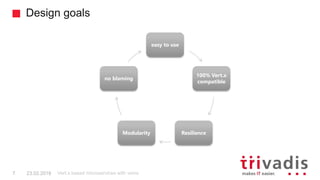
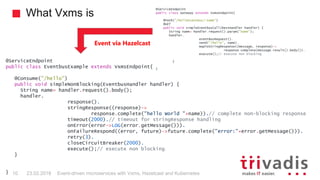
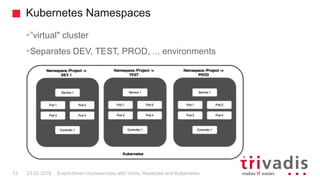
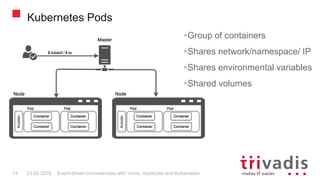
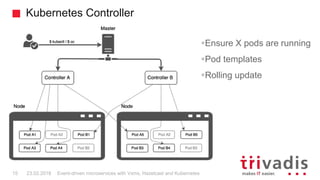
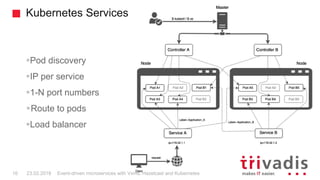
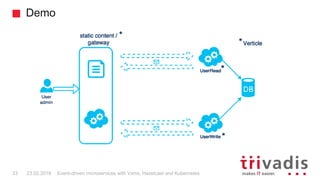
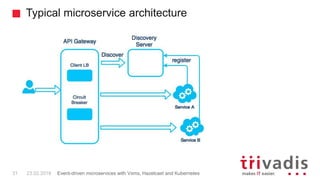
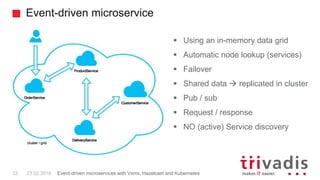
Vert.x is a toolkit for building reactive applications on the JVM. It uses Hazelcast as its default cluster provider. Vxms is an opinionated framework built on Vert.x that aims to make it easier to build reactive microservices. Kubernetes can be used to deploy Vert.x/Vxms microservices across multiple nodes and provides capabilities like service discovery, load balancing, and failover. Hazelcast can be configured to run in Kubernetes for node discovery and to provide an in-memory data grid for shared data, pub/sub messaging, and request/response patterns across microservices without an active service registry.