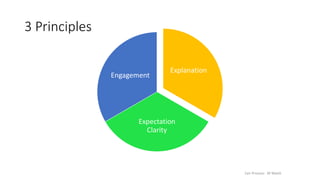
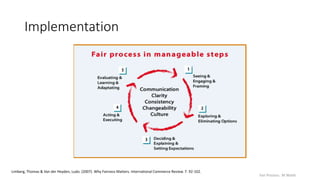
This document discusses fair process and its three key principles: explanation, expectation clarity, and engagement. It describes fair process as focusing on the process used to make decisions, rather than just the decisions themselves. People care more about how a decision was made than the actual outcome. The document outlines an activity where participants take on roles in a scenario and discuss a proposed change from the perspective of their roles to examine how well the principles of fair process were followed. It aims to analyze an implementation of fair process and examine everyday experiences for successes and opportunities regarding fair process.