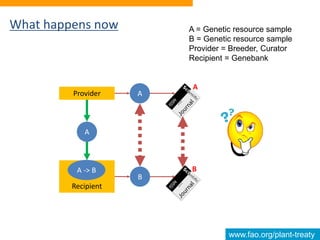
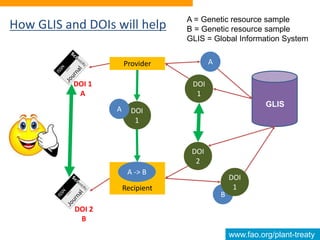
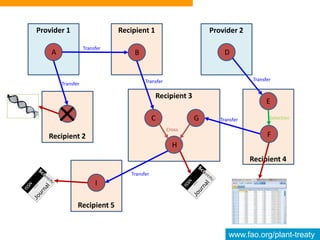
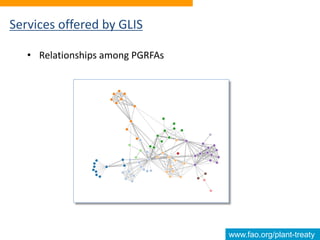
This document discusses the Global Information System (GLIS) of the International Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture (ITPGRFA). GLIS assigns Digital Object Identifiers (DOIs) to plant genetic resources to facilitate information sharing. It will integrate existing information systems and provide standardized descriptive data and links between genetic resources and related publications. Users can register DOIs for their plant collections through a web form, batch uploads, or automated integration using published application programming interfaces.