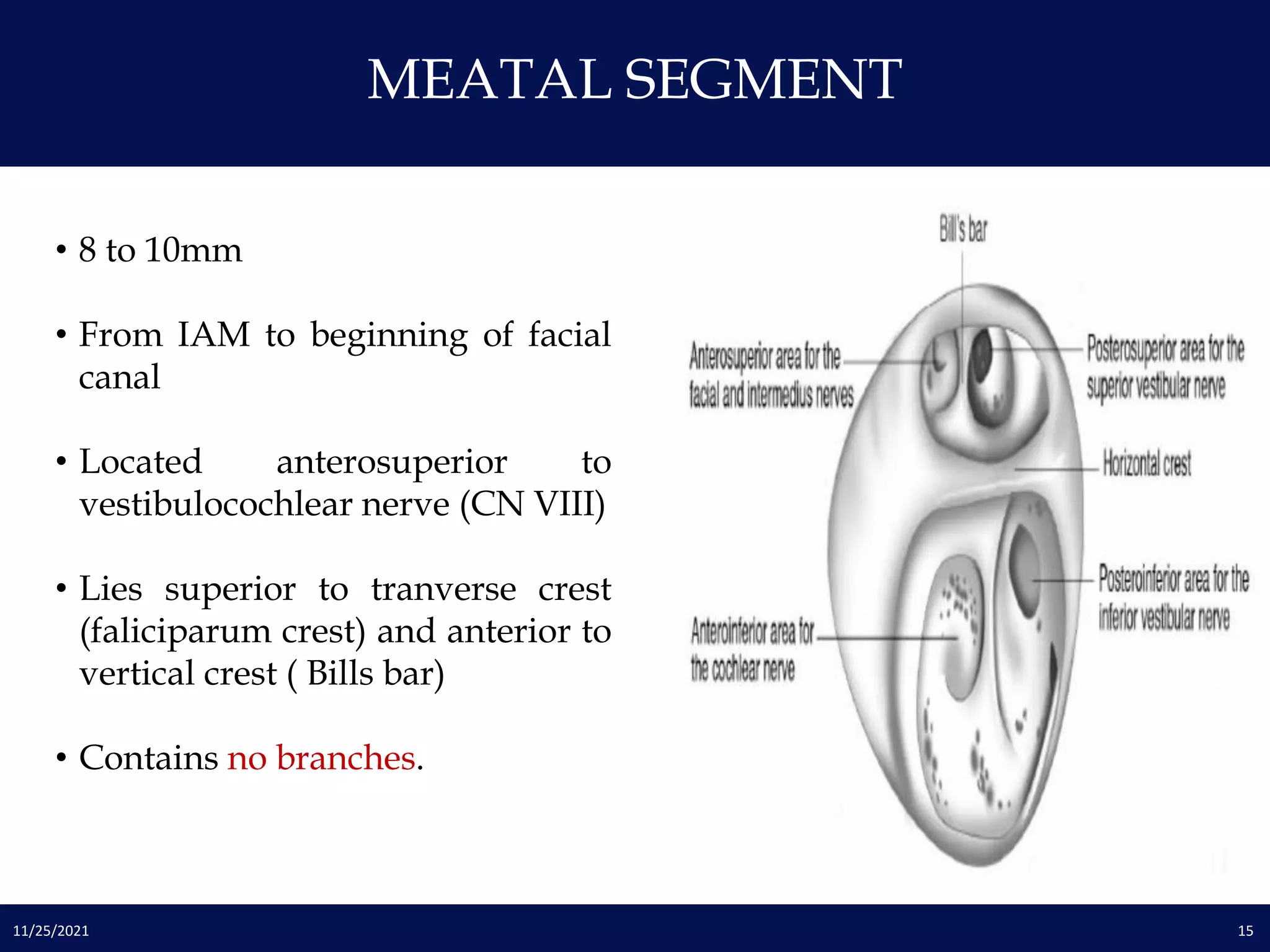
The facial nerve has three divisions - intracranial, intratemporal, and extratemporal. In the intratemporal portion, it passes through four segments within the facial canal: meatal, labyrinthine, tympanic, and mastoid. It gives off several branches including the chorda tympani and nerve to stapedius. The facial nerve exits the skull through the stylomastoid foramen and divides into five terminal branches in the parotid gland. Knowledge of the facial nerve's complex anatomy is important for ear and parotid surgeries.