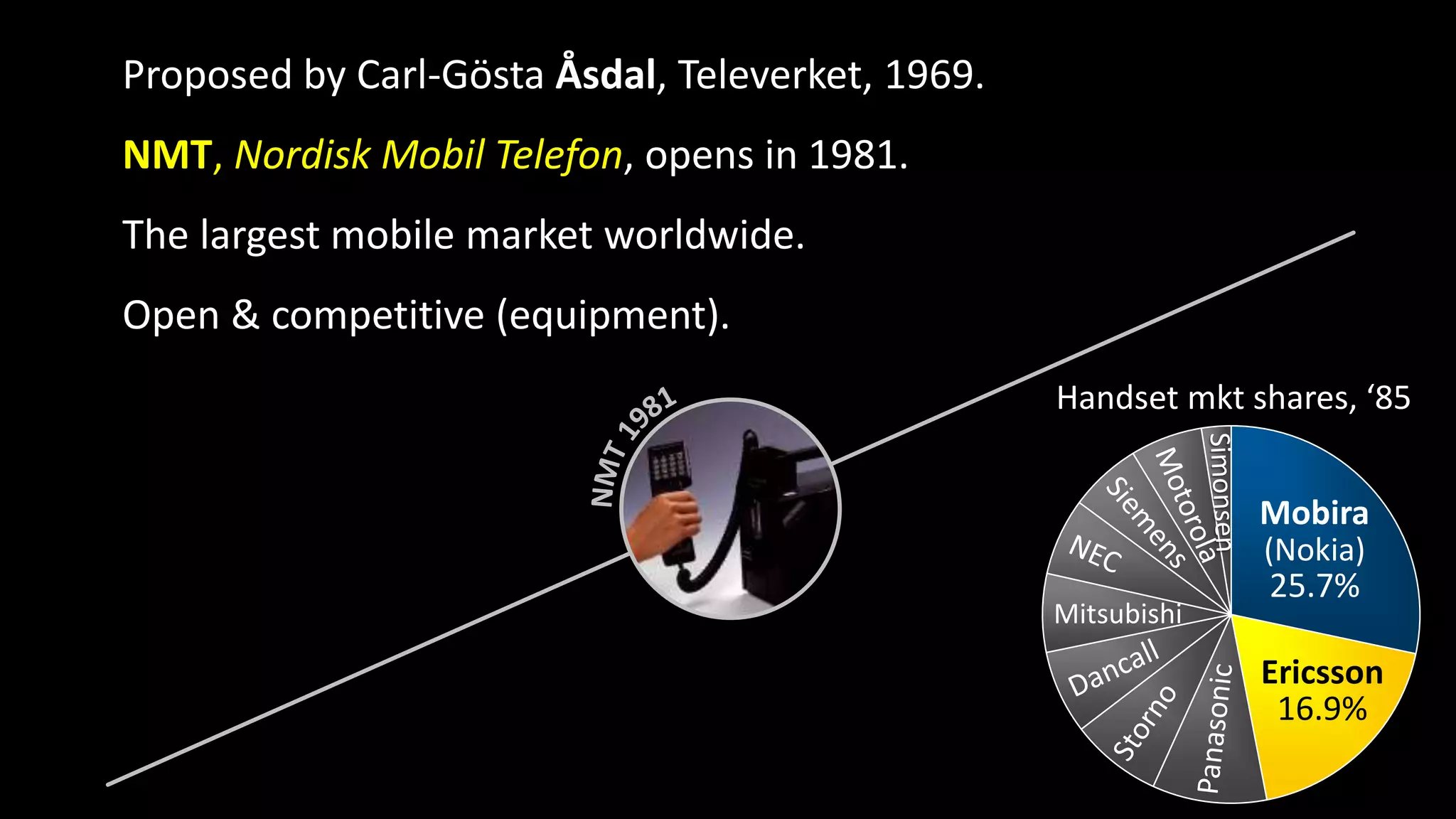
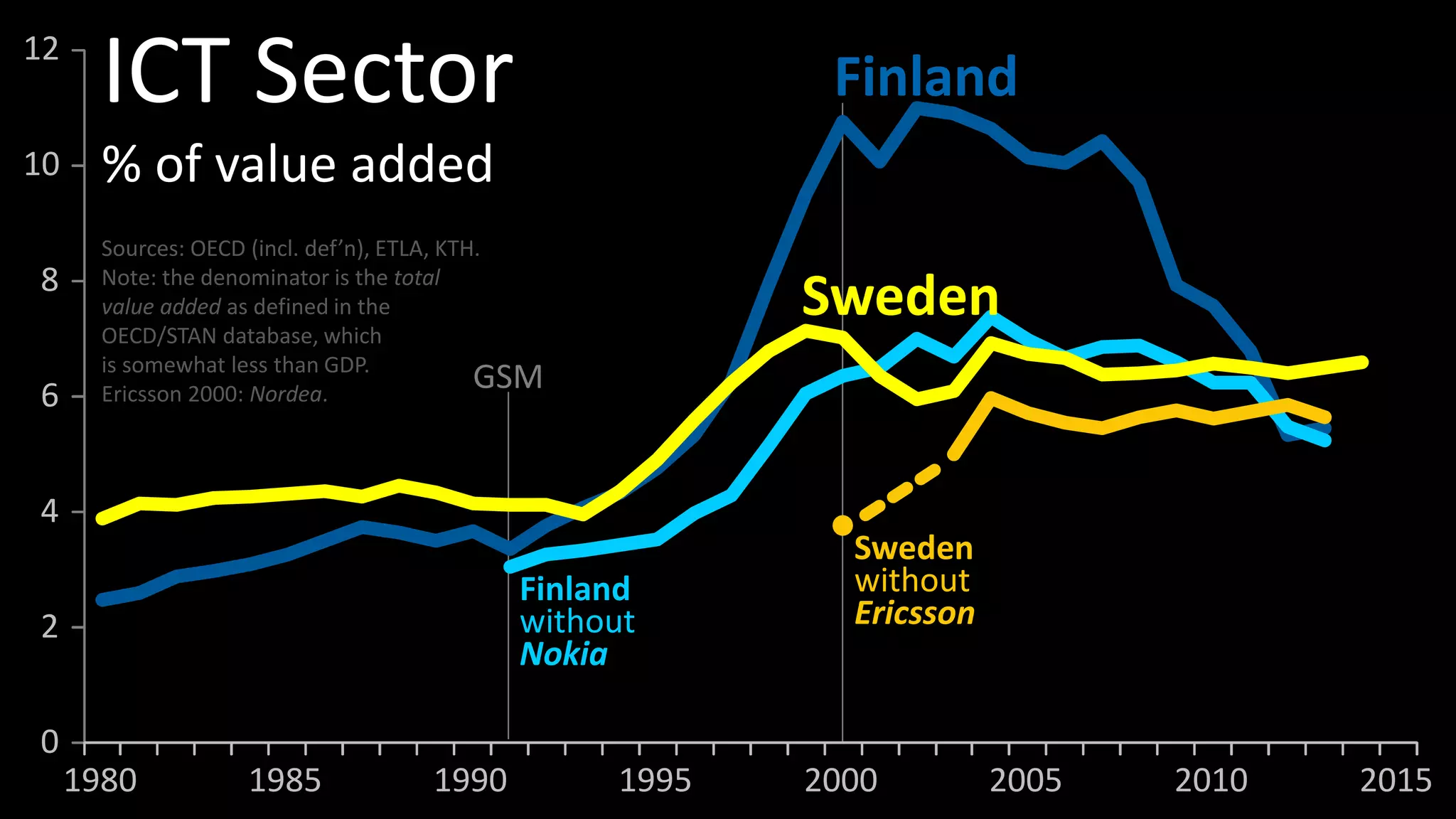
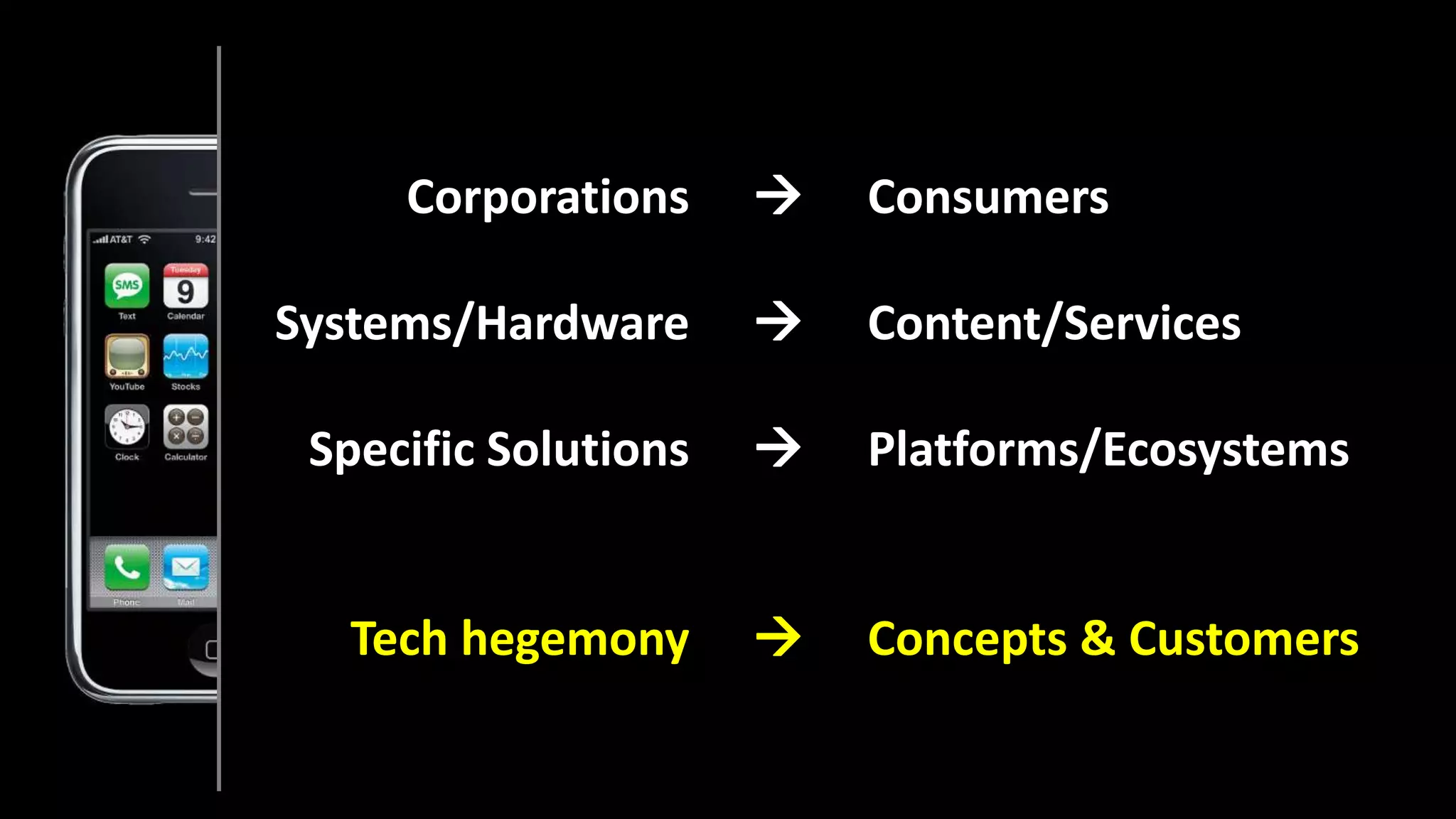
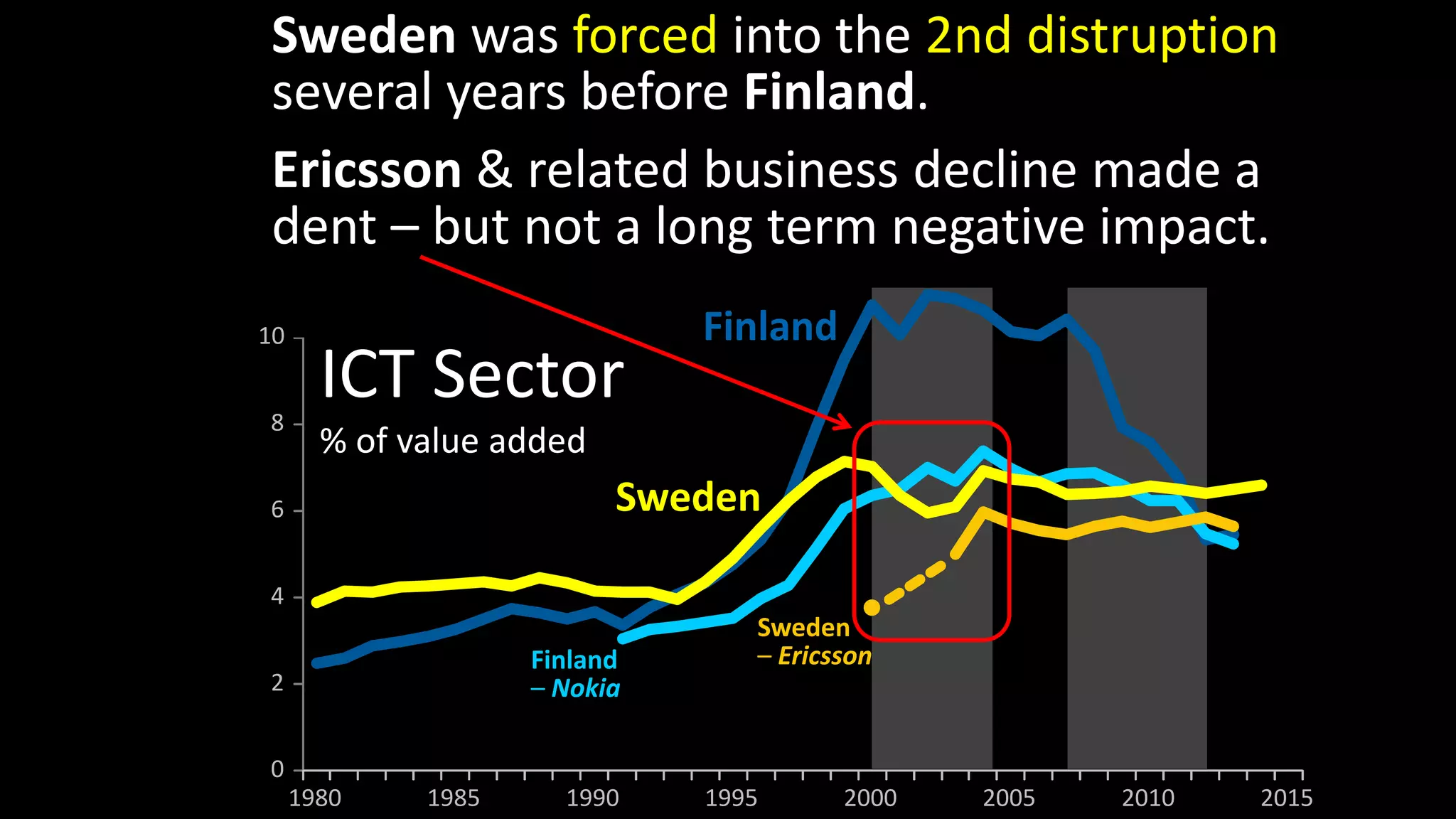
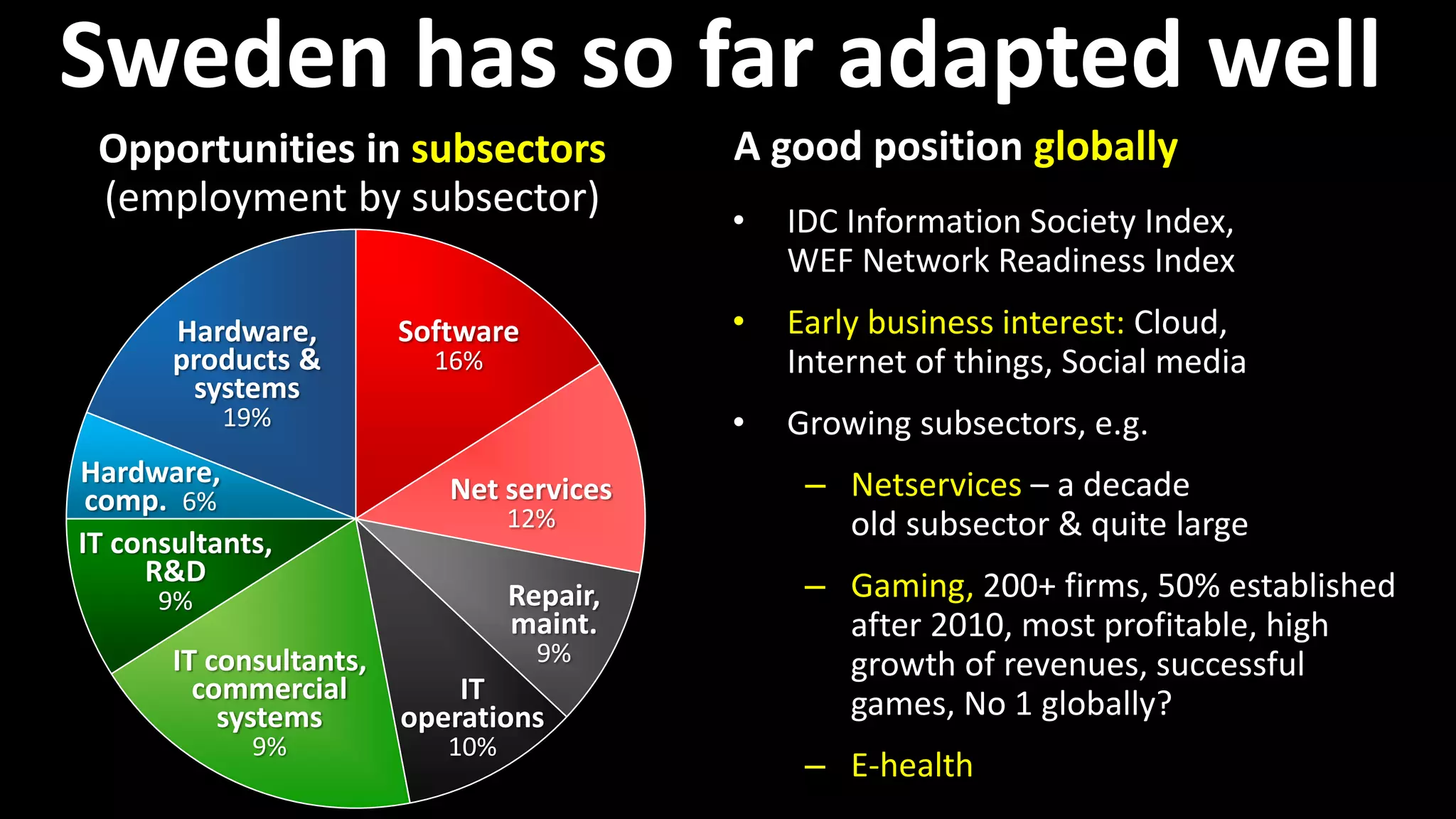
The document discusses the historical evolution and current status of the ICT sectors in Finland and Sweden, highlighting significant achievements and challenges since the 1980s. It notes the similar contributions of both countries to GDP and employment, but also points out Finland's decline in employment and research and development in ICT compared to Sweden's growth. The paper emphasizes the need for renewed Nordic cooperation to navigate the second disruption in the ICT landscape.