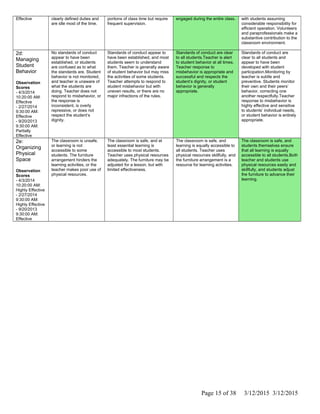
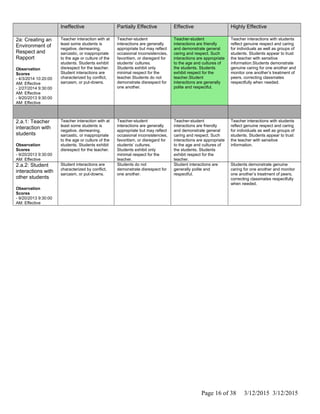
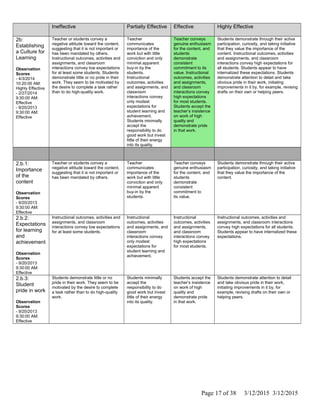
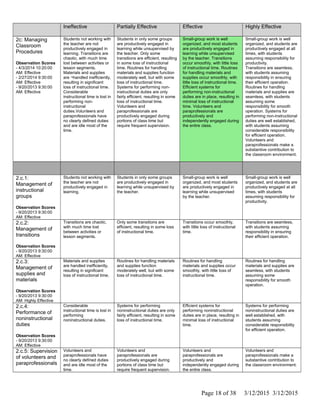
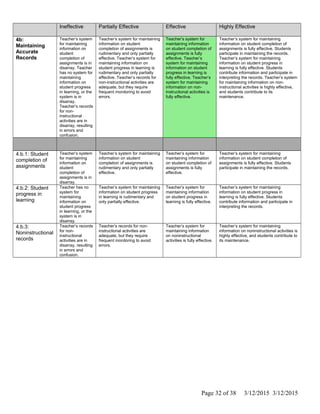
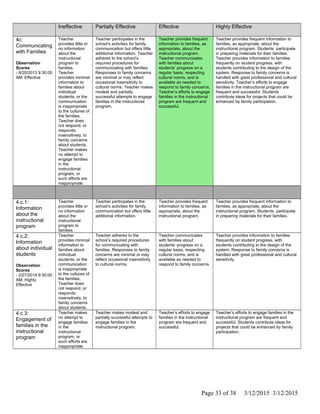
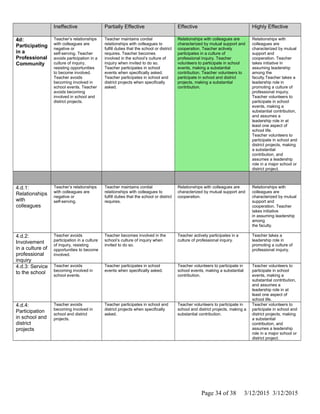
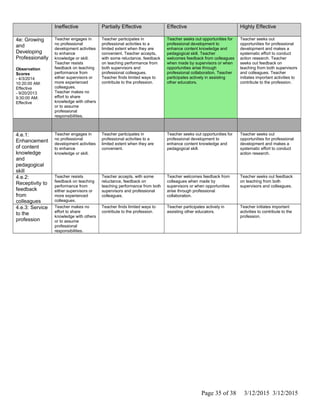
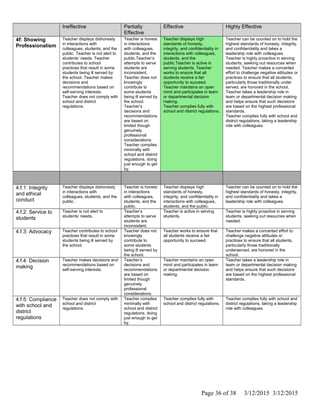
The document is Jennifer Brackin's evaluation from the 2013-2014 school year at Bradley Gardens Primary School. She received an overall rating of Effective. Her planning and preparation, classroom environment, instruction, and professional responsibilities were also rated as Effective based on observations. The evaluation was completed by Jennifer Edge and signatures from both the teacher and evaluator are present, indicating the teacher reviewed the full evaluation online.