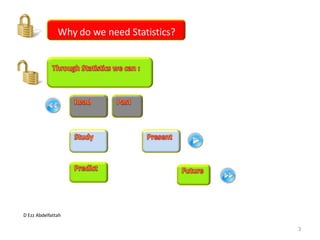
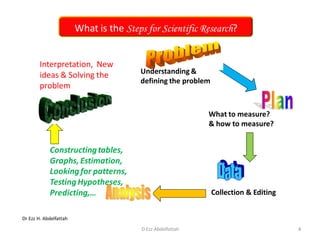
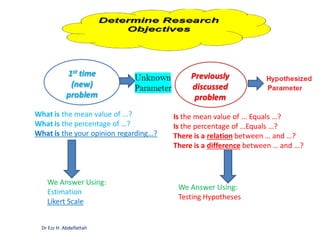
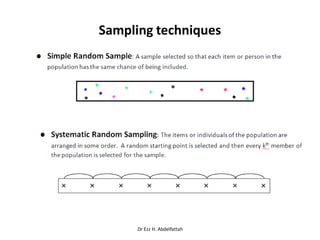
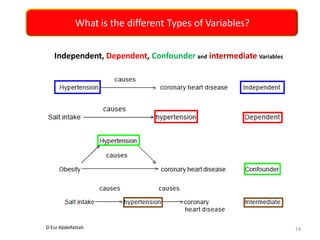
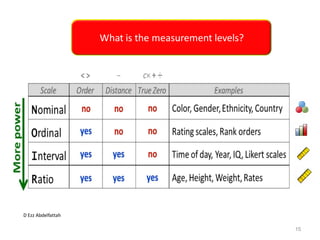
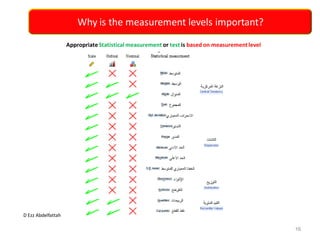
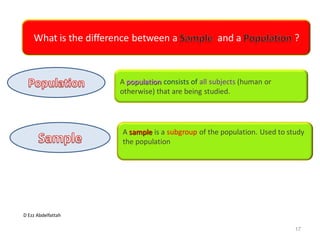
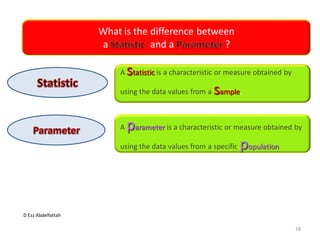
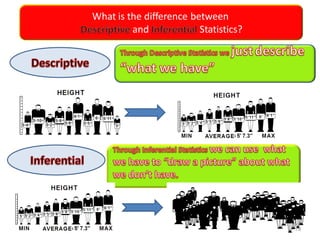
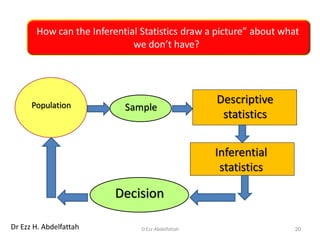
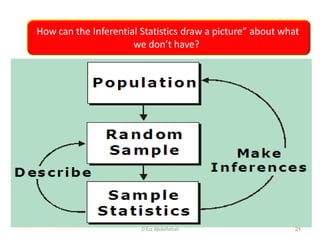
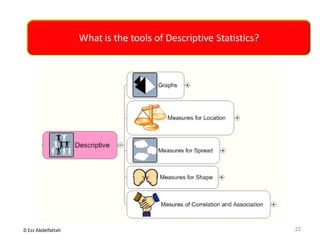
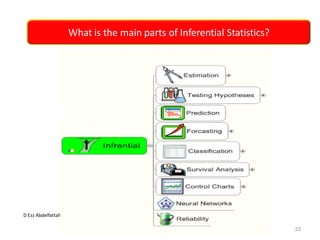
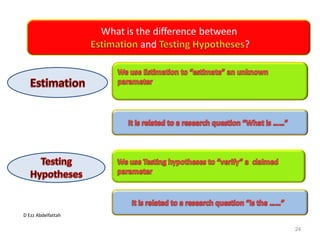
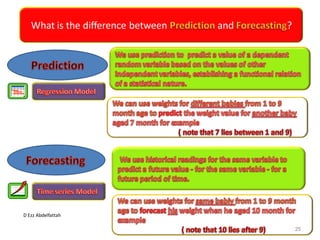
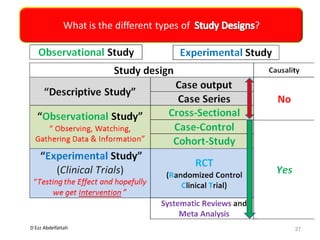
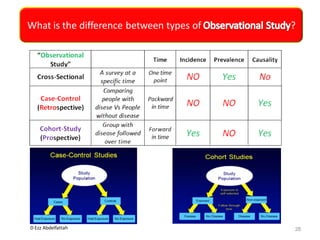
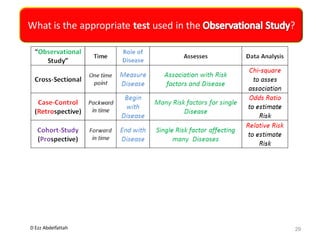
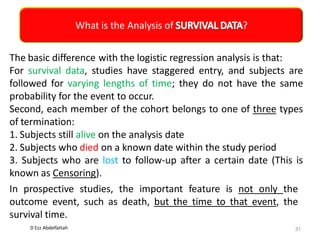
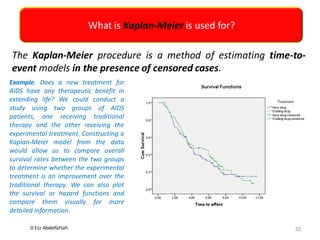
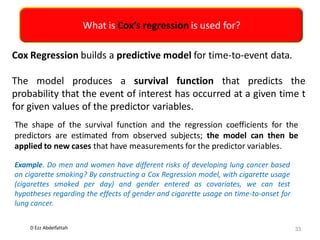
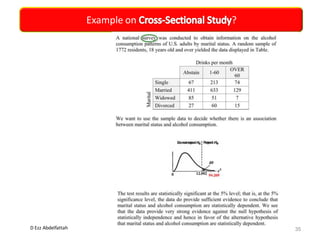
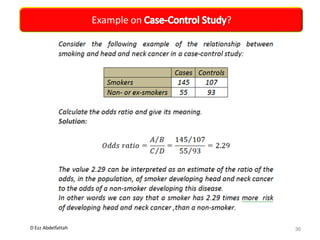
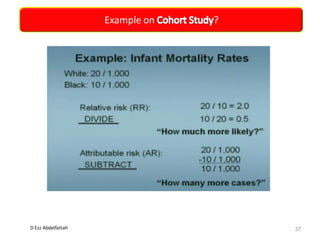
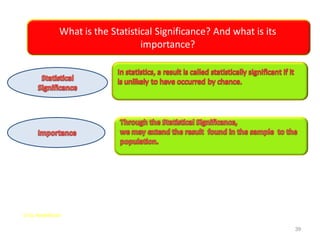
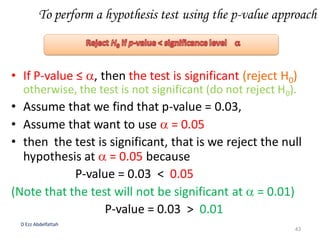
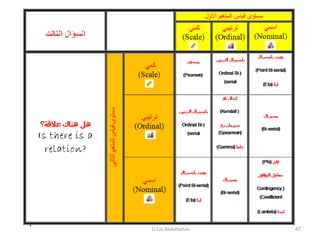
This document discusses the importance of statistical significance and p-values in hypothesis testing. It explains that the p-value is the probability of observing results as extreme or more extreme than what was actually observed, assuming the null hypothesis is true. A lower p-value provides stronger evidence against the null hypothesis. The decision to reject the null hypothesis depends on comparing the p-value to the pre-determined significance level (alpha), typically 0.05. If the p-value is less than the significance level, then the result is considered statistically significant and the null hypothesis can be rejected.