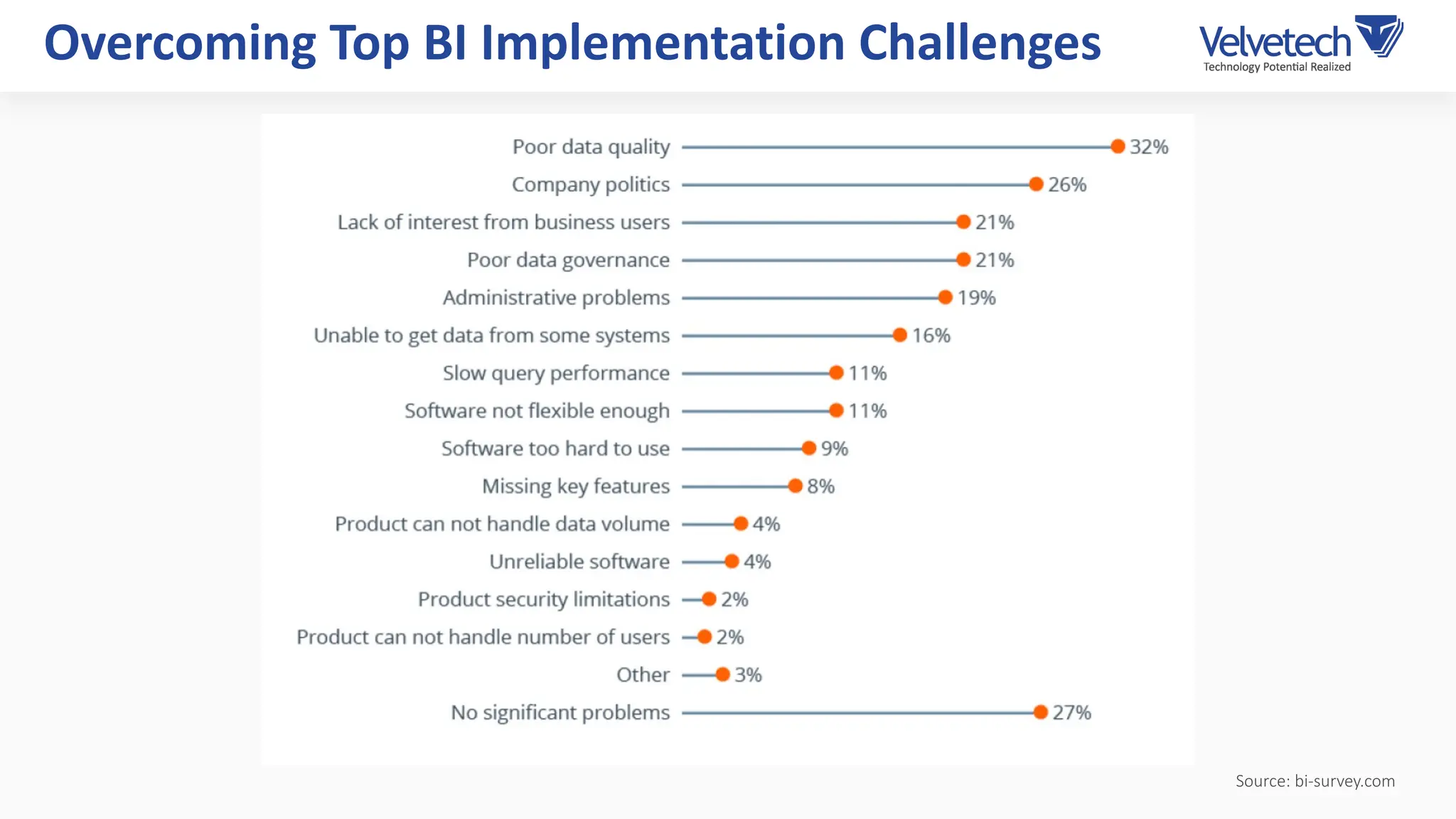
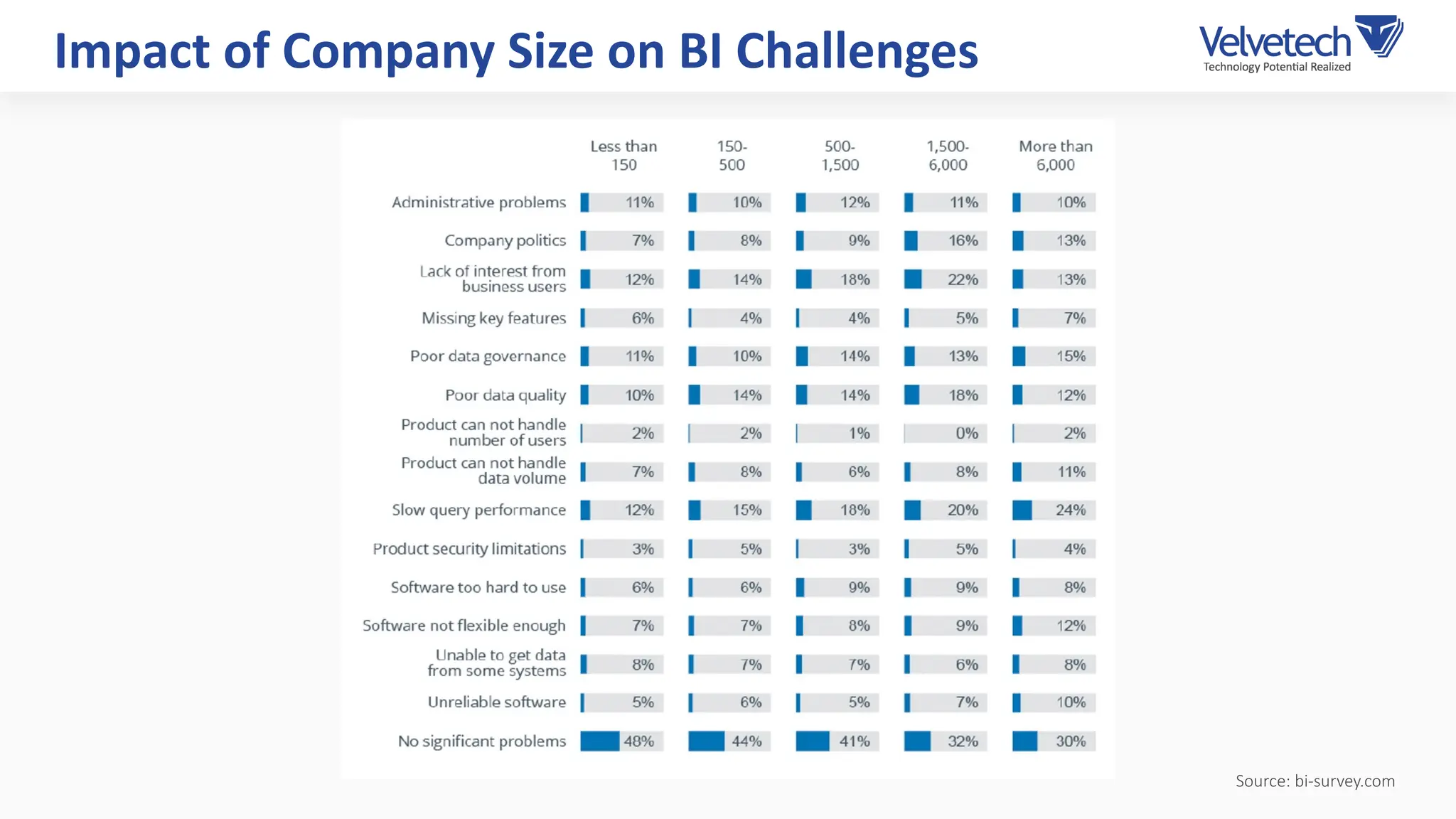
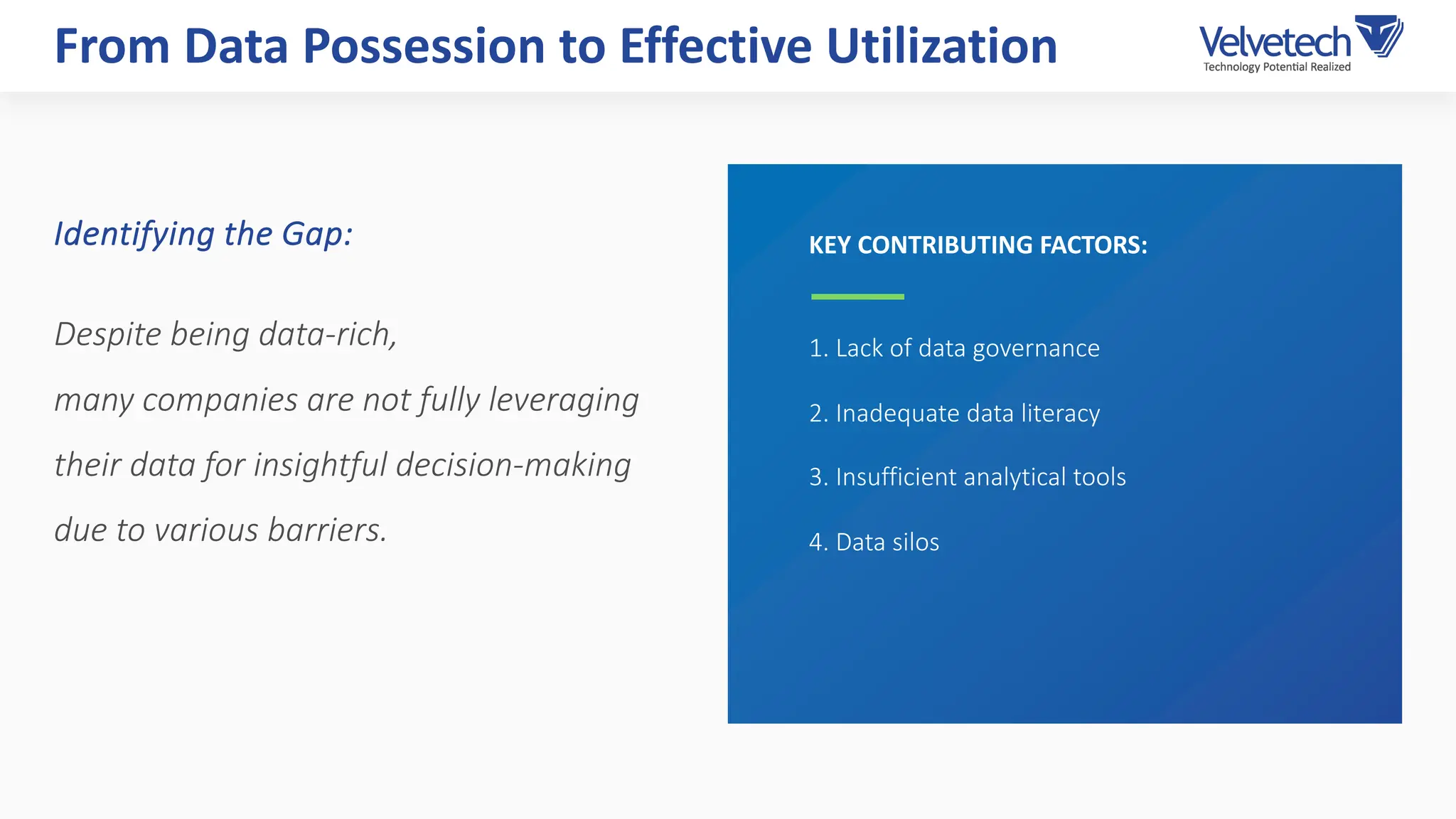
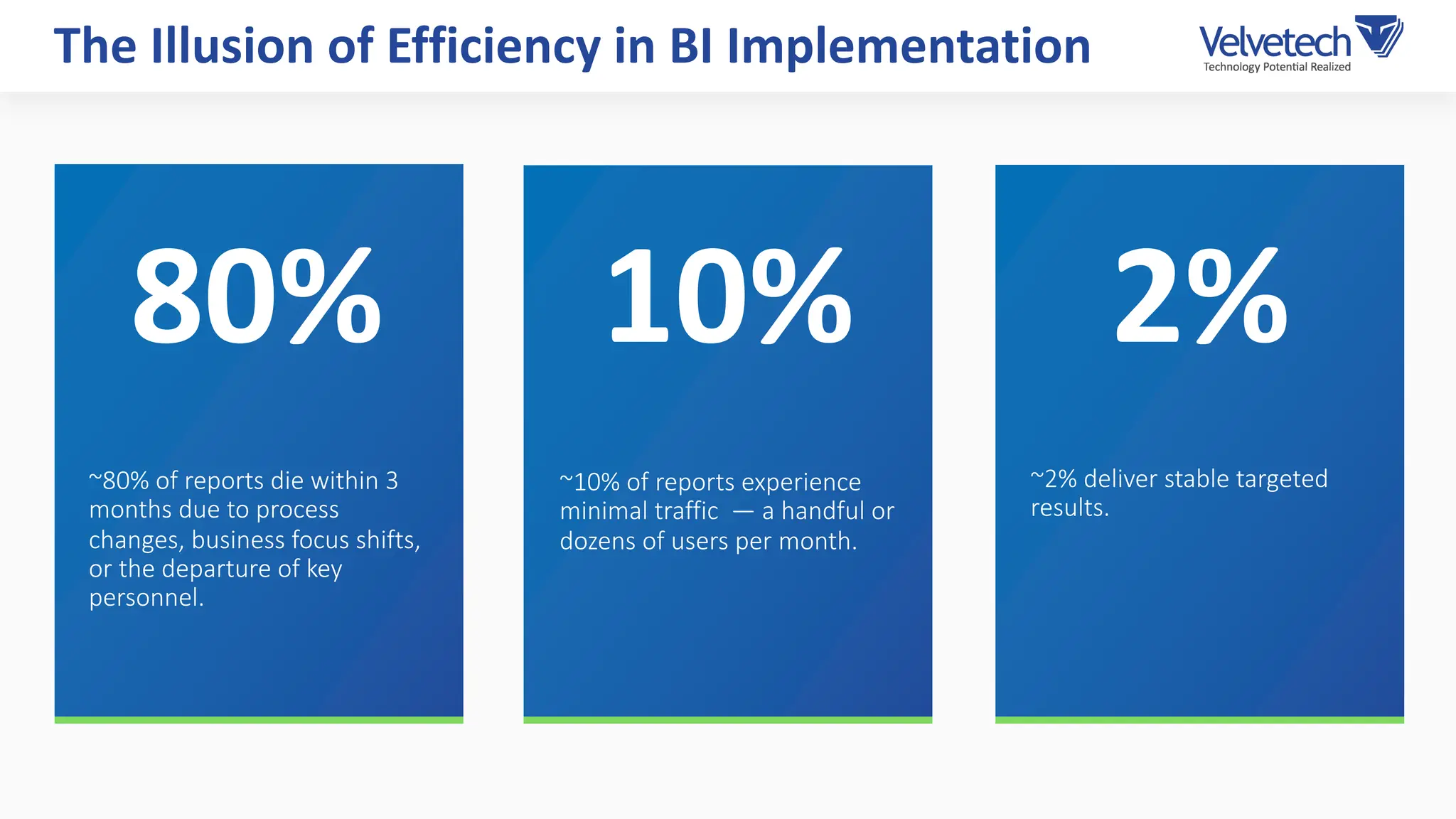
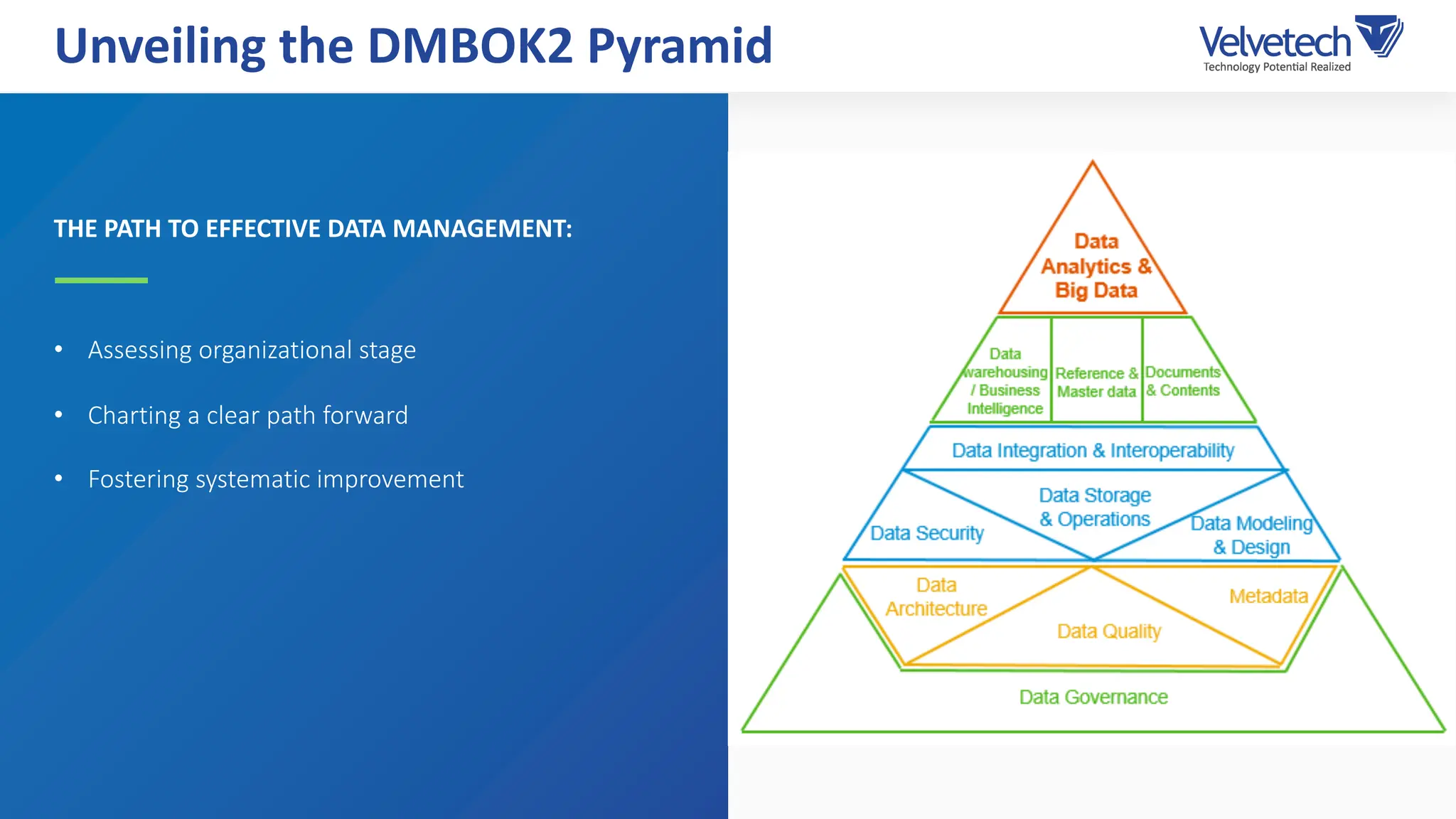
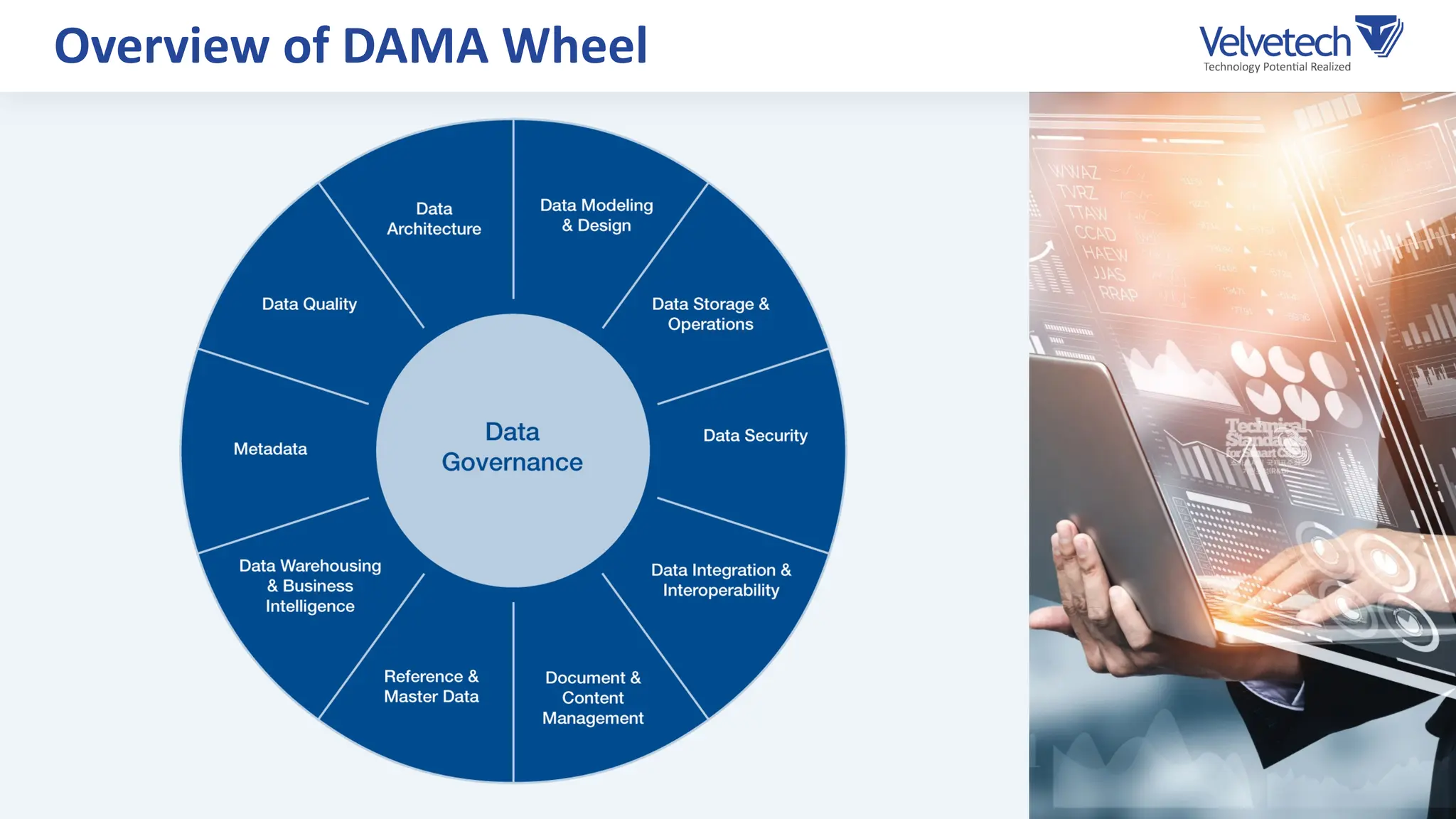
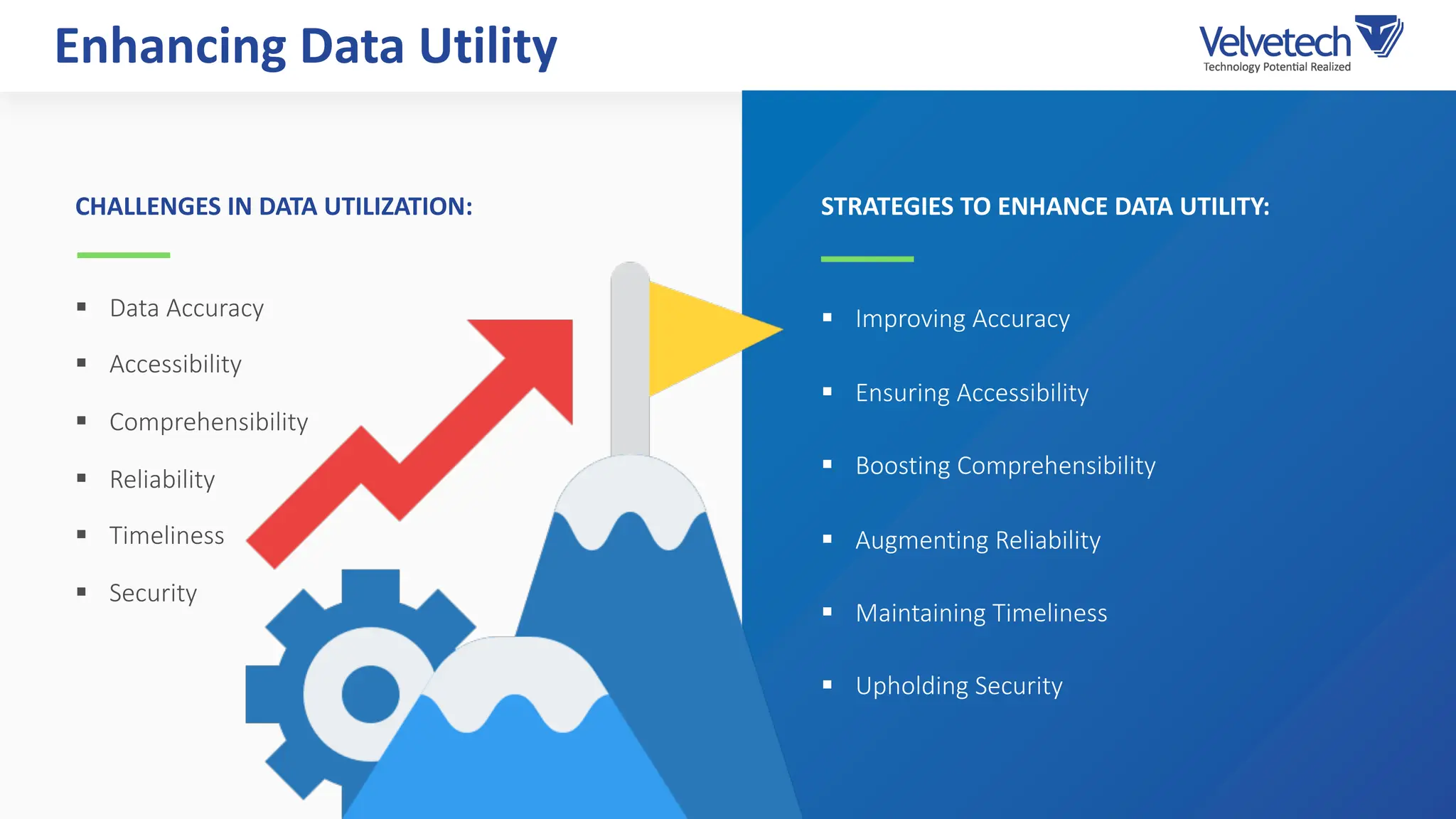
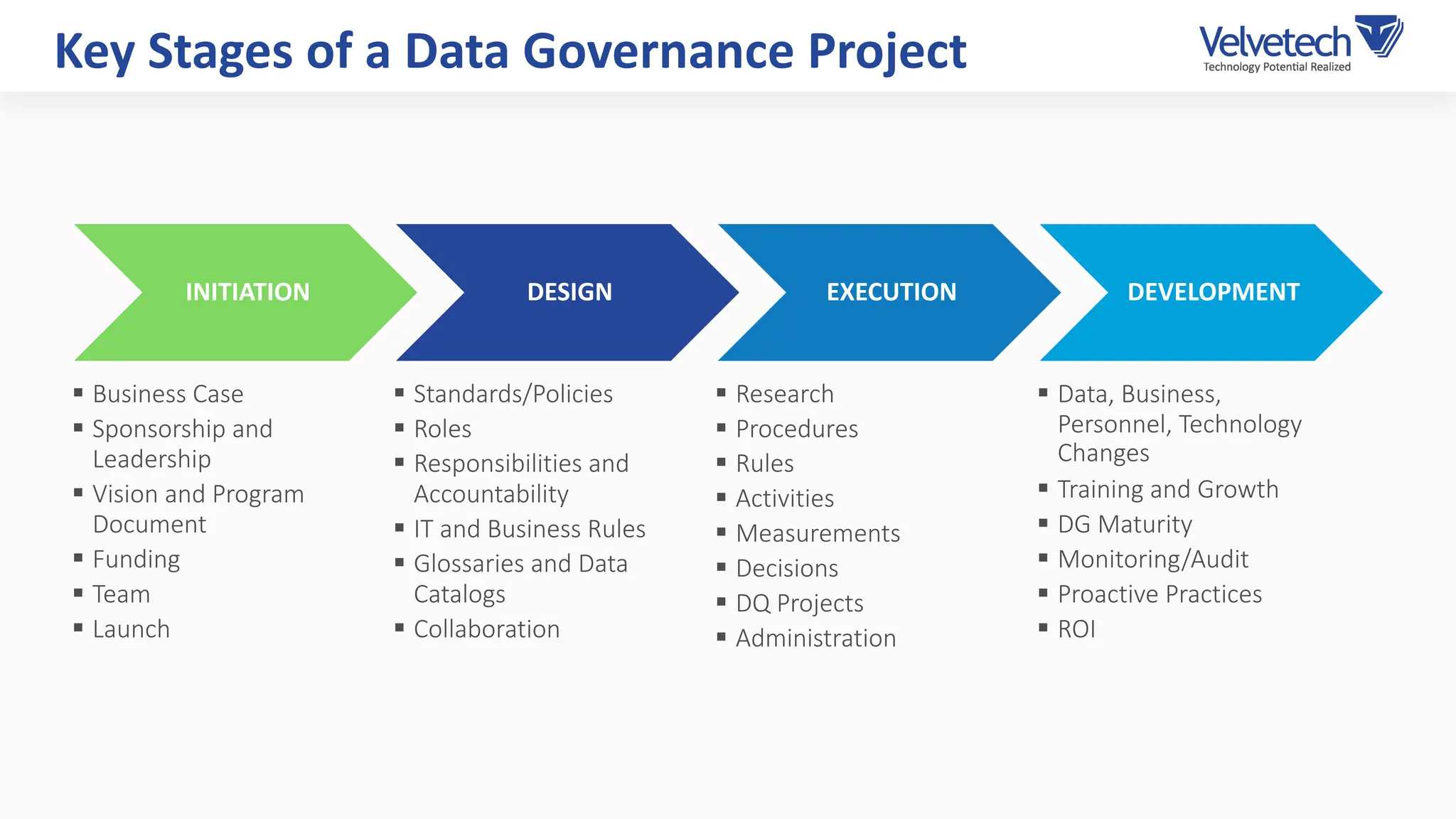
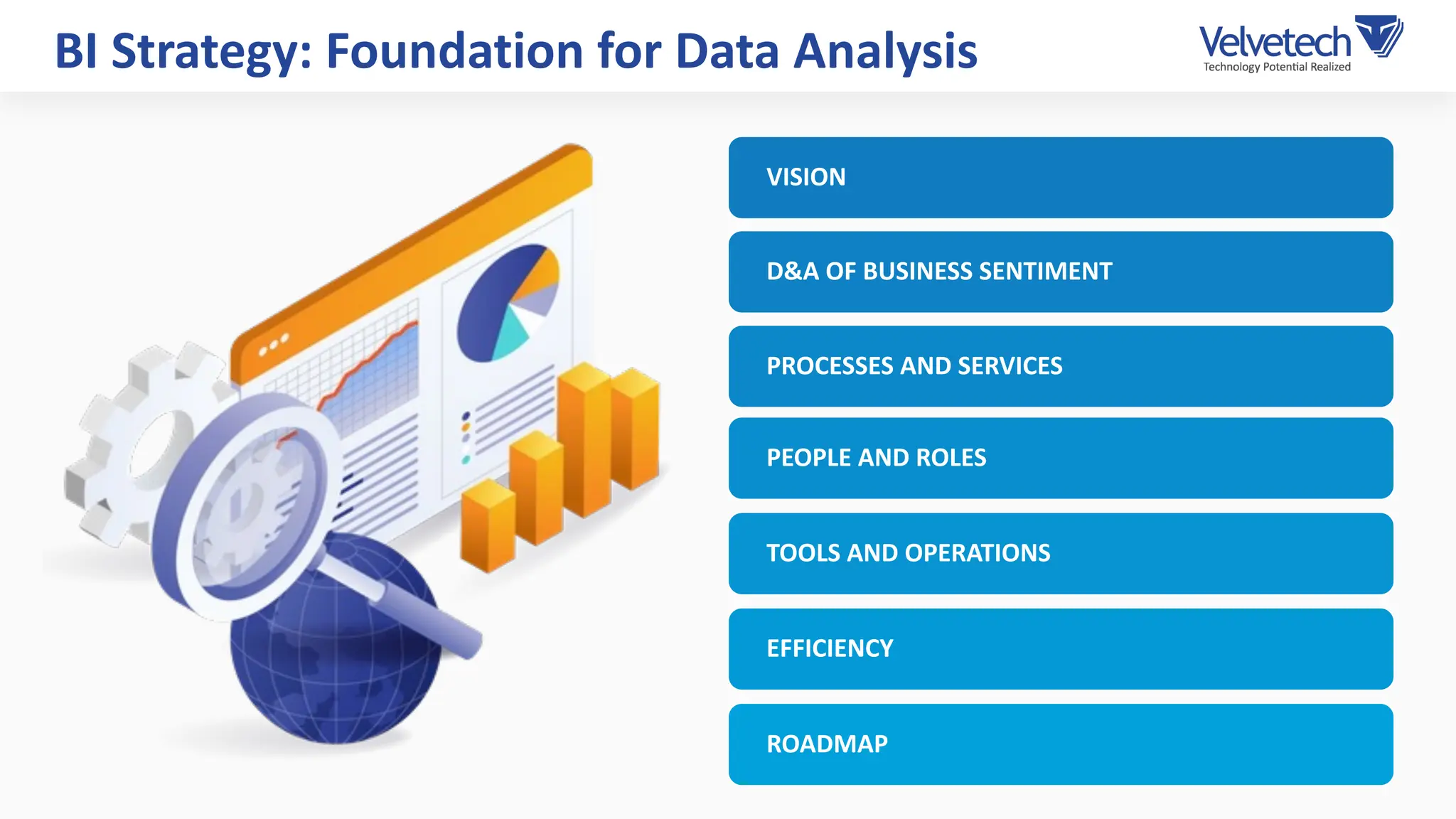
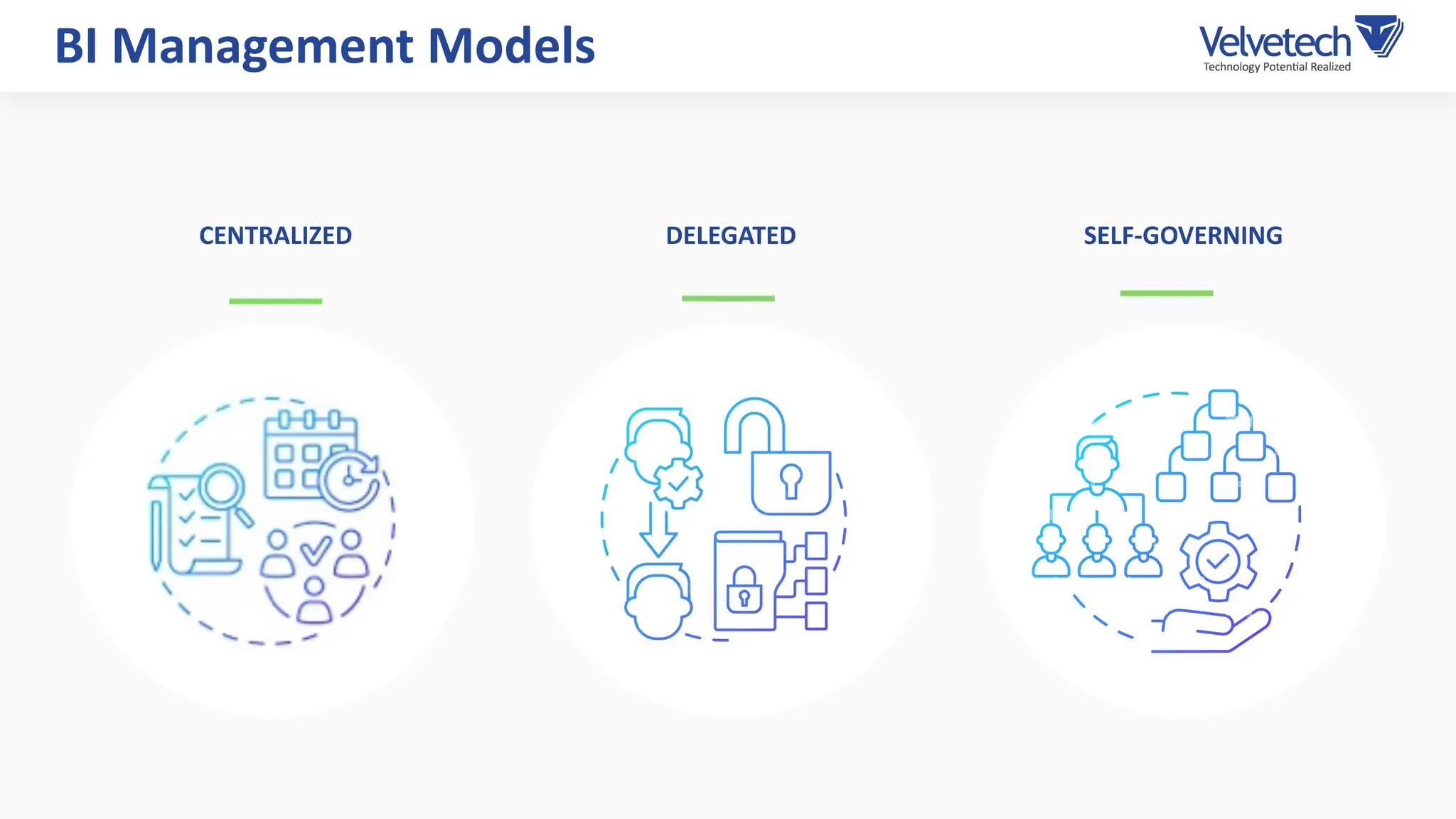
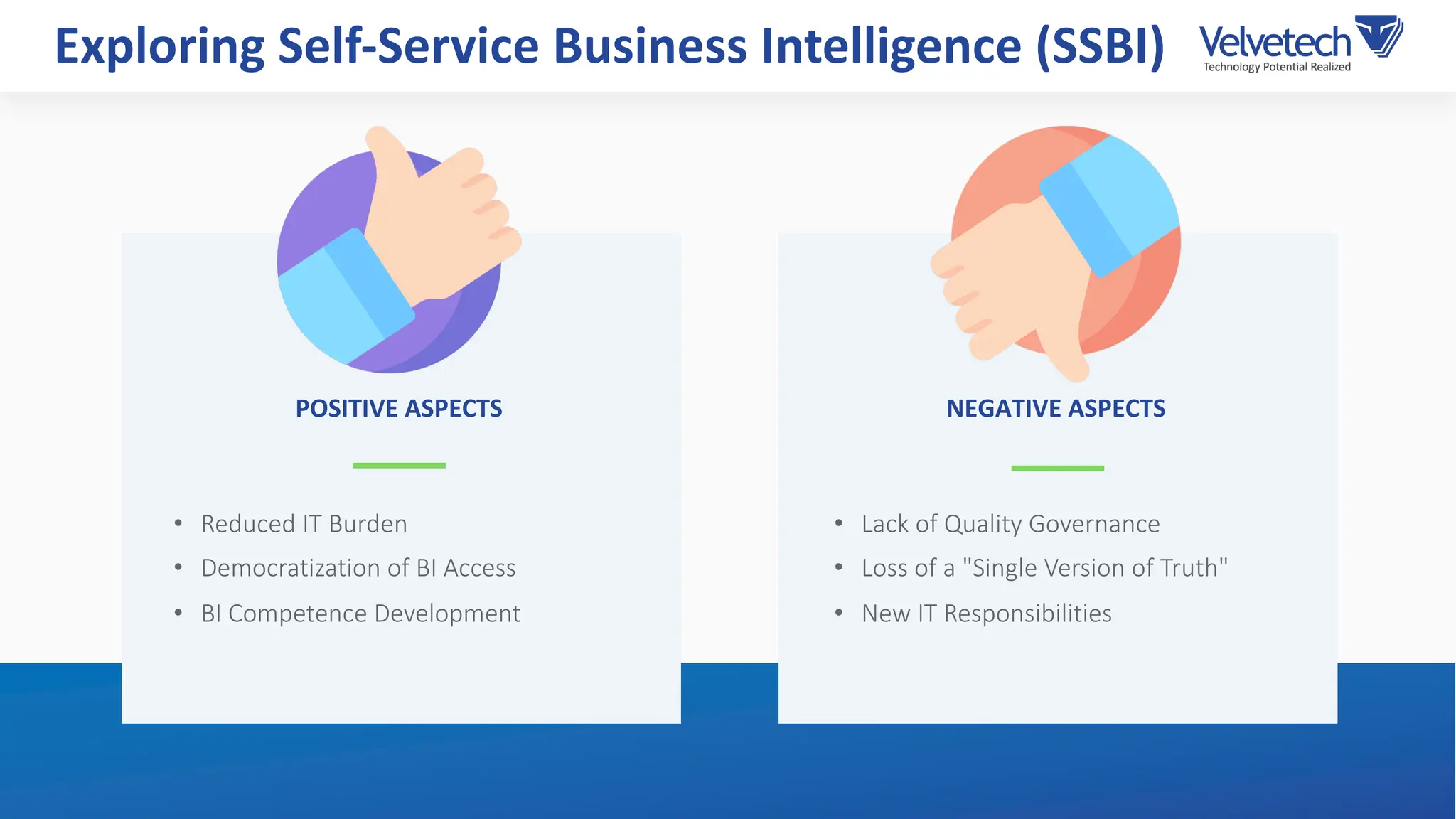
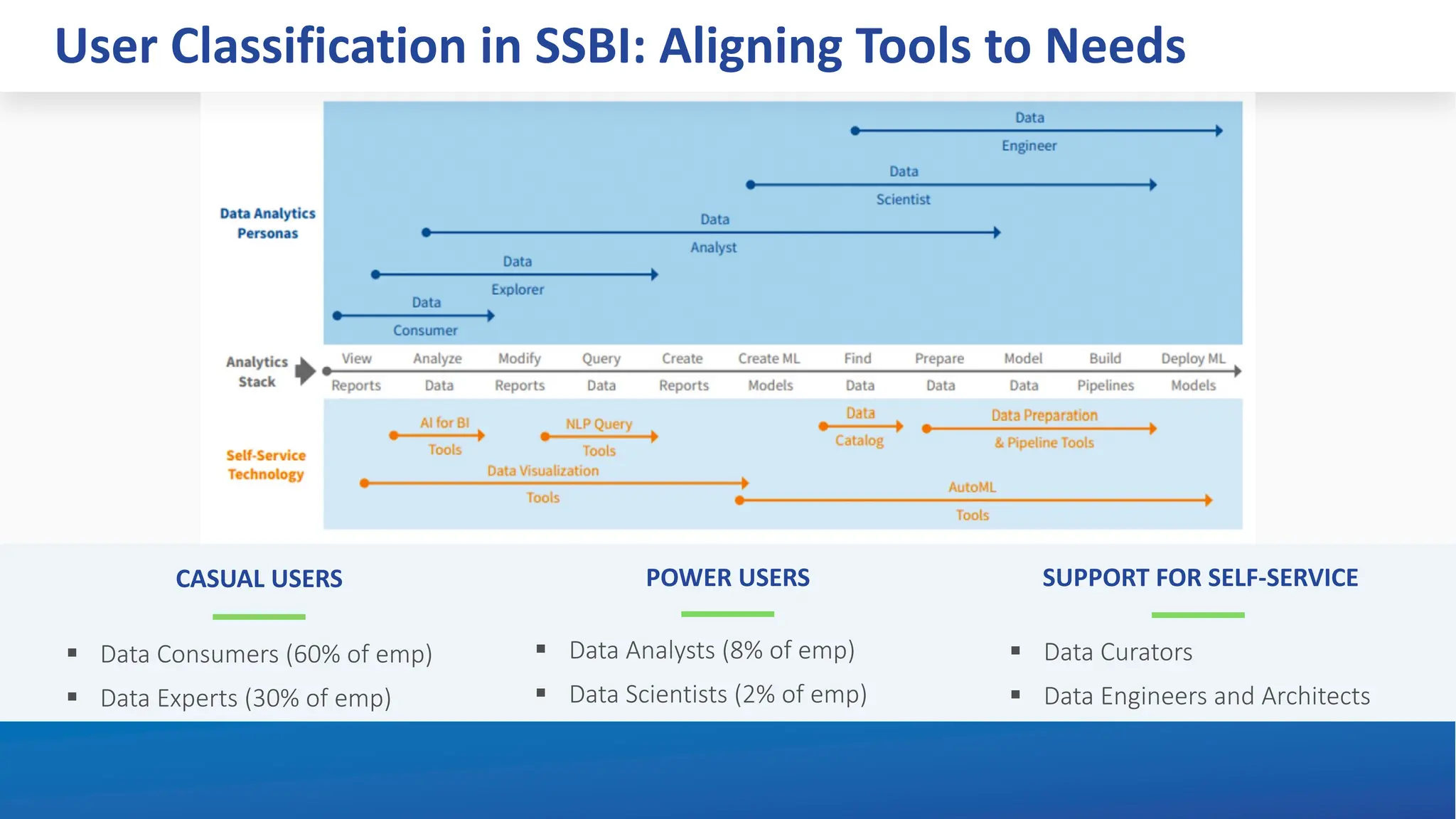
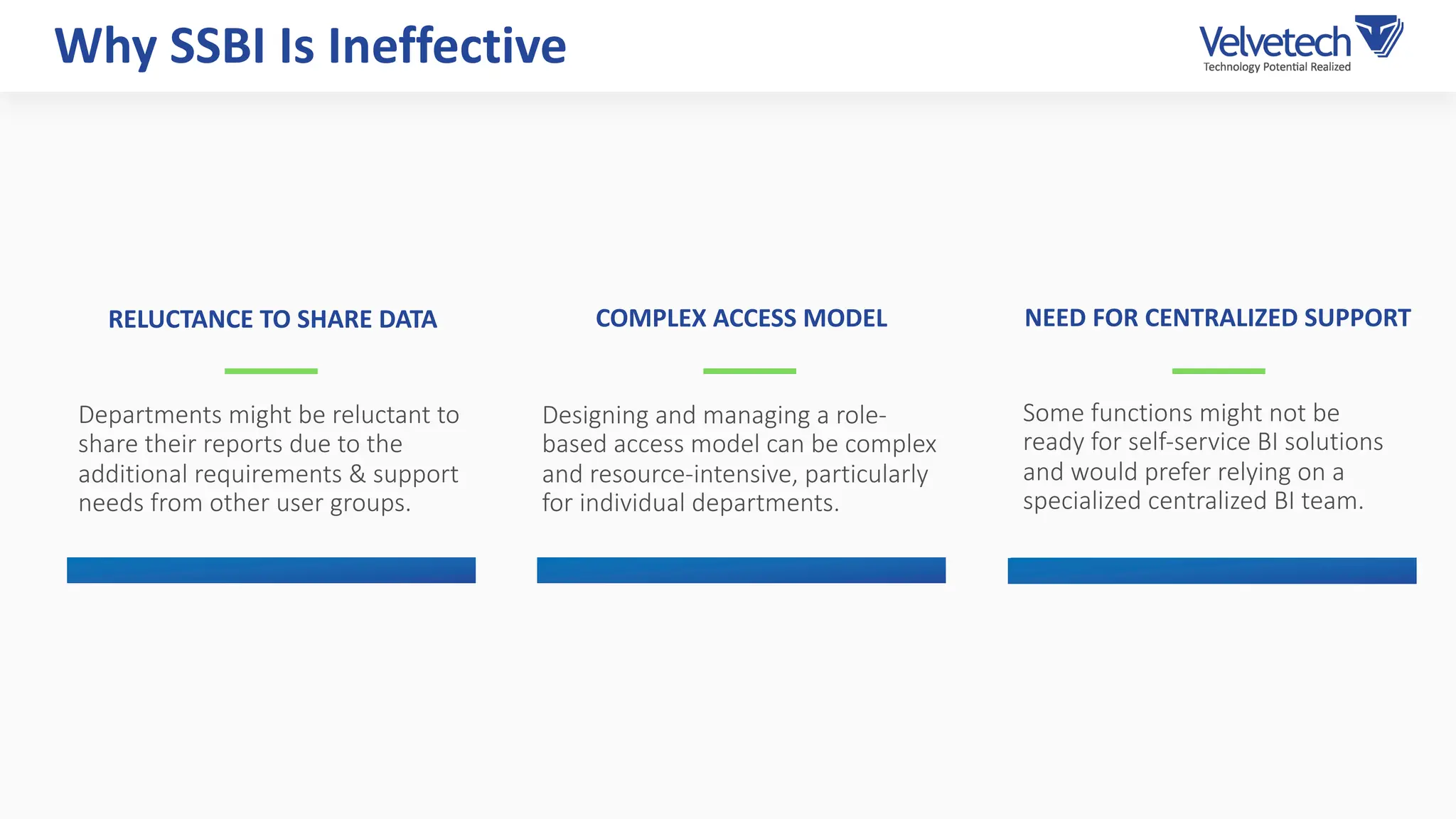
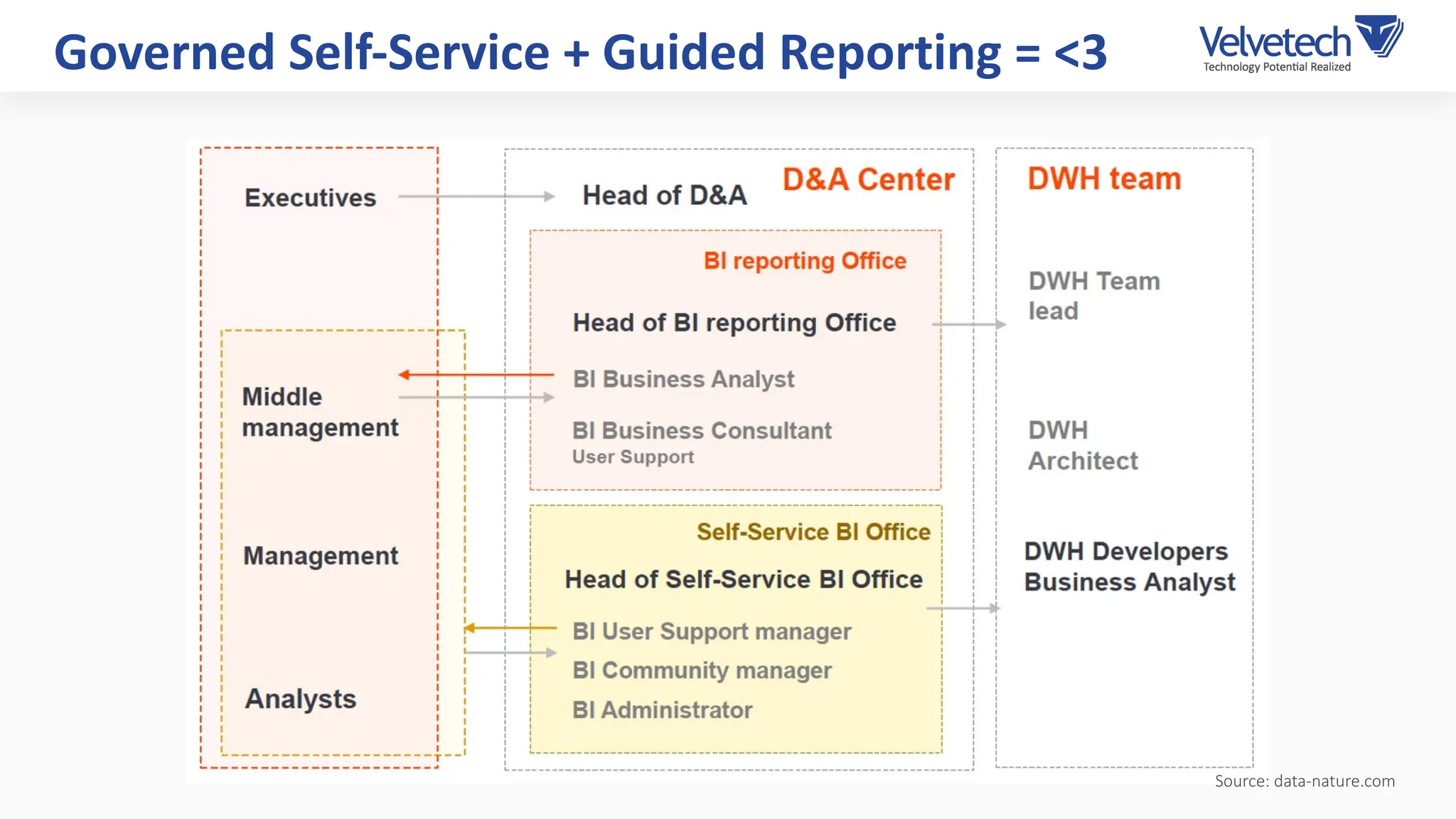
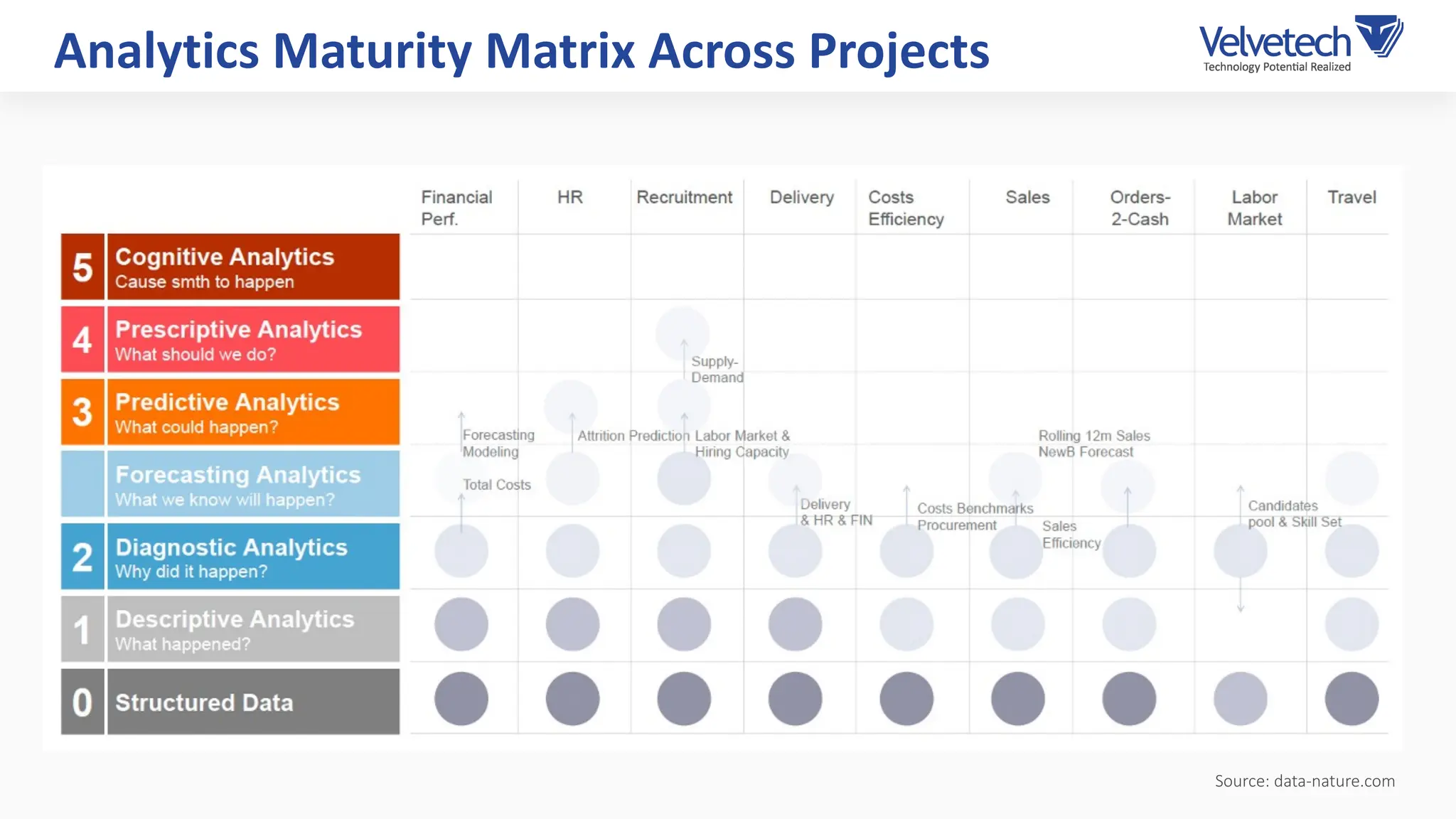
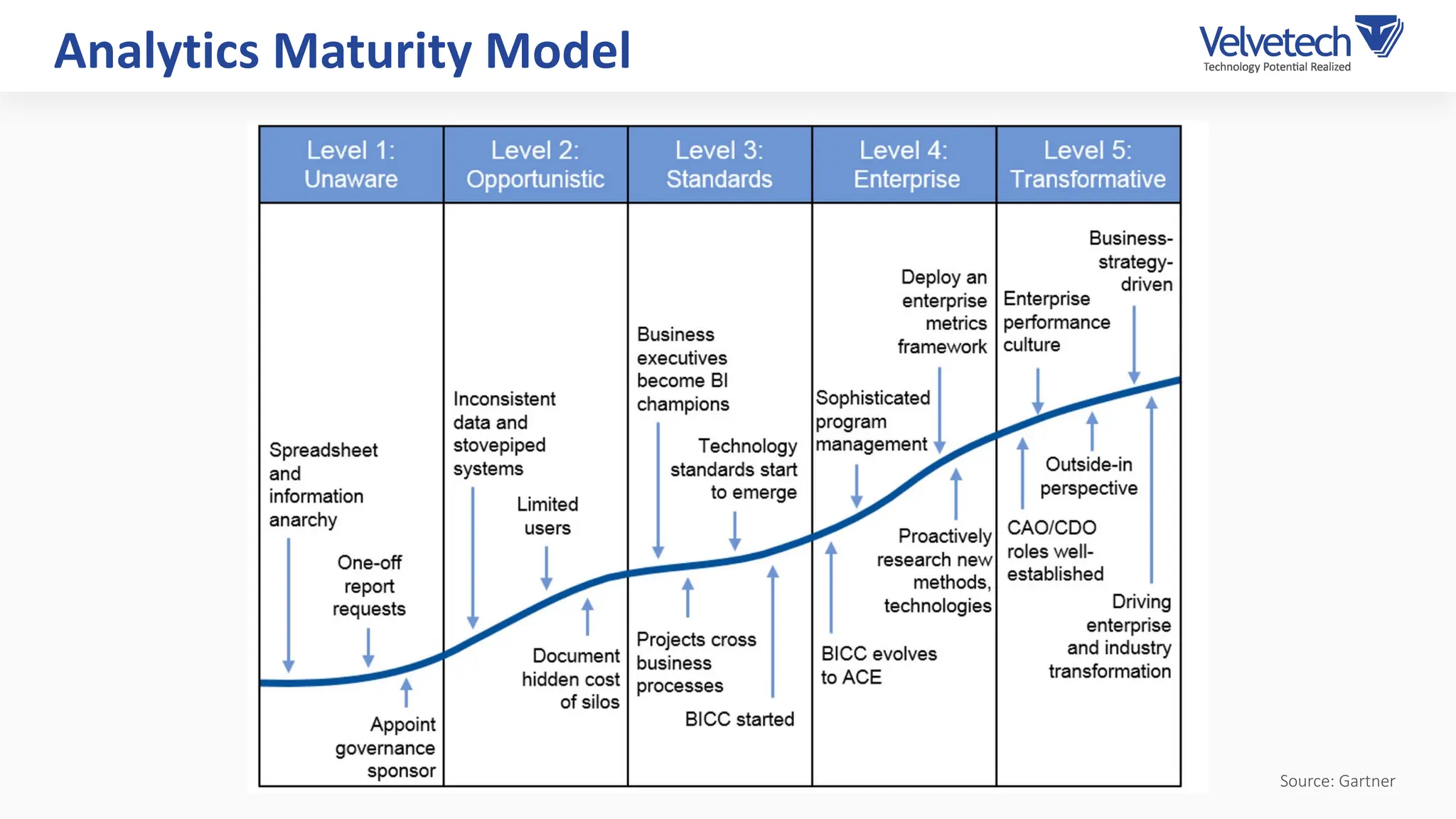
The document explores the transformation of business operations through Business Intelligence (BI), emphasizing the importance of data-driven decision-making. It highlights the challenges in BI implementation, such as data quality issues, insufficient company-wide adoption, and the illusion of BI efficiency, along with best practices for overcoming these barriers. The document also discusses various management models, strategies for enhancing data utility, and the need for a structured BI approach to improve organizational efficiency.