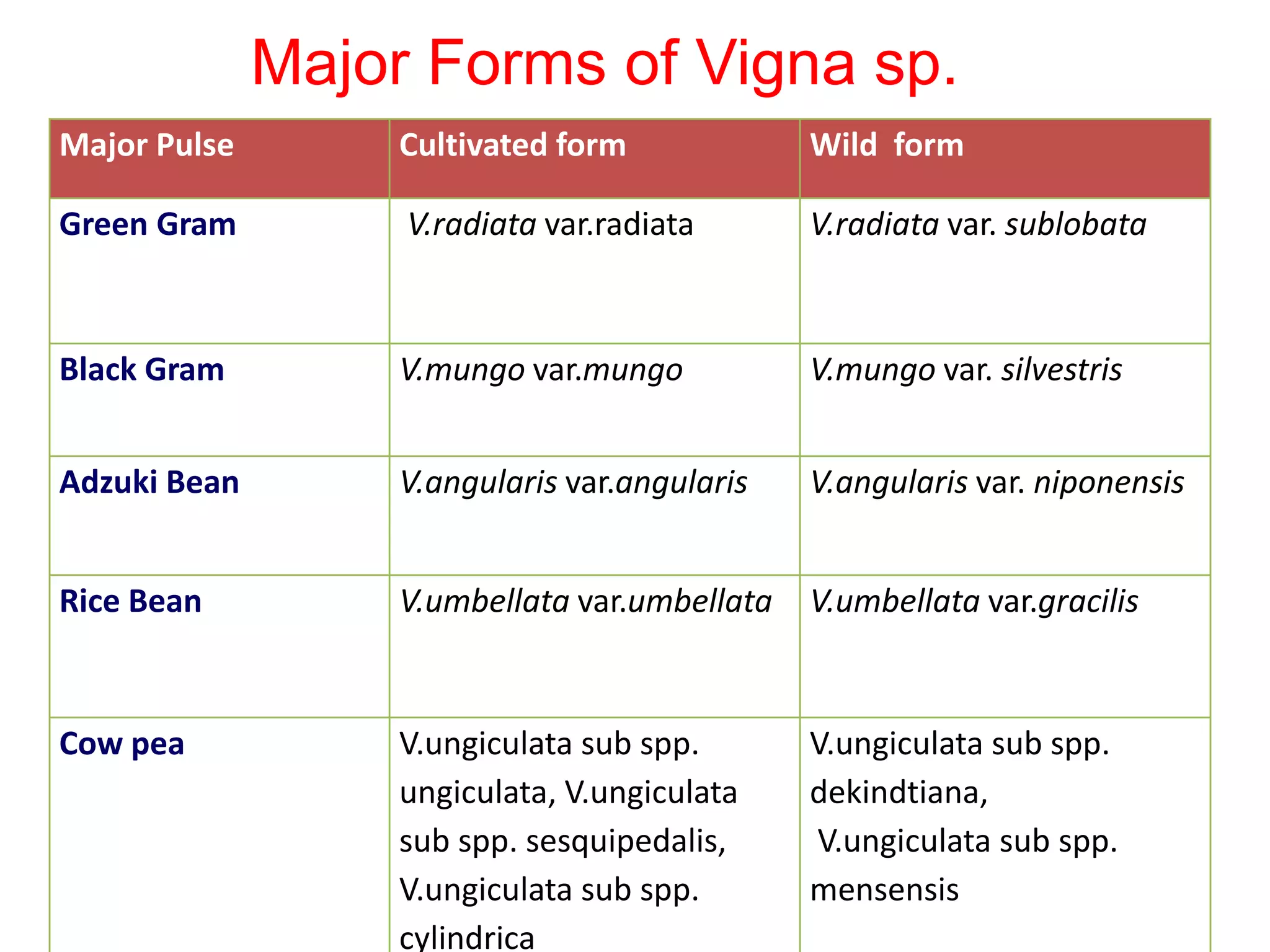
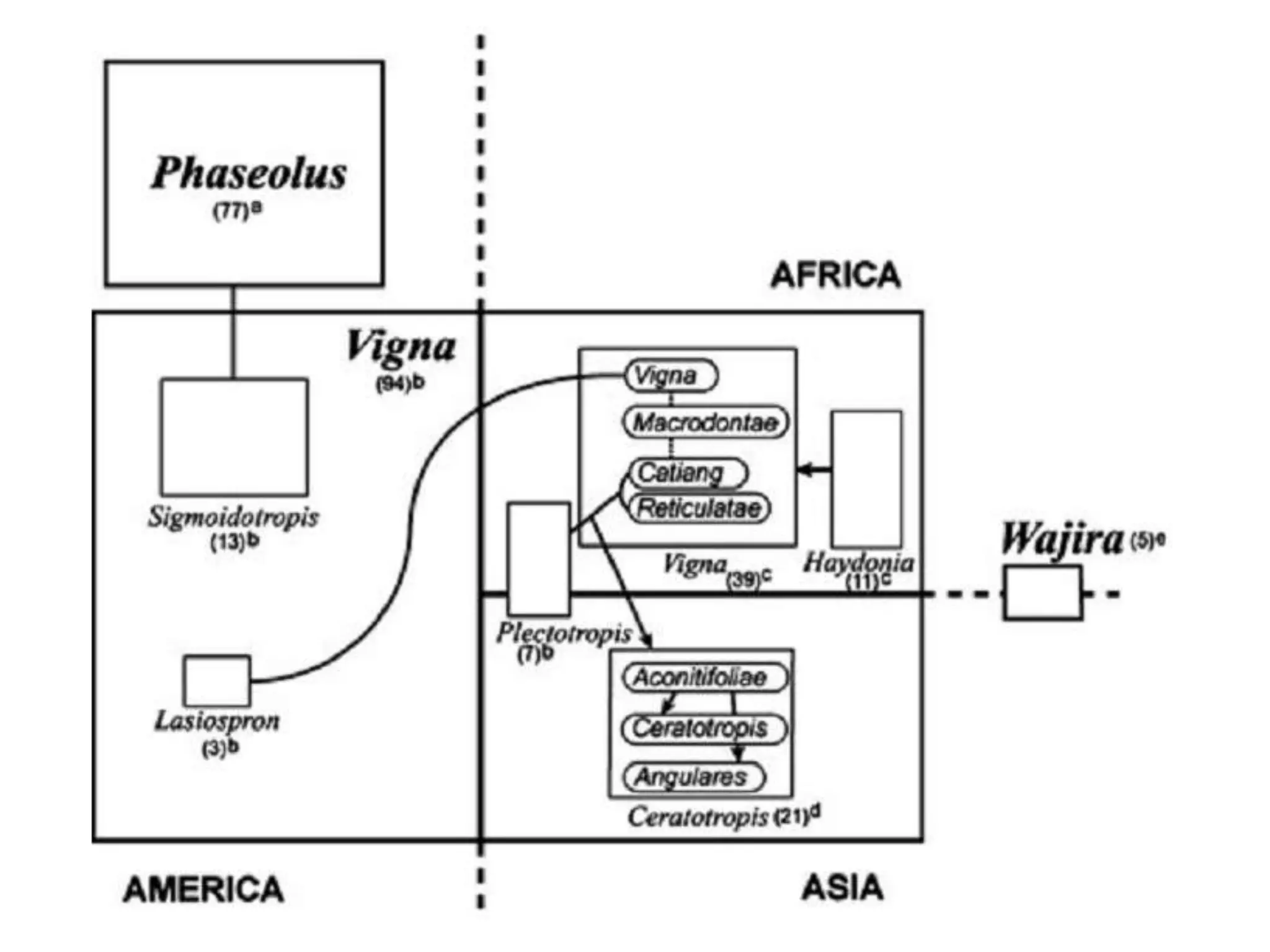
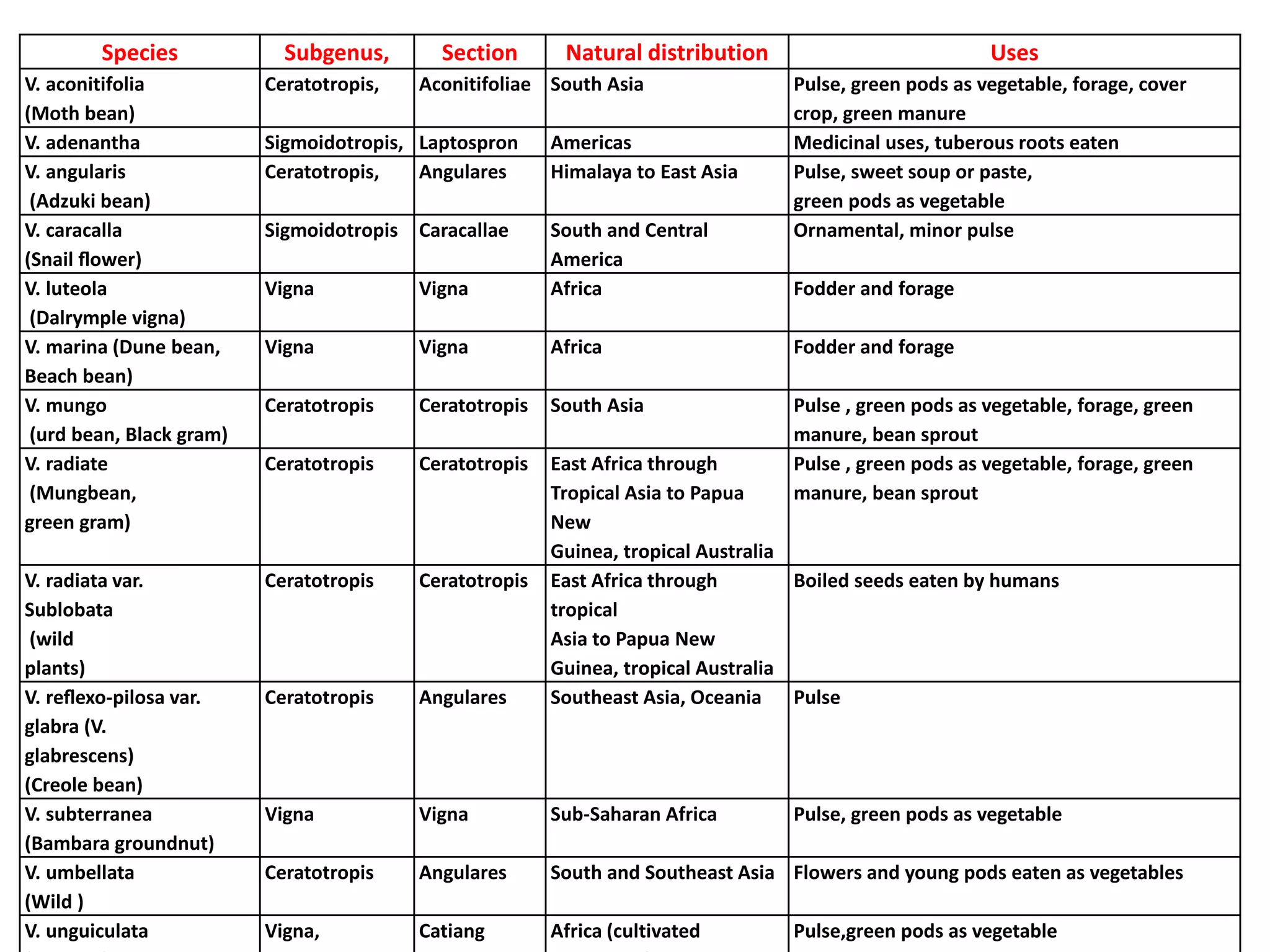
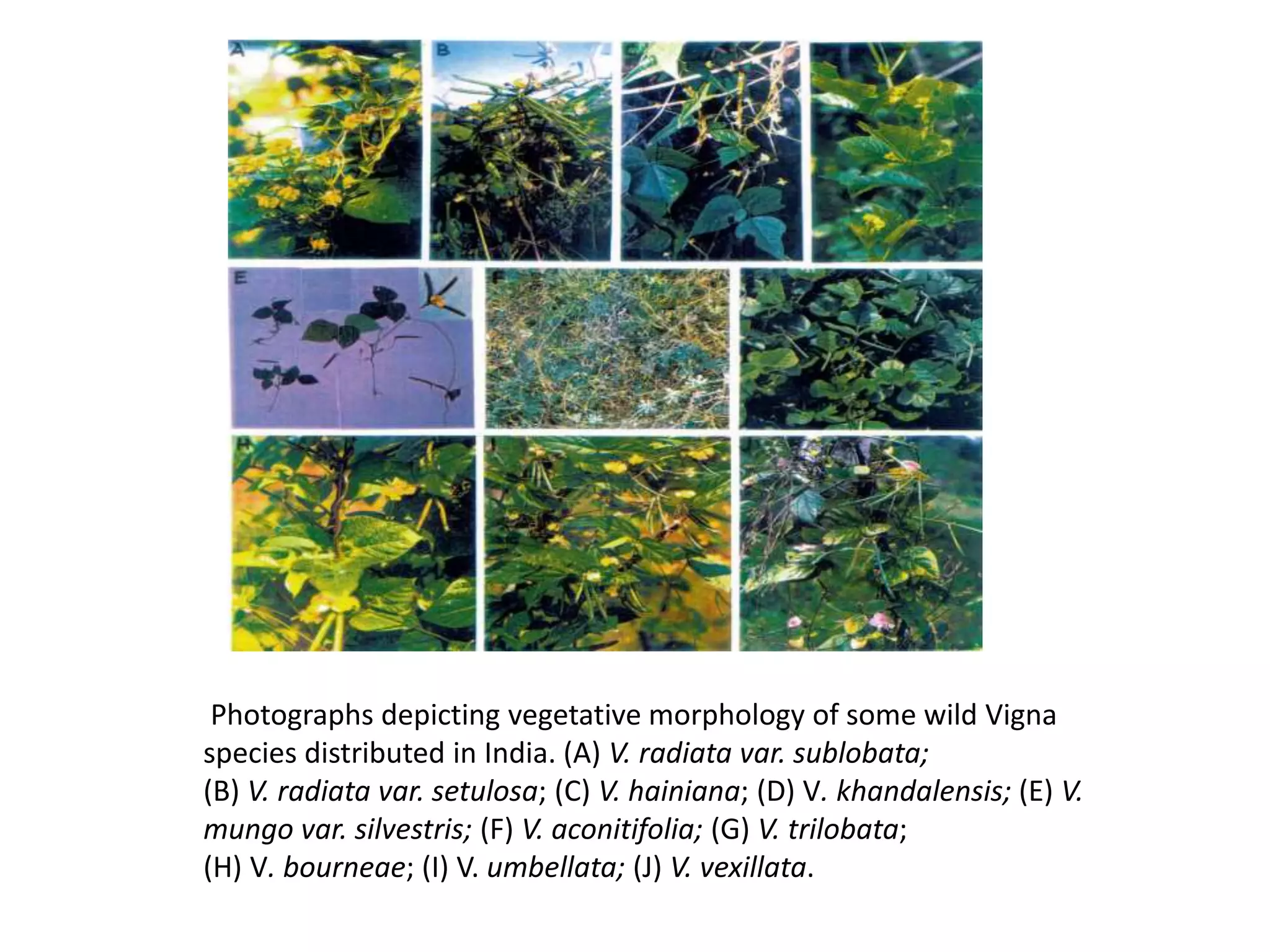
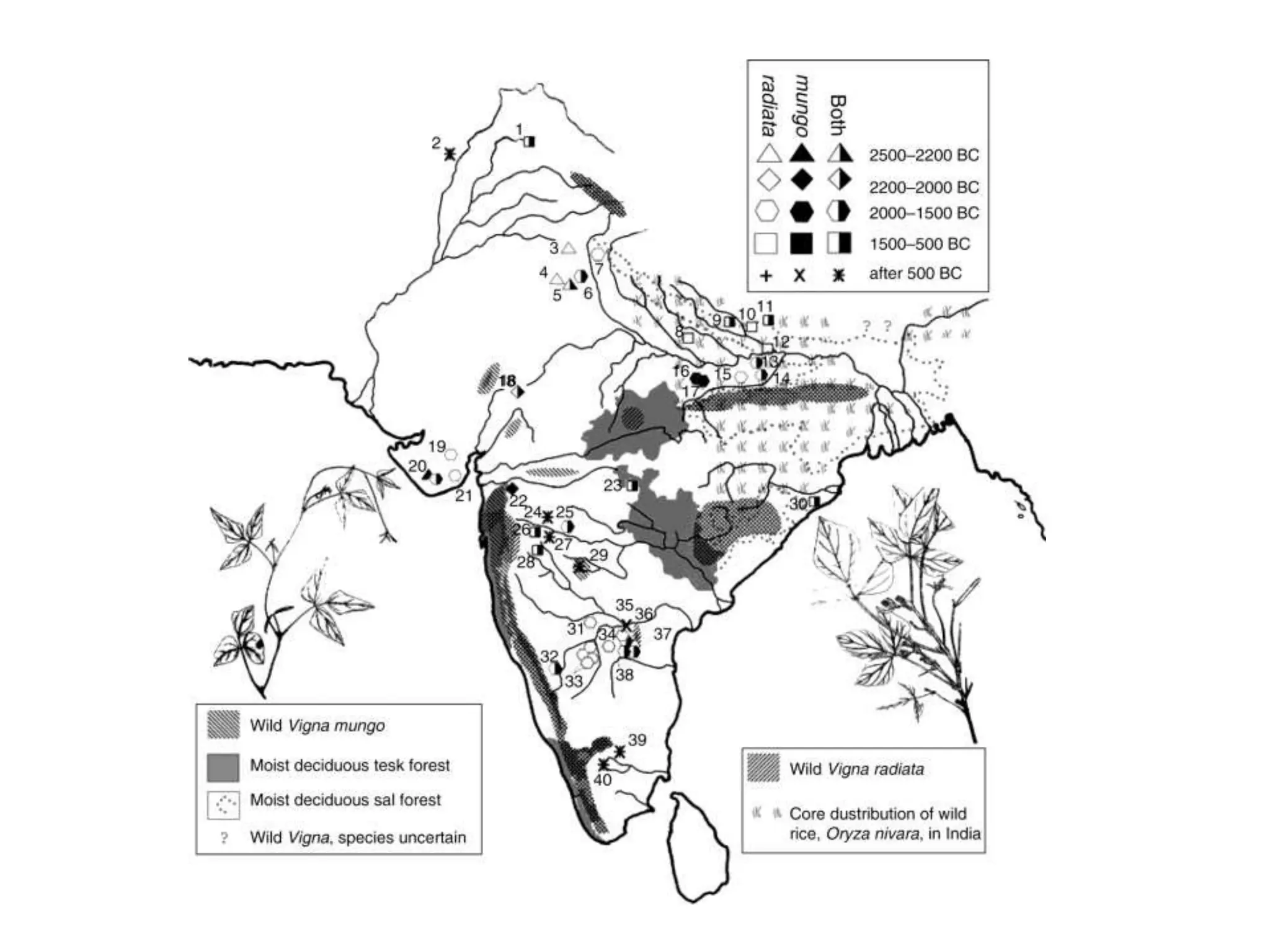
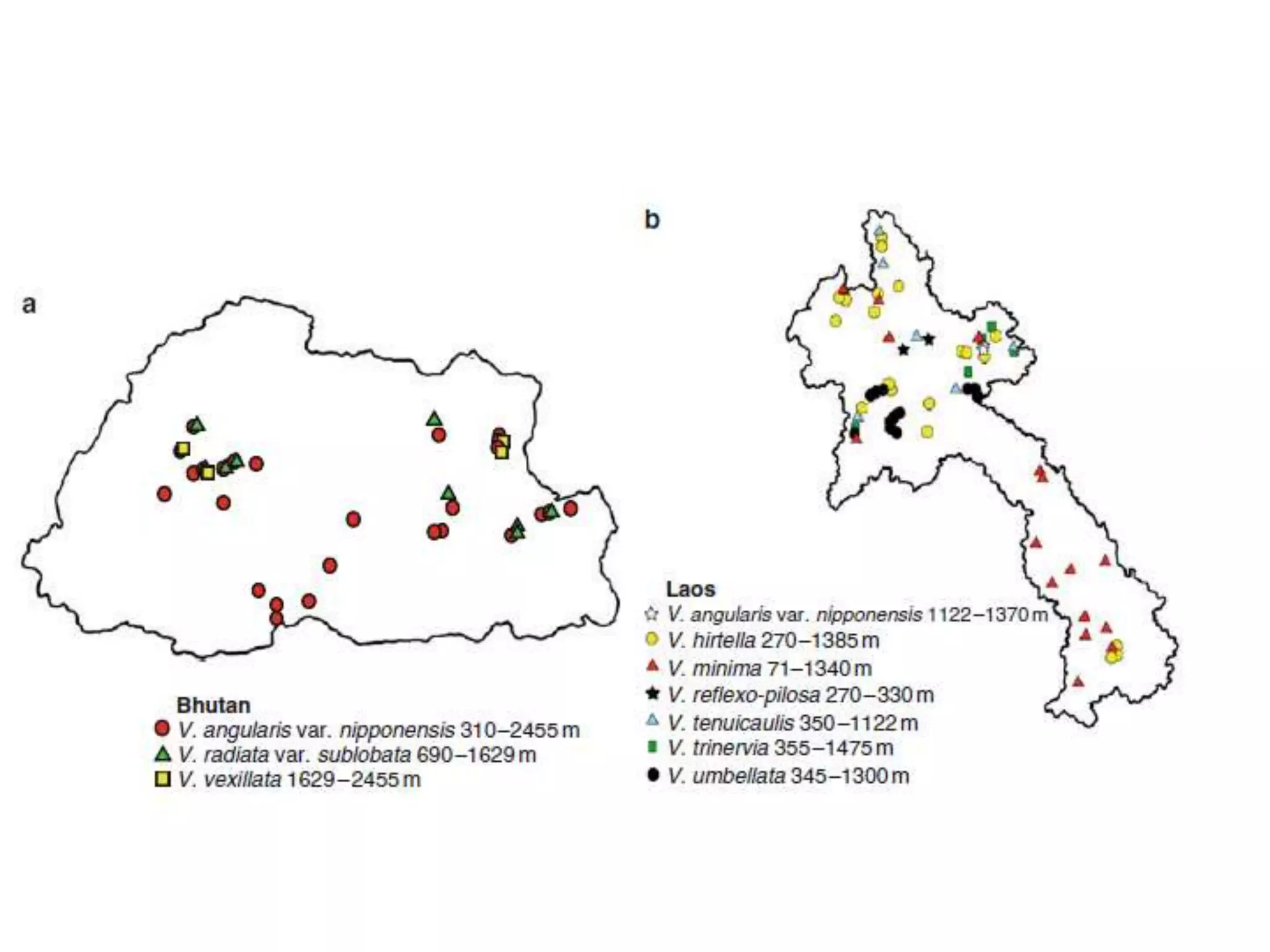
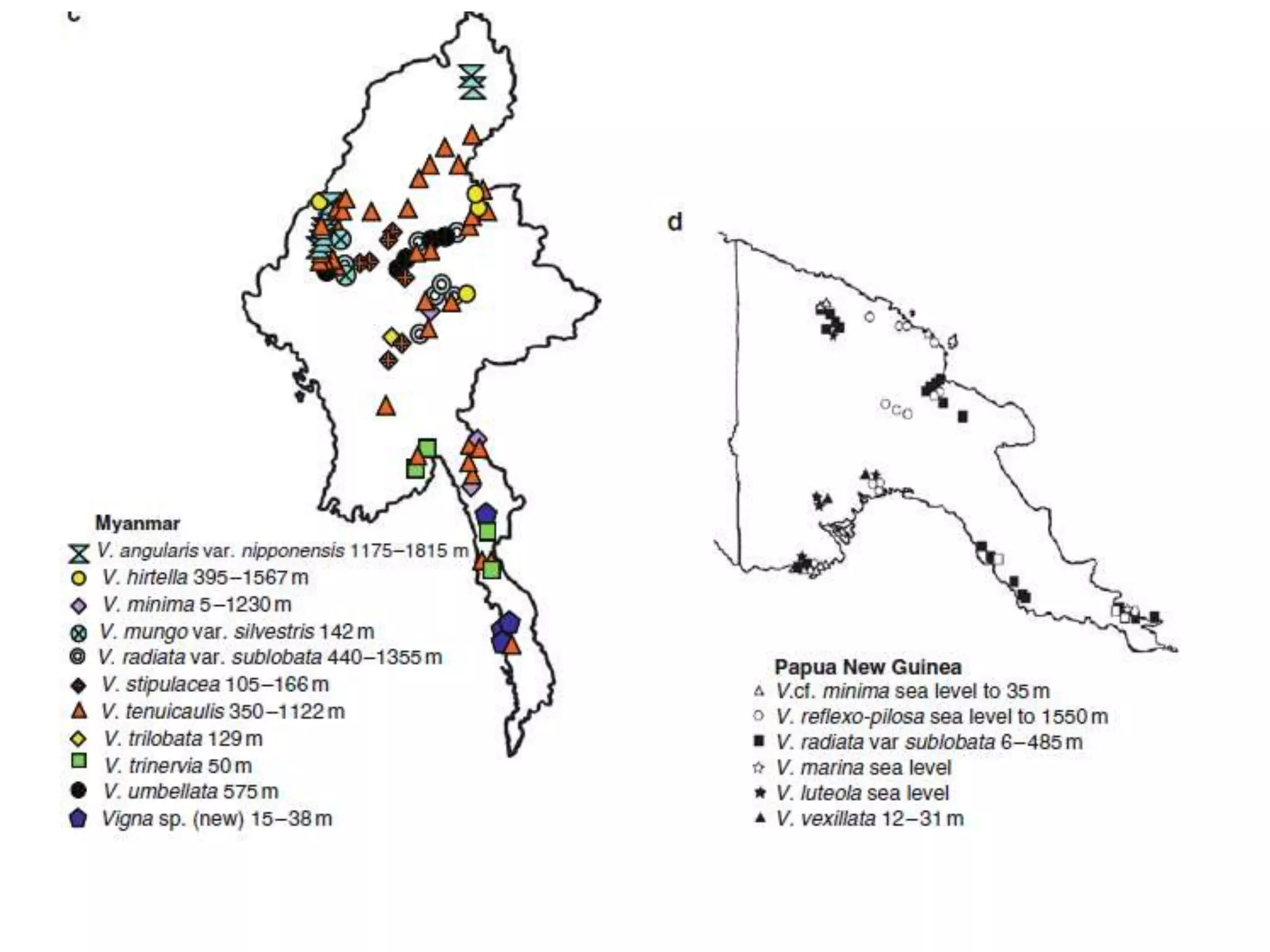
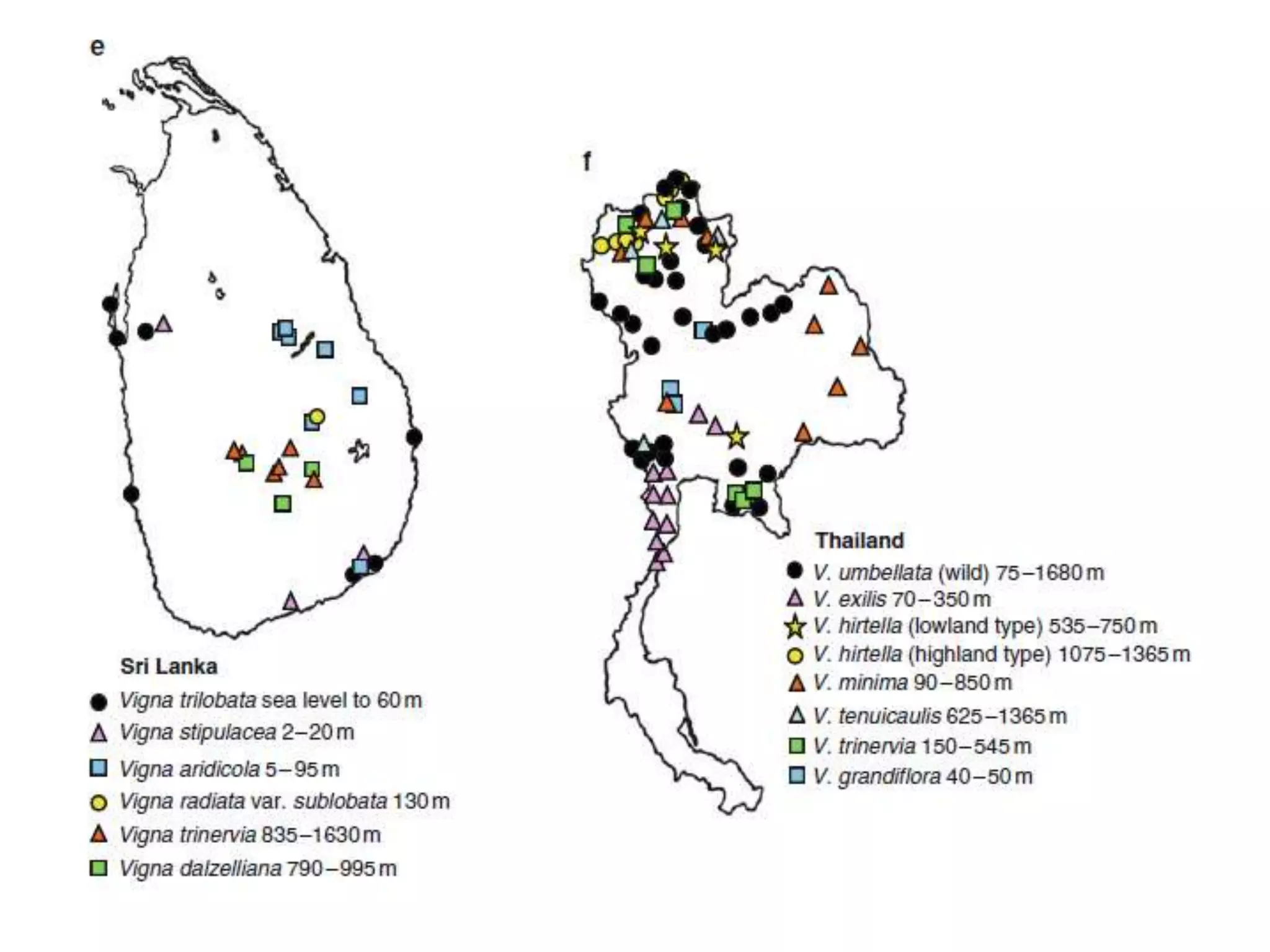
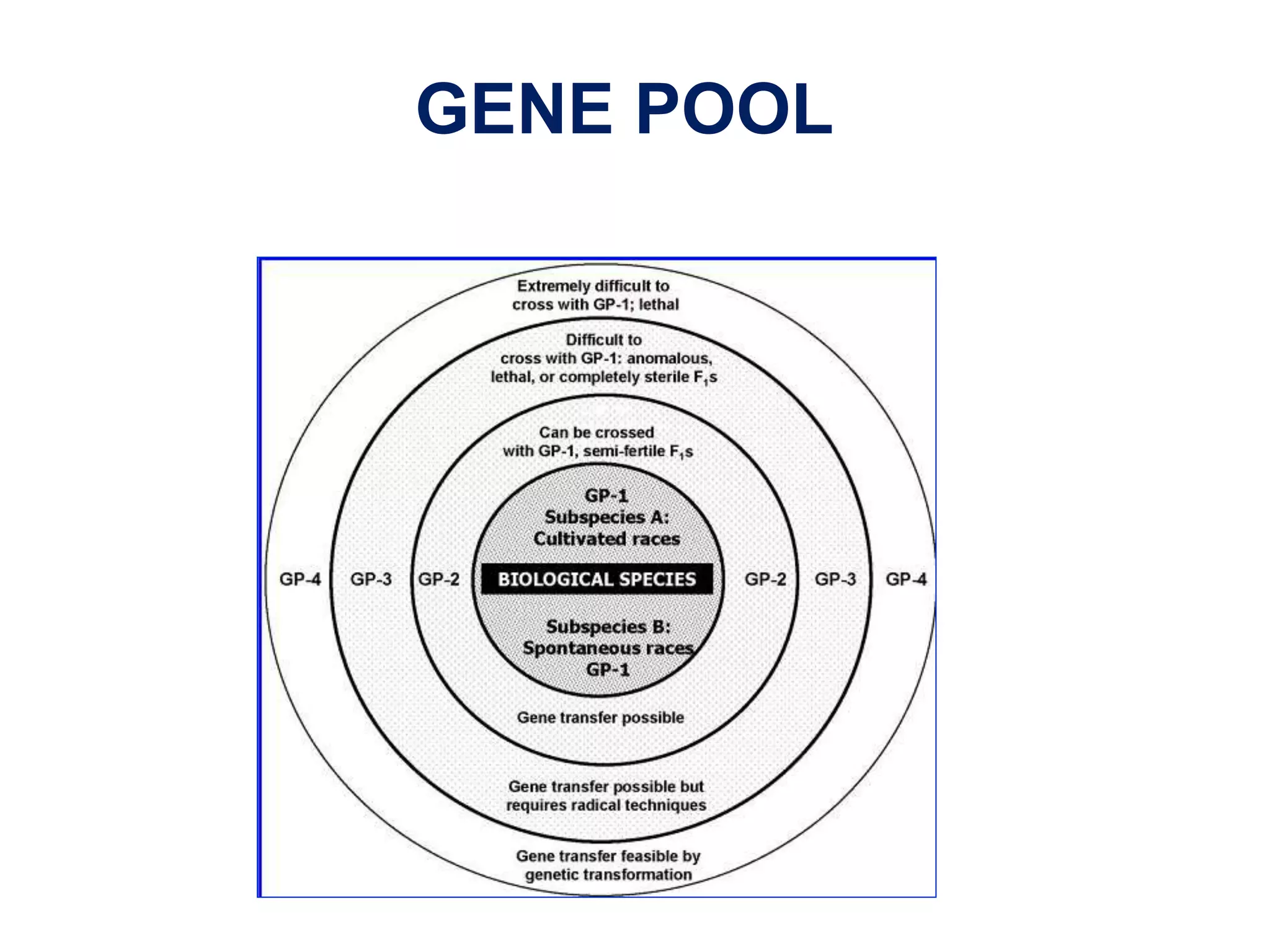
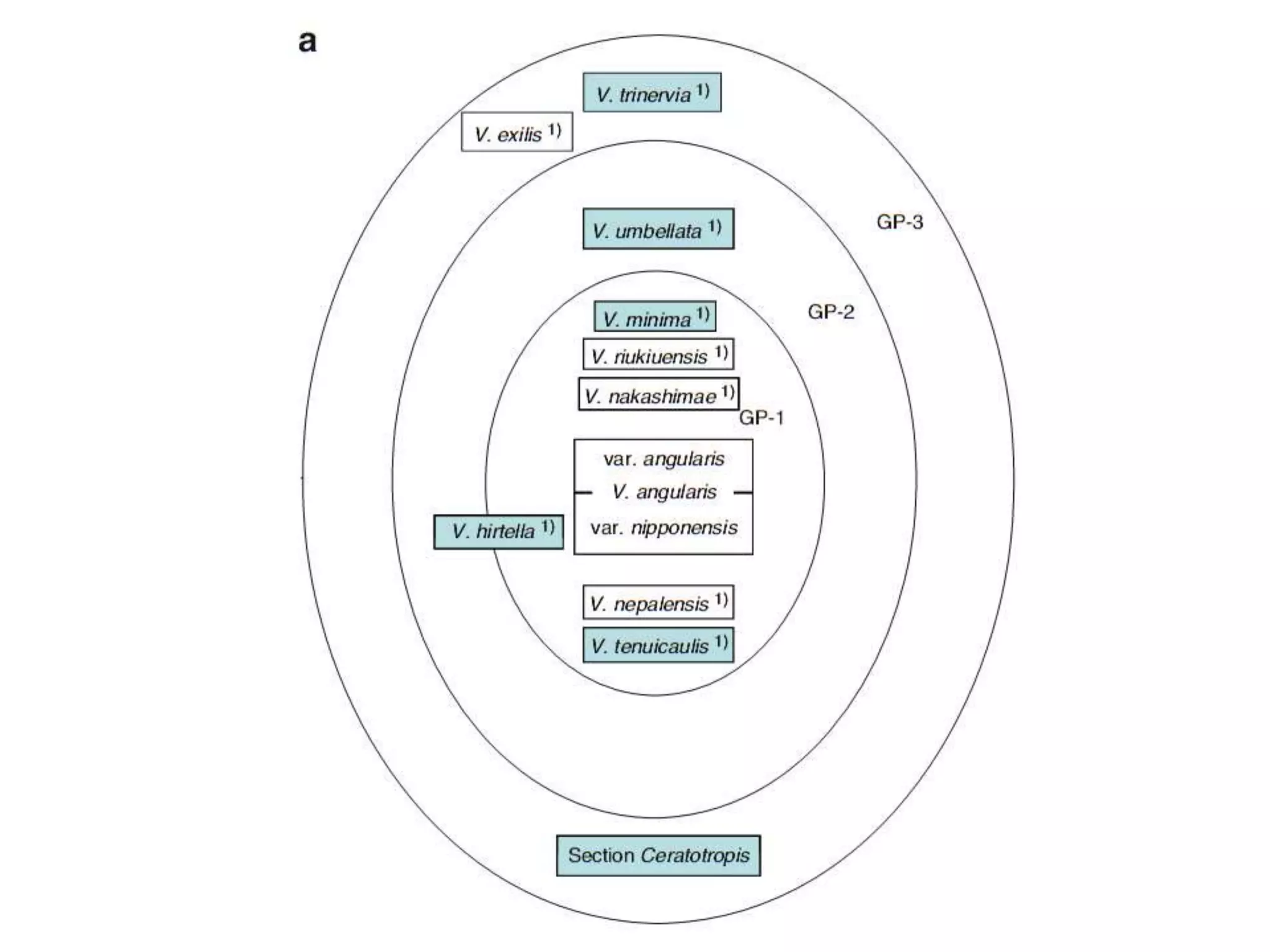
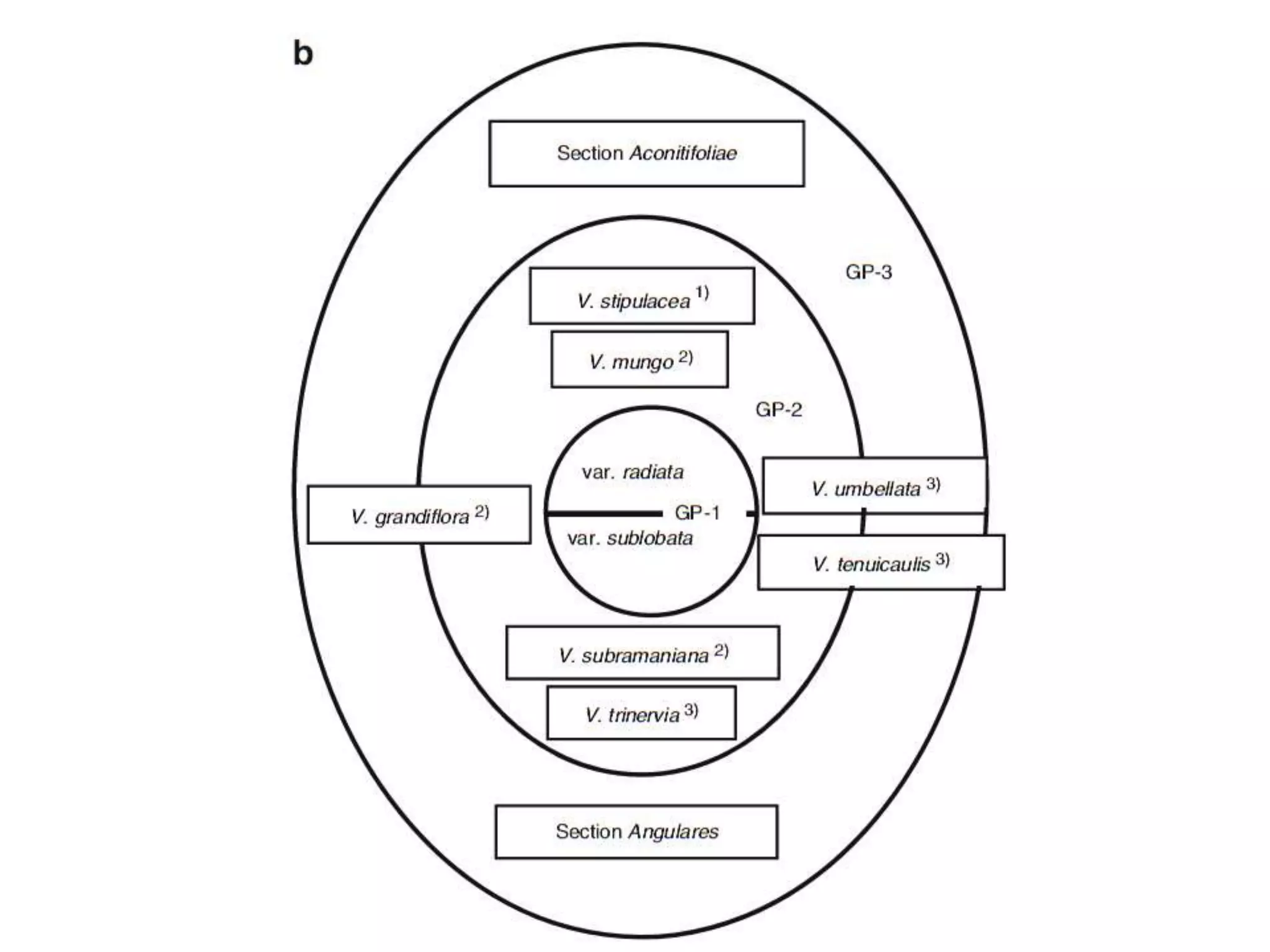
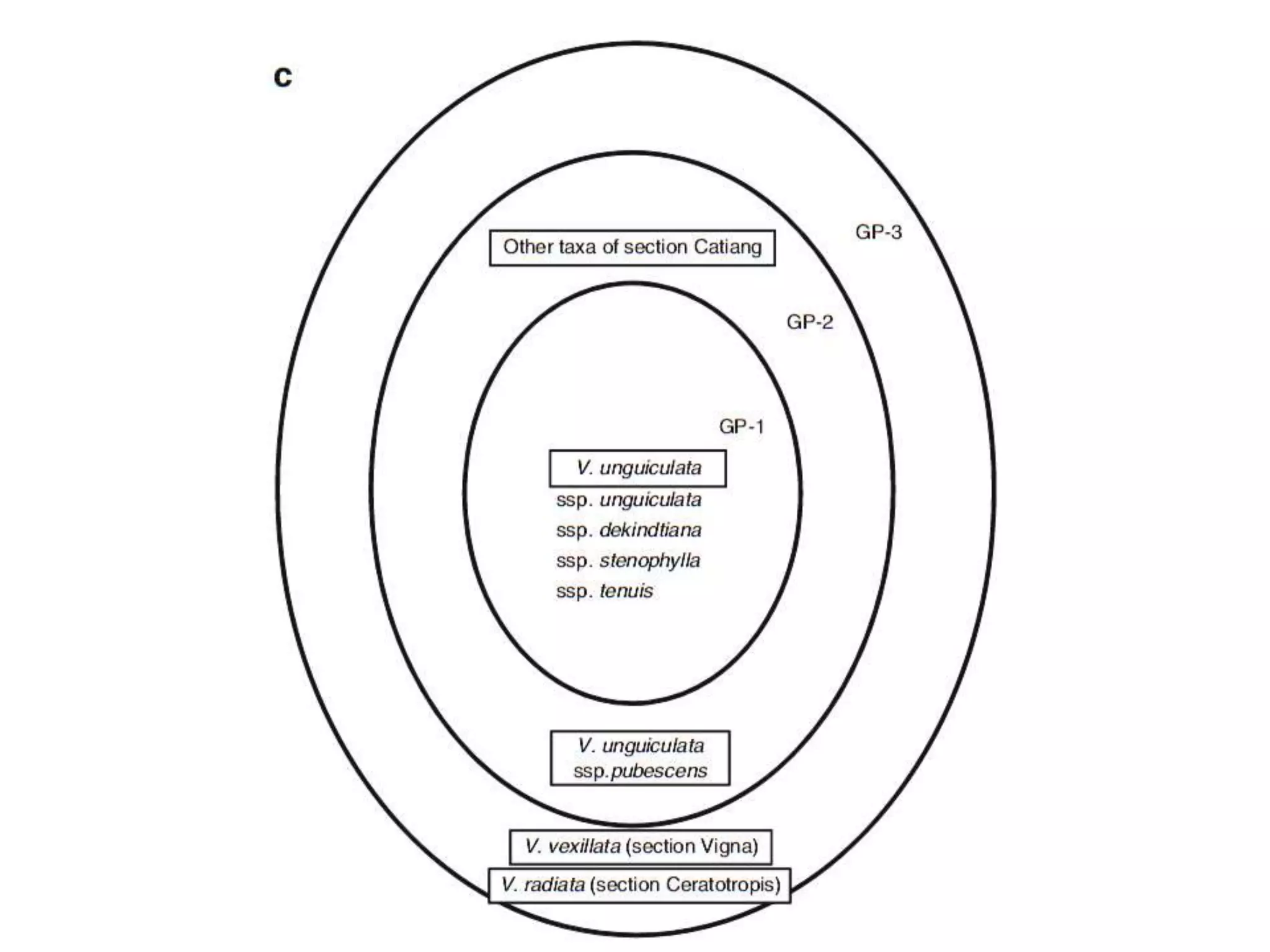
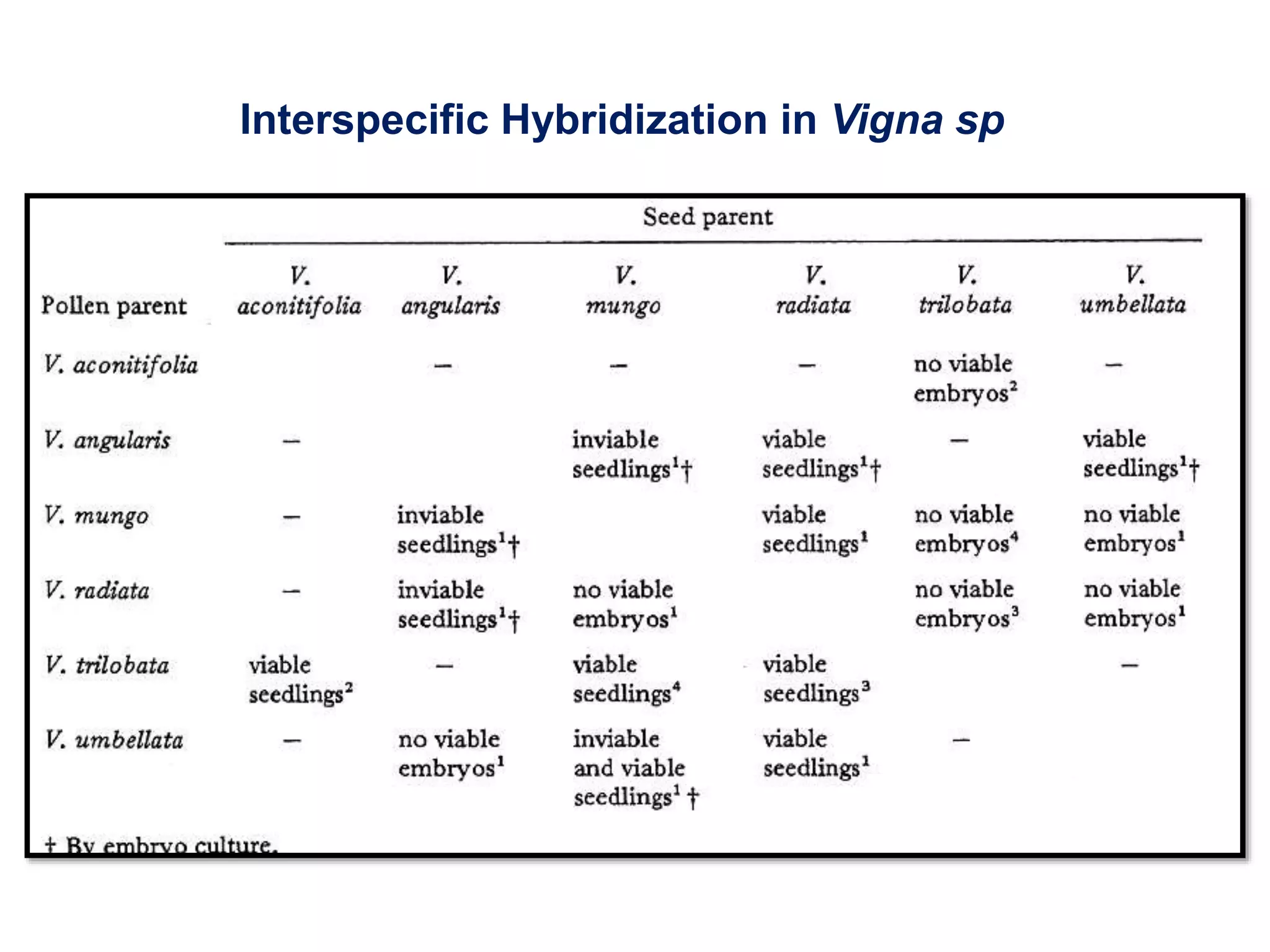
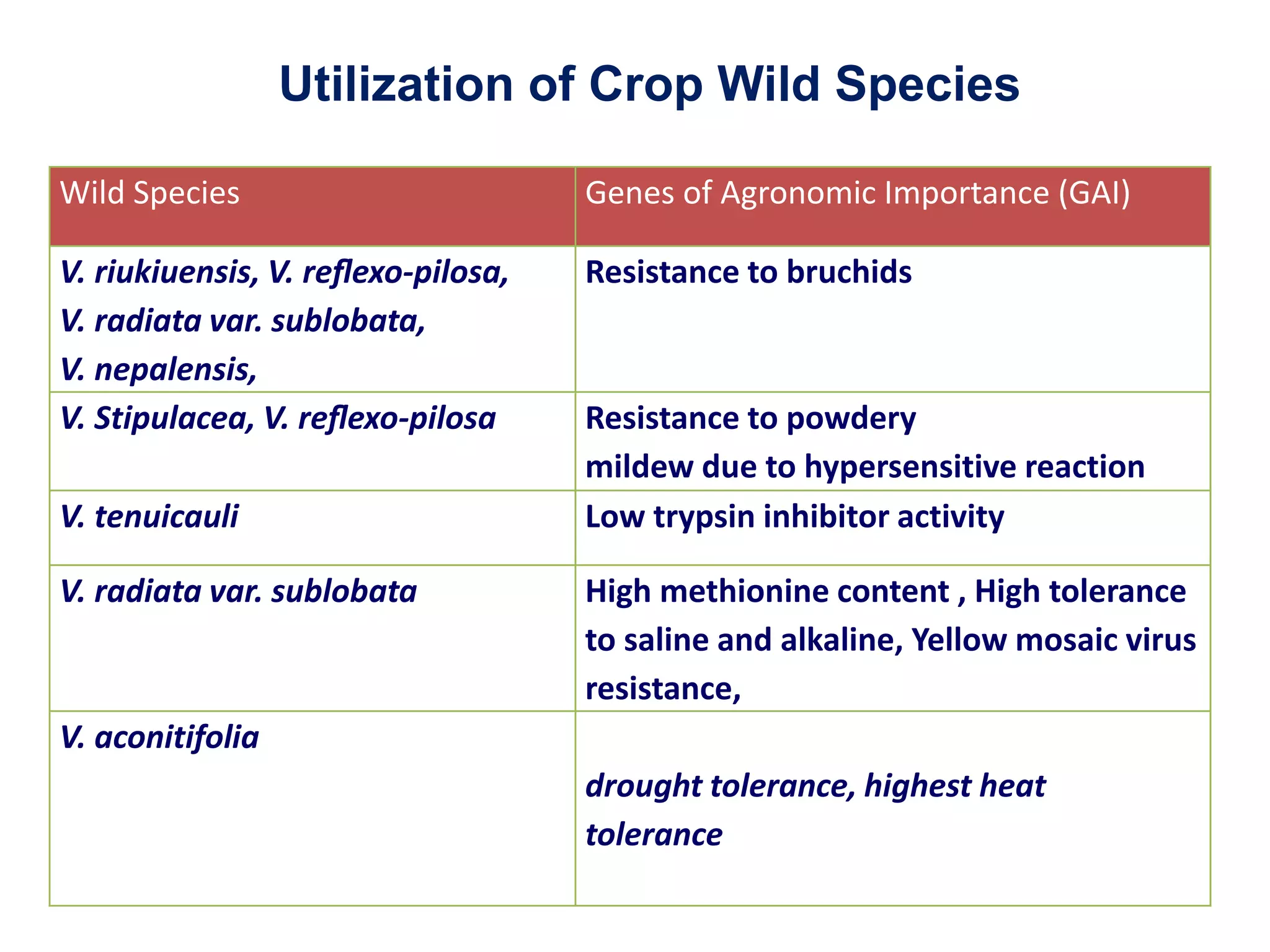
This document discusses the evolution and domestication of Vigna species. It describes the taxonomy of Vigna, identifying six subgenera containing approximately 90 species. The subgenus Ceratotropis represents a distinct group in Asia, while the subgenus Sigmoidotropis of the Americas is more closely related to Phaseolus. Six major cultivated Vigna species are identified along with their wild progenitors. The document also discusses distinguishing characteristics, origins, uses, natural distributions, and interspecific hybridization of various Vigna species. It identifies wild species as sources of genes for agricultural traits like resistance to bruchids, powdery mildew, and trypsin inhibitor activity.