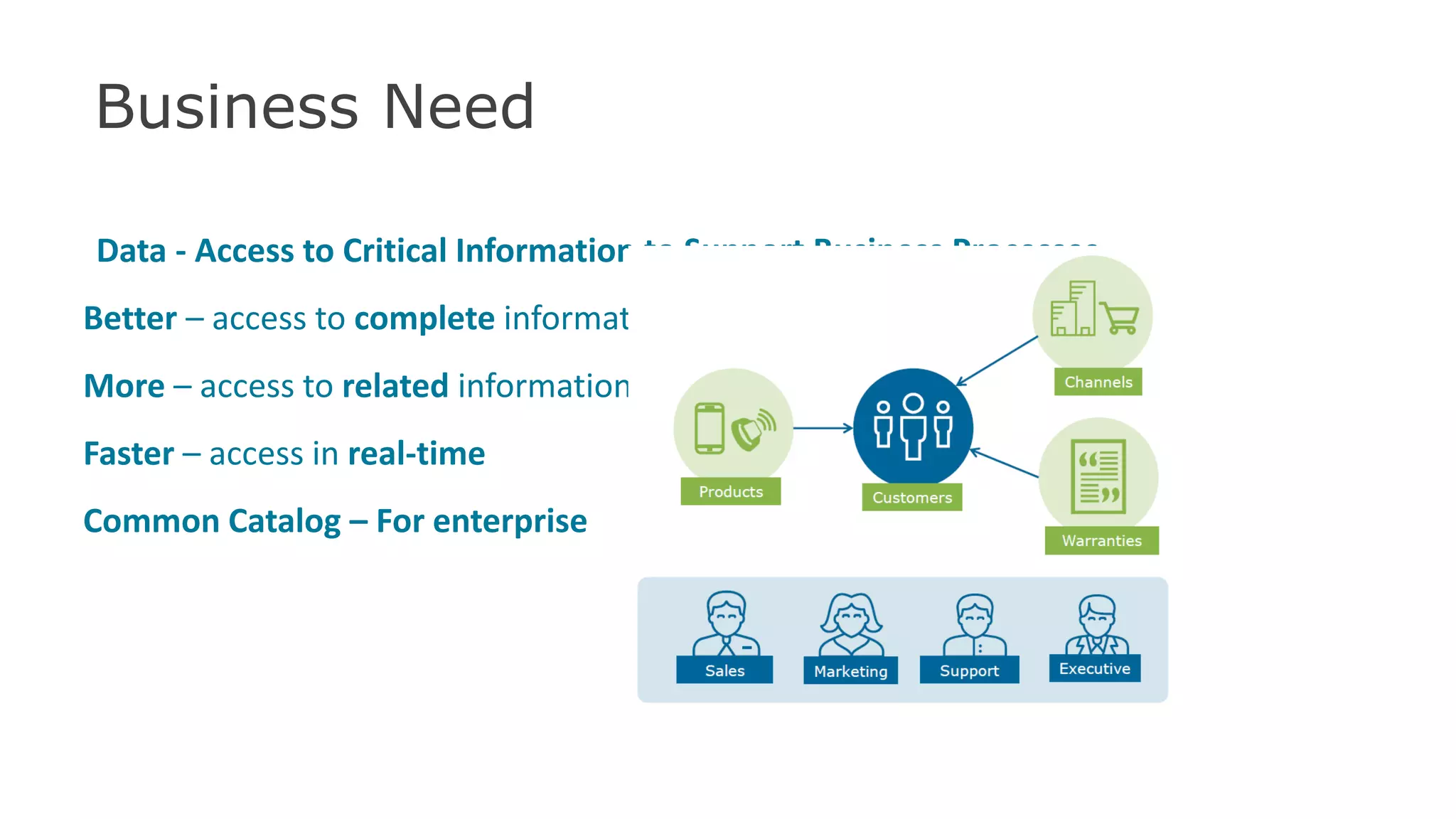
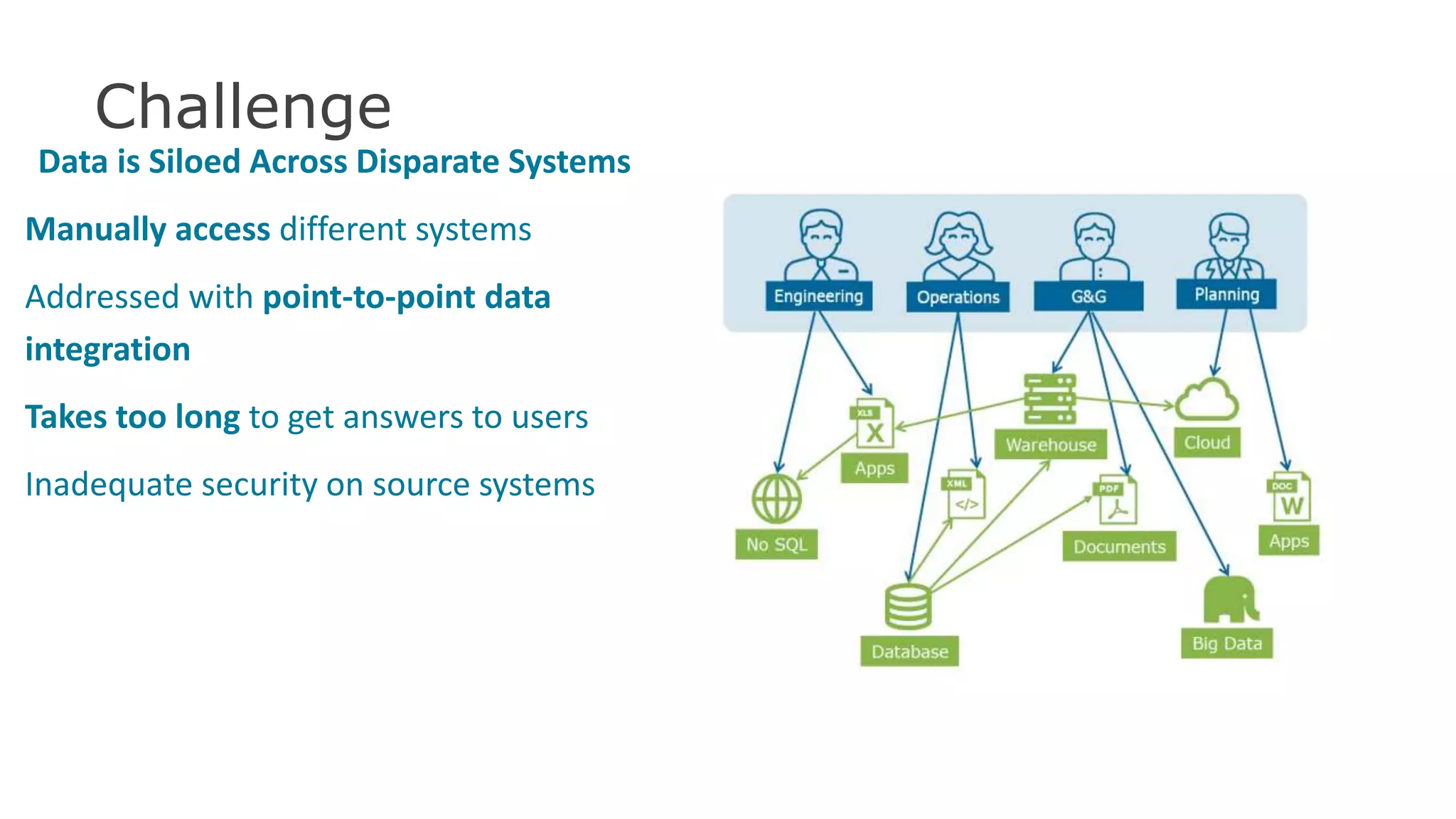
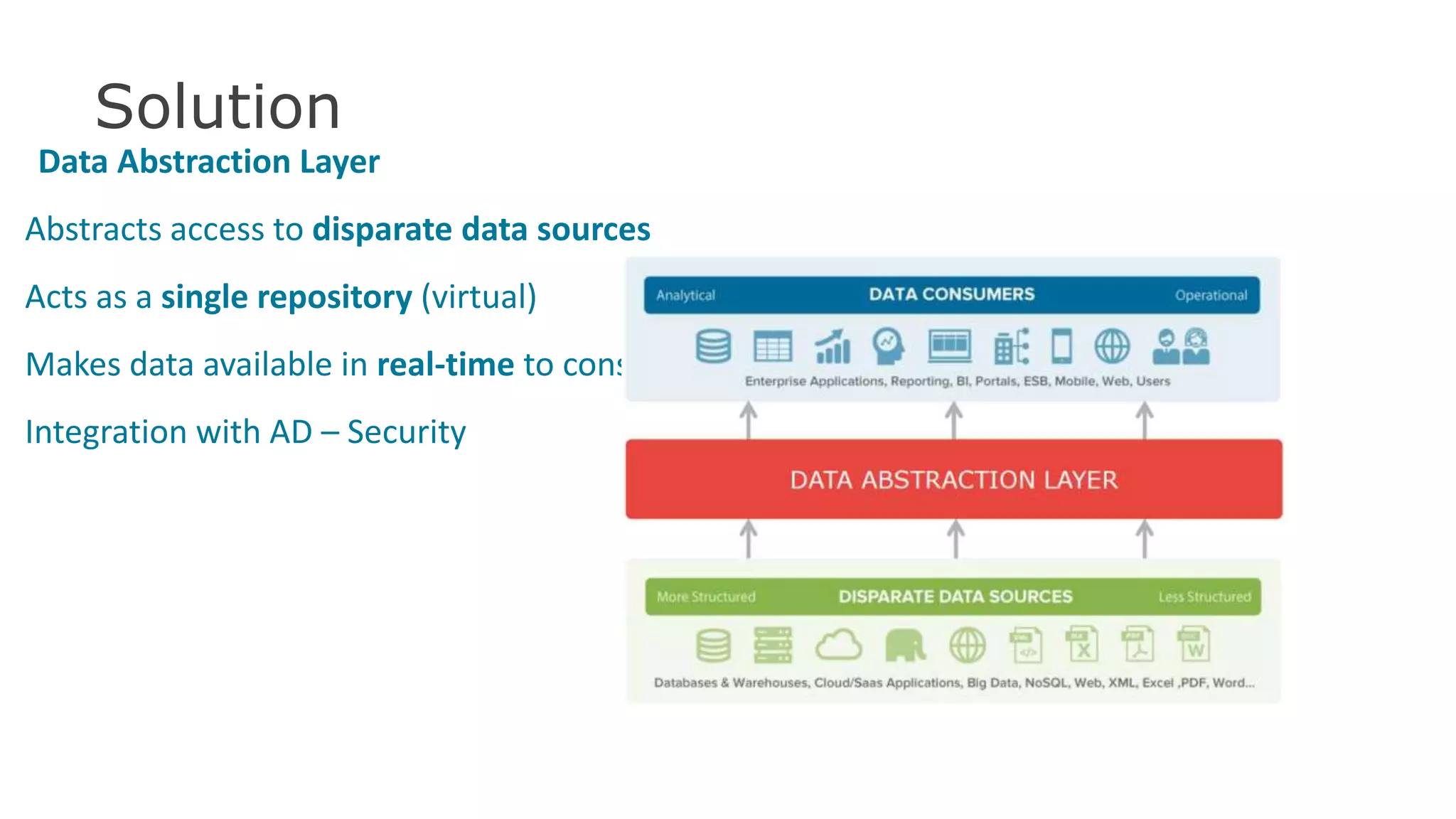
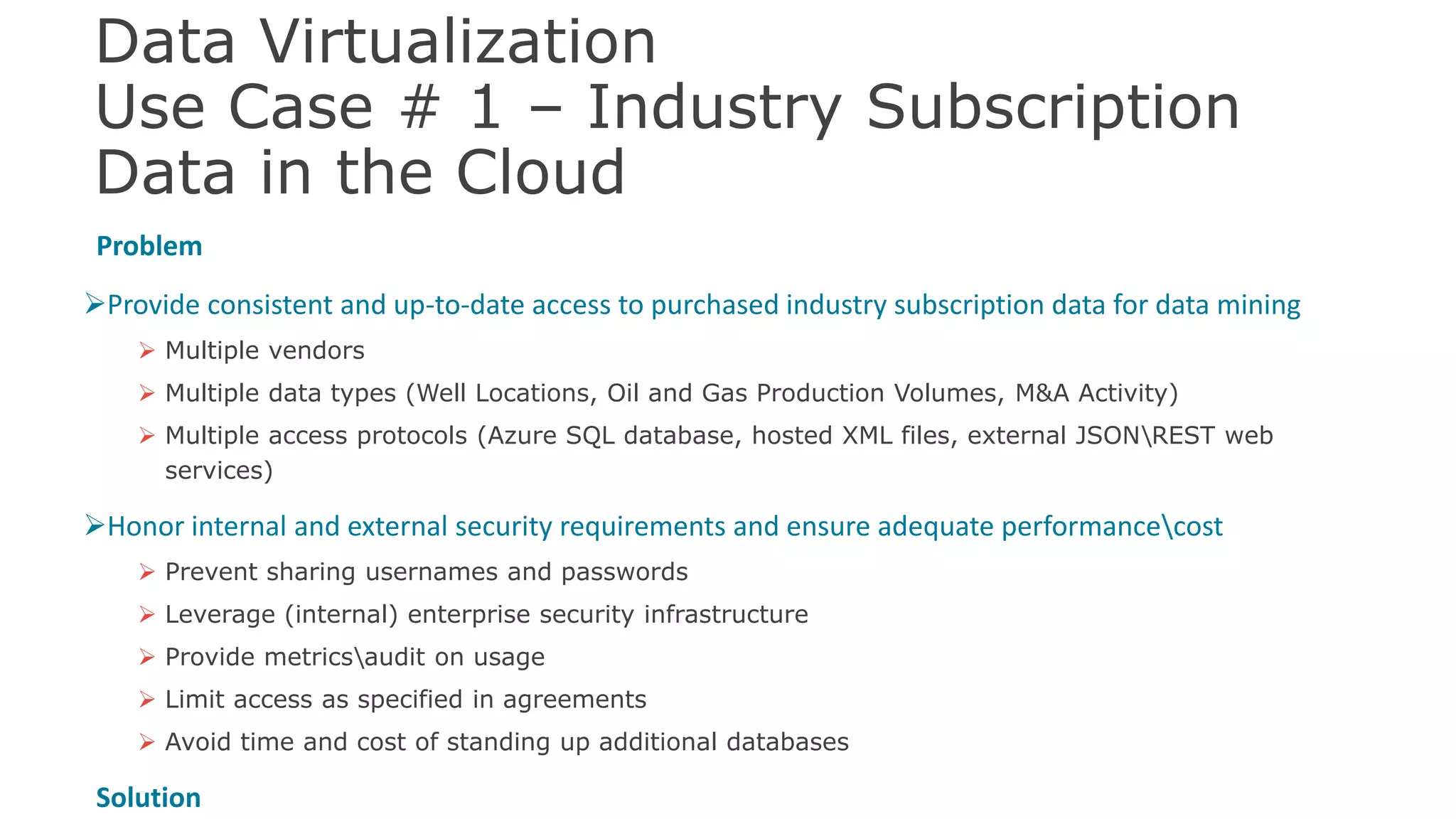
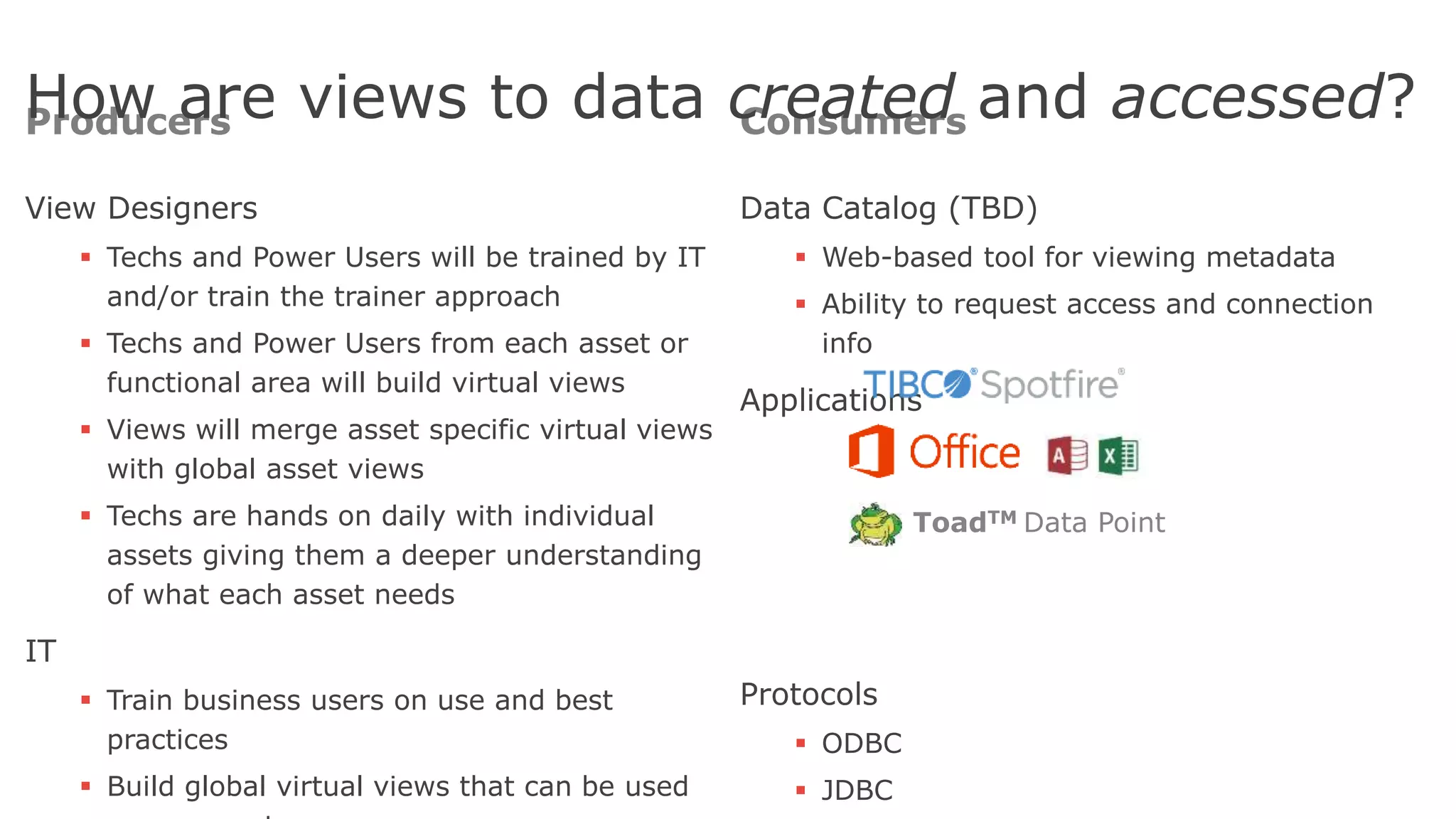
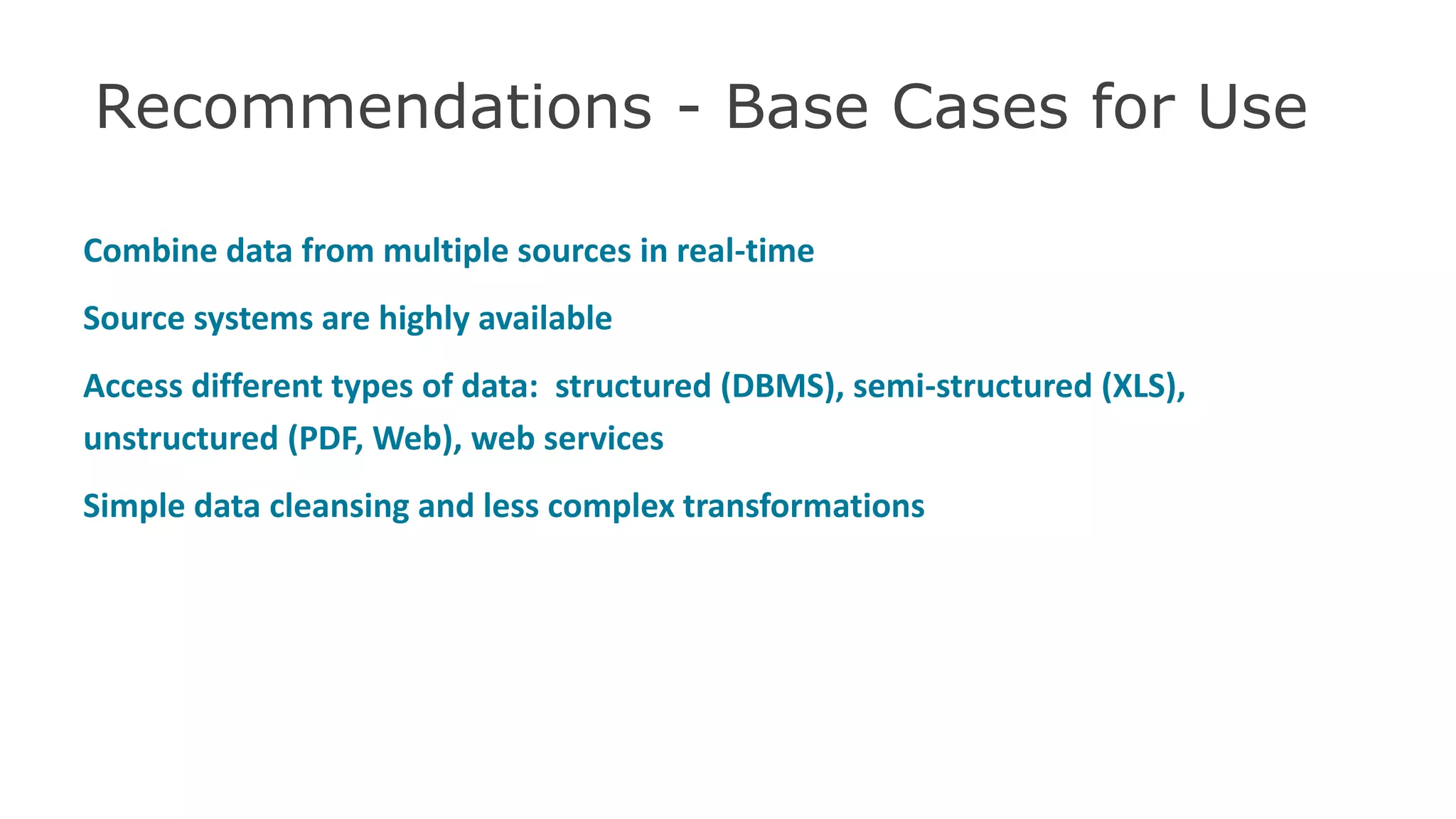
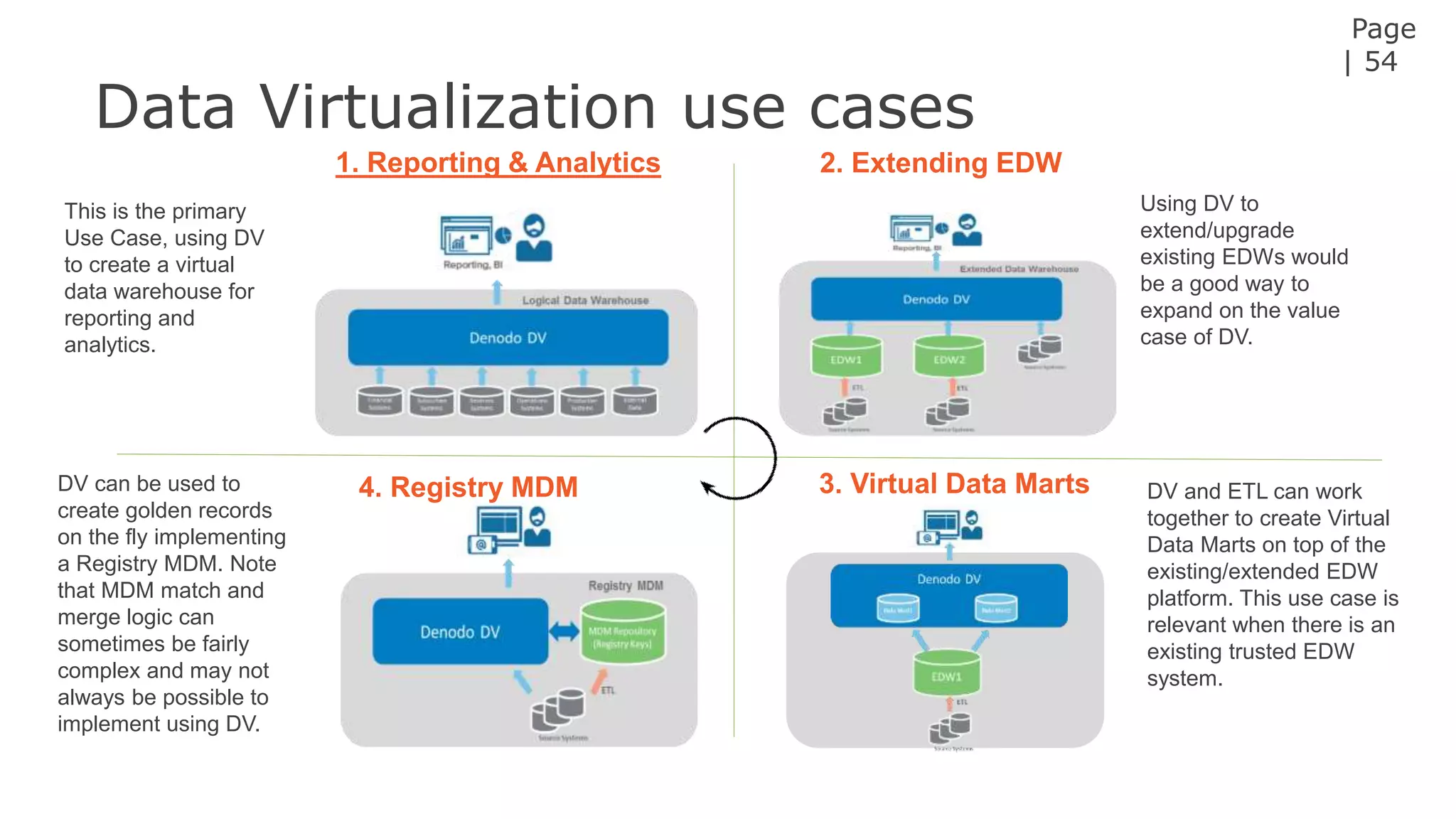
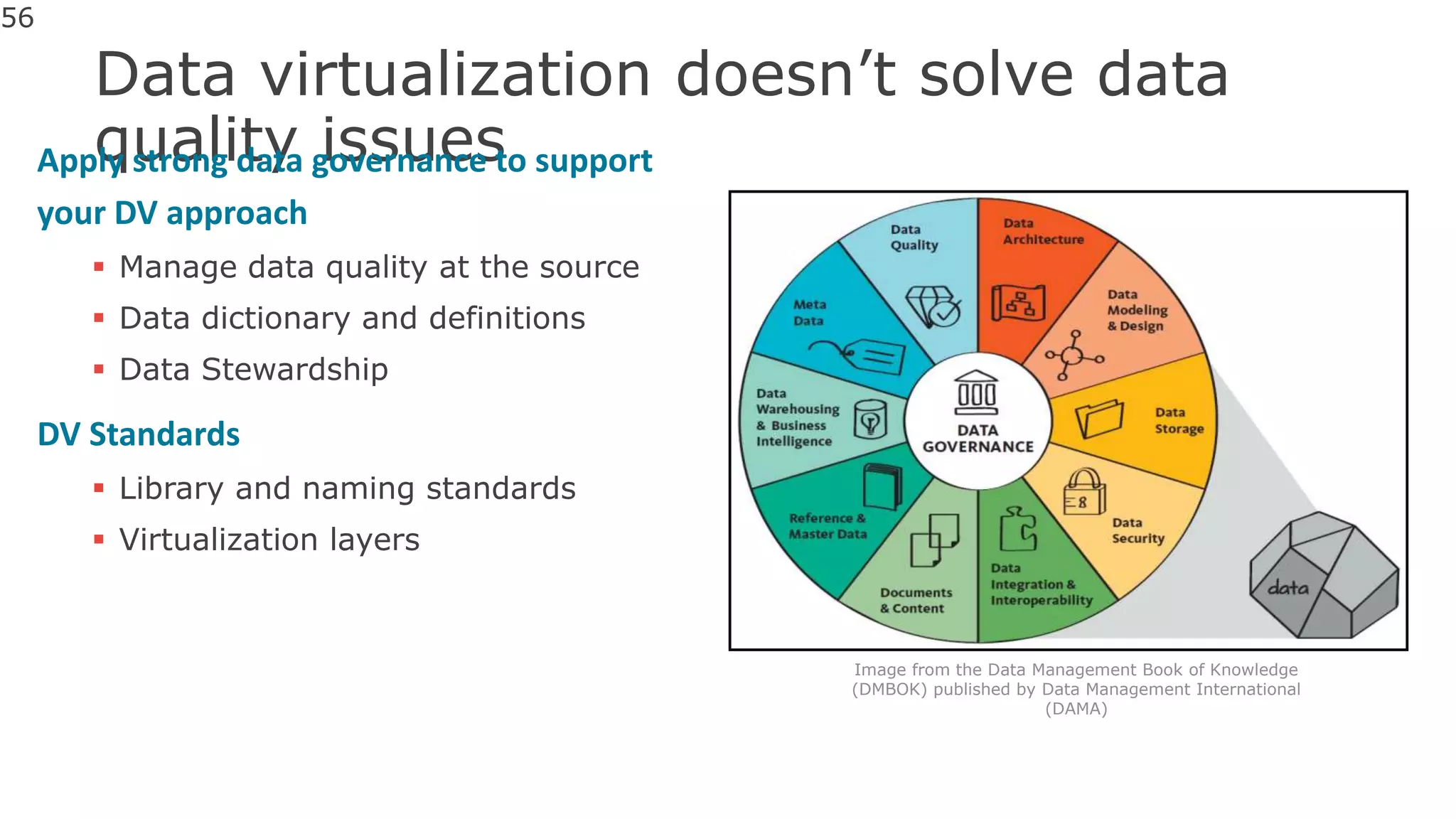
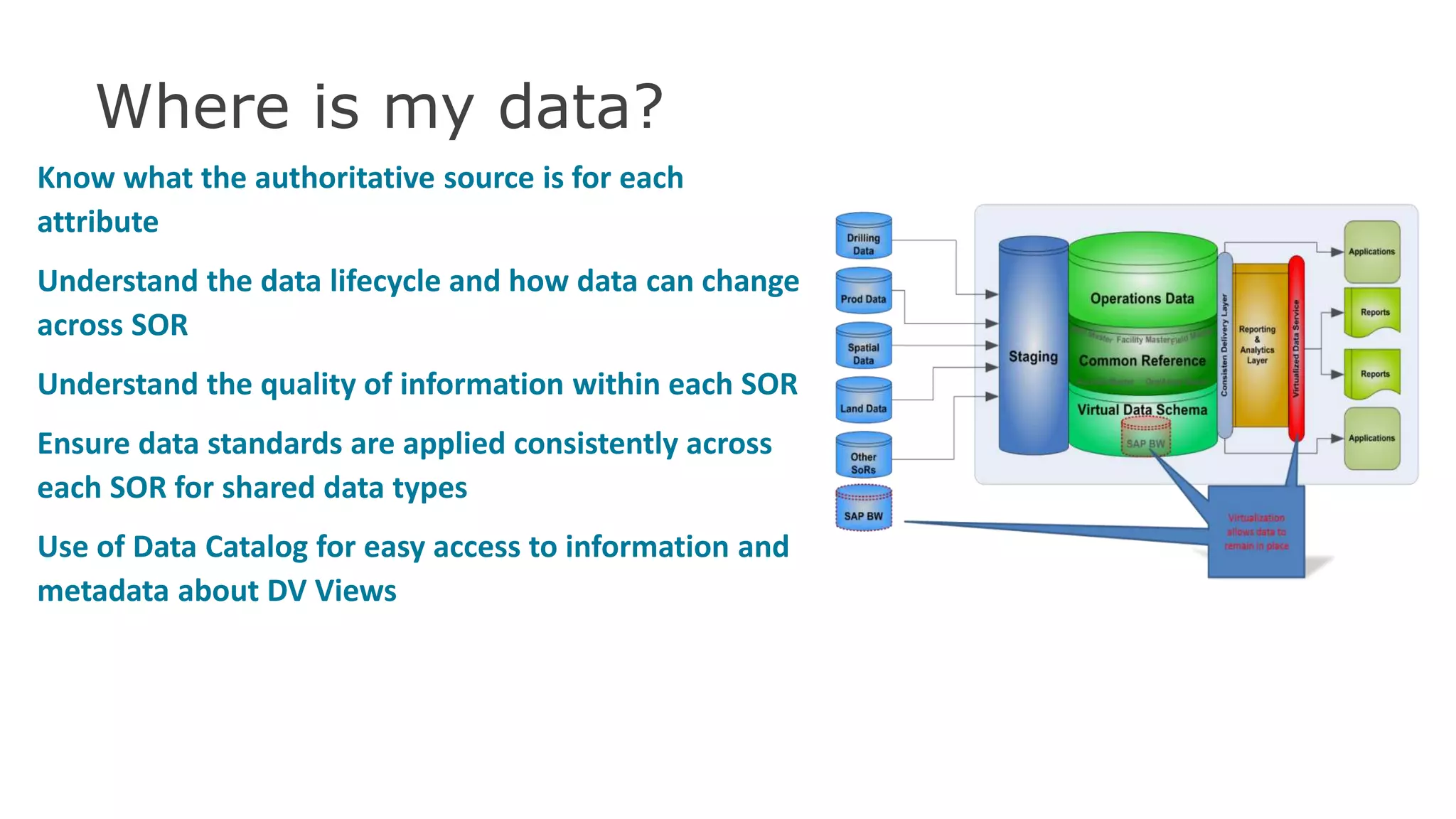
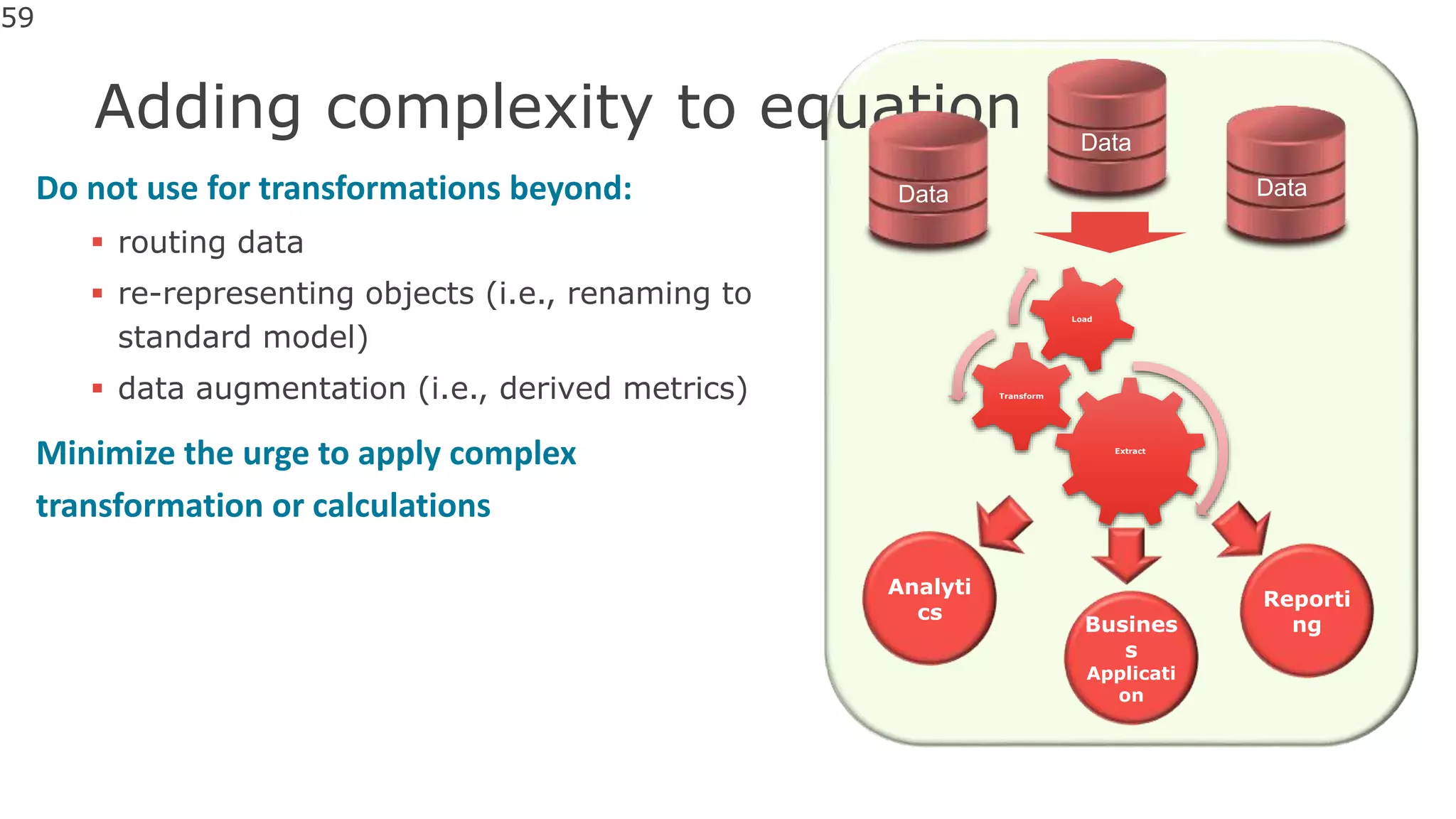
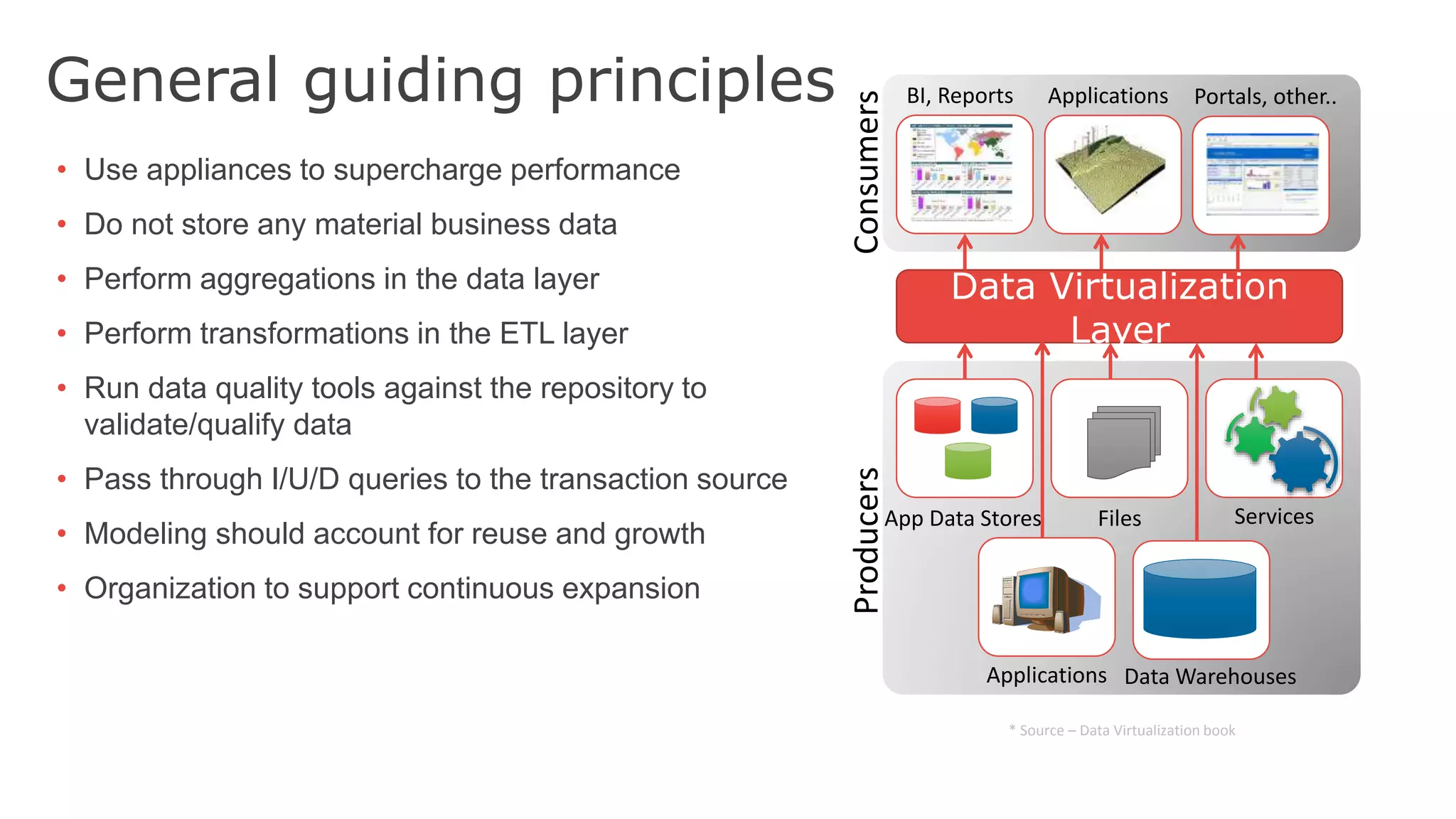
The document discusses the significance of hybrid data ecosystems (HDE) in modern enterprises and the benefits of data virtualization for accessing and integrating diverse data sources. It highlights the challenges associated with HDEs, such as data ownership and quality, while presenting data virtualization as a solution that abstracts access to disparate data and provides real-time information. The document concludes that embracing HDEs and leveraging virtualization technology is essential for businesses to optimize data utilization and drive decision-making.