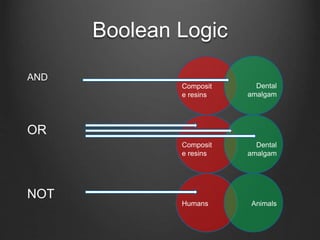
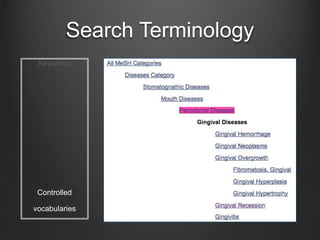
The document provides information about conducting literature searches for systematic reviews and meta-analyses. It discusses search foundations, databases, constructing effective searches using keywords and controlled vocabularies, Boolean logic, common search techniques, and standards for reporting search methodology. The goal of the search is to identify every relevant study on the topic to comprehensively capture available data for analysis and allow reproducibility. Effective searches require breaking topics into components, using synonyms and related terms, and searching multiple databases which can result in thousands of results.














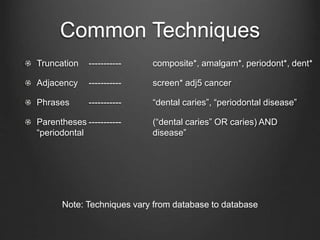
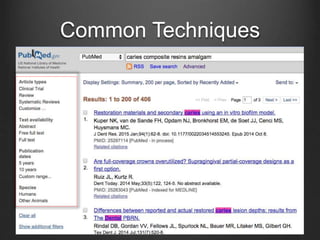
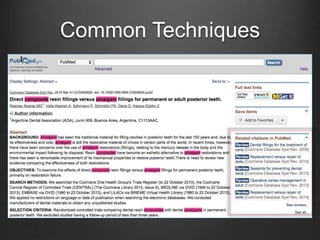
![Common Techniques
PubMed
MeSH dental caries[mesh]
Major MeSH dental caries[majr]
Title dental caries[title]
Title/Abstract dental caries[title/abstract]
Journal journal of dental research[journal]
Author maceachern m[author]
Refer to ‘Search Builder’ in PubMed Advanced for other fields](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2015dent610-151027121012-lva1-app6891/85/Extensive-Literature-Searching-22-320.jpg)