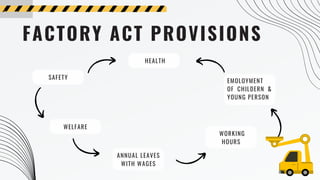
The 1948 Factory Act came into force in 1949 to ensure safety measures and promote worker health and welfare in factories employing 10 or more power-driven workers or 20 or more without power. It covers all of India except mines, military units, railways, hotels and restaurants. The act's goals are to protect workers from long hours, provide healthy conditions, ensure safety precautions, and allow state regulation through inspectors. It includes provisions for health, safety, working hours, welfare, annual leave and rules for employing children and young people. The Bhopal Gas Tragedy highlighted gaps in the Factory Act's safety and emergency protocols, leading to legal and regulatory reforms to strengthen industrial safety standards and oversight.