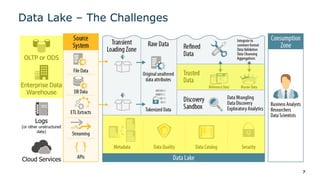
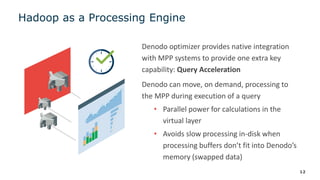
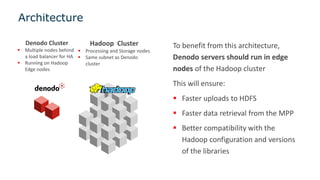
The document outlines a webinar series on data virtualization, focusing on key challenges in data integration and performance for big data scenarios, as presented by Denodo's experts. It covers various topics including modern data architecture, big data integrations, and optimization techniques, specifically highlighting the use of Hadoop as a data source and processing engine. The session aims to showcase best practices for efficiently managing large data volumes without requiring data replication.