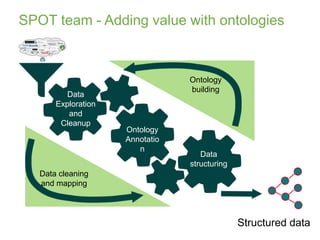
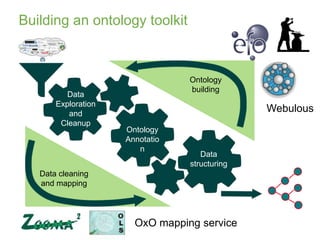
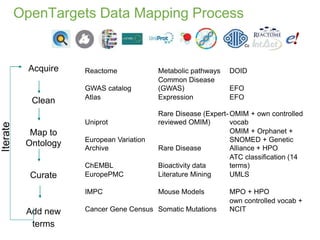
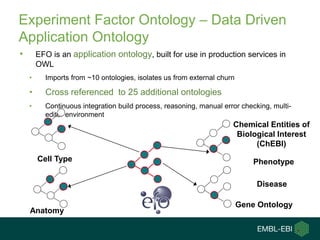
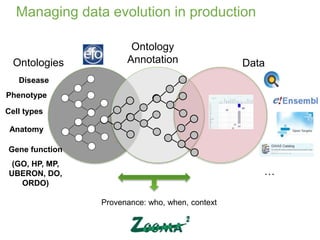
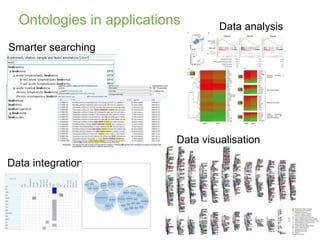
1) The document discusses EBI's efforts to facilitate semantic alignment of its resources through building ontologies and annotating data with ontologies.
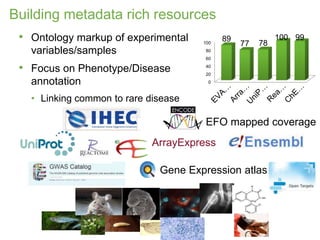
2) It describes EBI's work developing ontologies like the Experiment Factor Ontology and using ontologies to enhance search, data visualization, and data integration.
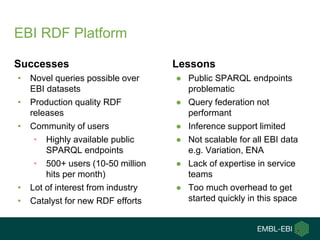
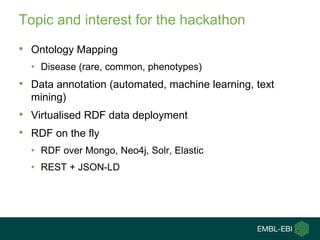
3) The challenges of representing EBI data in RDF are discussed, and future directions are outlined that could make RDF deployment simpler and enable more interesting queries over EBI data.