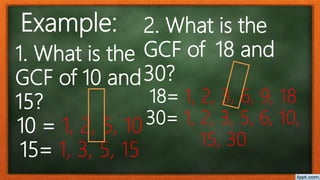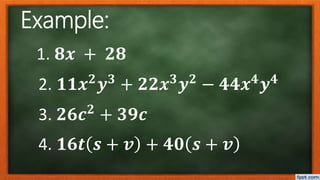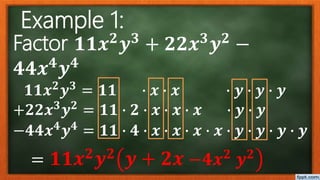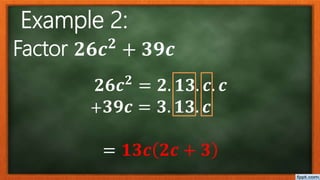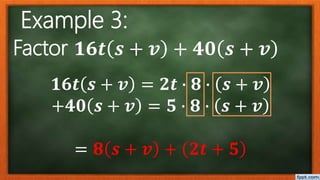This document discusses factoring polynomials with common factors. It defines a factor as a number that divides another number without a remainder. The greatest common factor (GCF) is the largest factor common to two or more numbers. The document provides examples of finding the GCF of various numbers and polynomial terms. It explains that a polynomial is an expression involving variables and coefficients using addition, subtraction, multiplication, and exponents. The document outlines the steps to factor polynomials by finding the GCF of coefficients, identifying common variables, dividing each term by the GCF, and writing the factored form. It provides examples of factoring different polynomials.