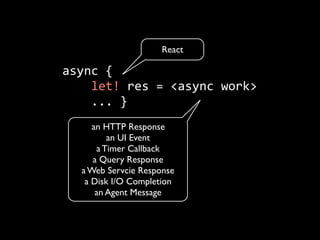
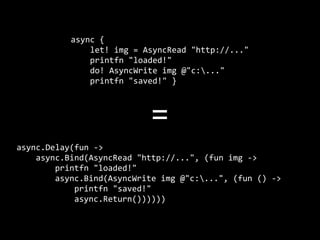
The document discusses asynchronous programming in F#, highlighting its features such as immutability and its ability to handle concurrency challenges like shared state, code locality, I/O parallelism, and scaling across multiple machines. It emphasizes the complexities of asynchronous workflows and offers examples demonstrating F#'s strengths in functional and concurrent programming. Additionally, it presents F# as a modern, efficient language that supports production-level development.