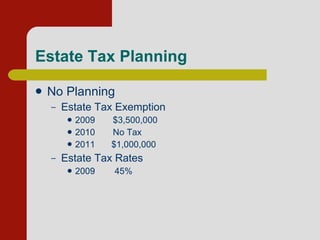
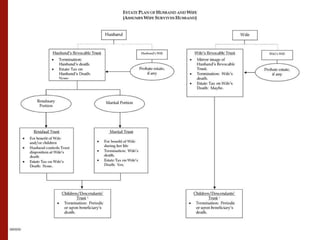
This document summarizes an estate planning seminar that discusses the basic reasons for estate planning including planning for incapacity, avoiding probate, proper disposition of estate assets, estate tax planning, and creditor protection. It outlines various estate planning tools like powers of attorney, trusts, wills, and beneficiary designations that can help achieve these goals. Specific planning strategies are discussed for different asset classes like retirement accounts, real estate, businesses, and life insurance. Estate and gift tax planning techniques including utilizing exemptions and the marital deduction are also covered. Examples are provided showing how estate planning can reduce costs, taxes, and complexity when distributing assets after death.
![ESTATE PLANNING SEMINAR Presented By: Bhavik R. Patel Sandberg Phoenix & von Gontard PC One City Centre, 15 th Floor St. Louis, MO 63101 (314) 446-4328 (Phone) (314) 727-7166 (Fax) e-mail: [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/estateplanninggeneral101-12615372833113-phpapp01/75/Estate-Planning-101-1-2048.jpg)