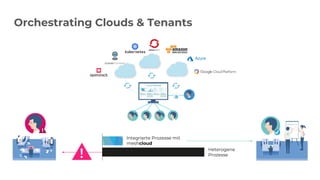
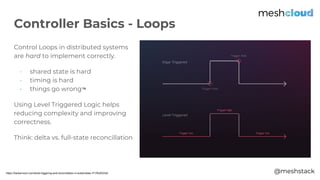
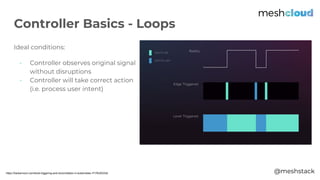
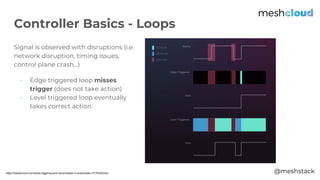
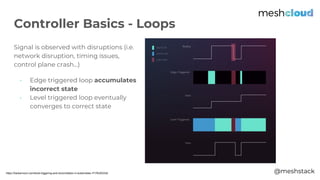
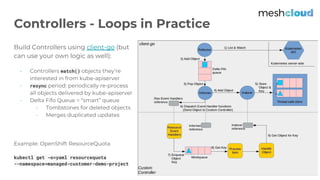
The document discusses a Kubernetes meetup held in Frankfurt on March 25, 2019, focusing on extending Kubernetes through various tools and methods provided by meshcloud. It covers architectural components like kube-apiserver, controllers, and custom resource definitions, emphasizing their roles in managing multi-cloud environments. Key examples of extending Kubernetes, such as using Operators and custom APIs, are also presented to illustrate capabilities in orchestration and infrastructure management.