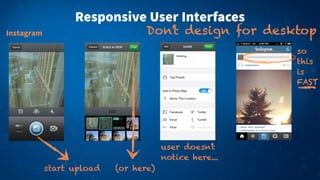
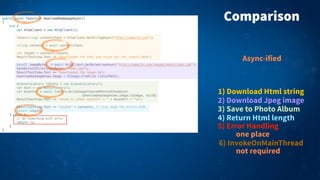
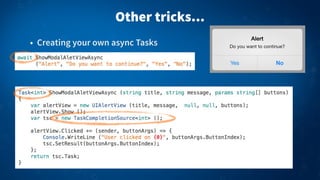
1) Async and await syntax in C# allows long-running and blocking tasks to run asynchronously without blocking the main thread or UI. This keeps the user interface responsive.
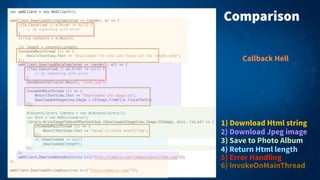
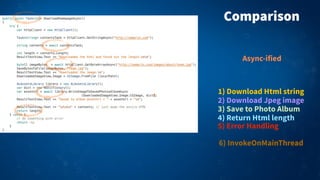
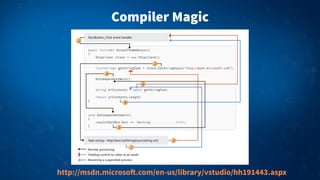
2) Async methods return Task or Task<T> objects and use the await keyword to suspend execution until the awaited task completes. This avoids "callback hell" and makes asynchronous code appear synchronous and easier to read.
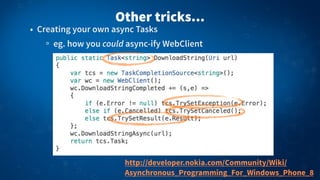
3) Popular platforms and frameworks like .NET, Xamarin, Android and iOS have adopted async APIs, allowing asynchronous programming in mobile apps across these platforms using C# and a common syntax.