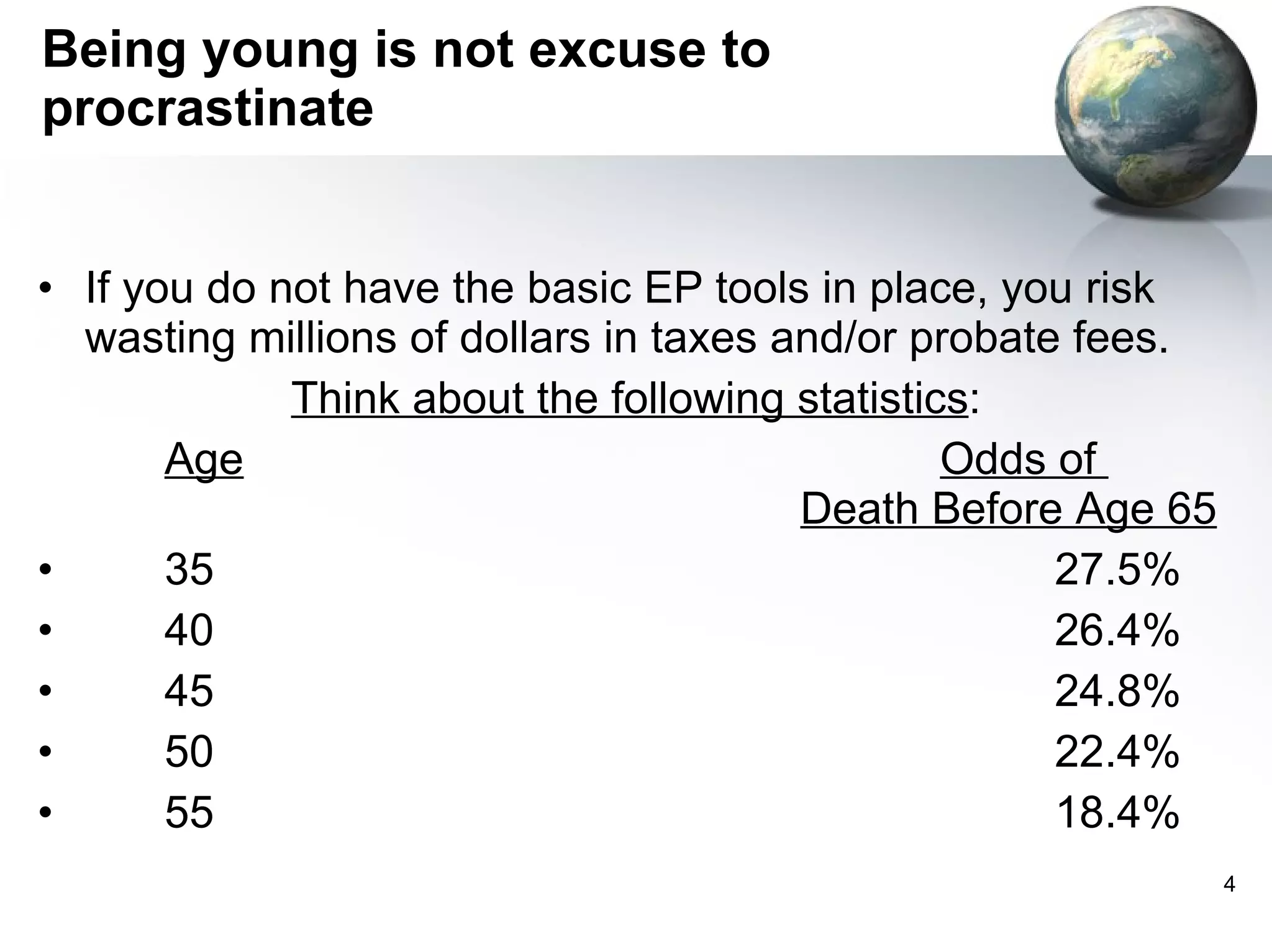
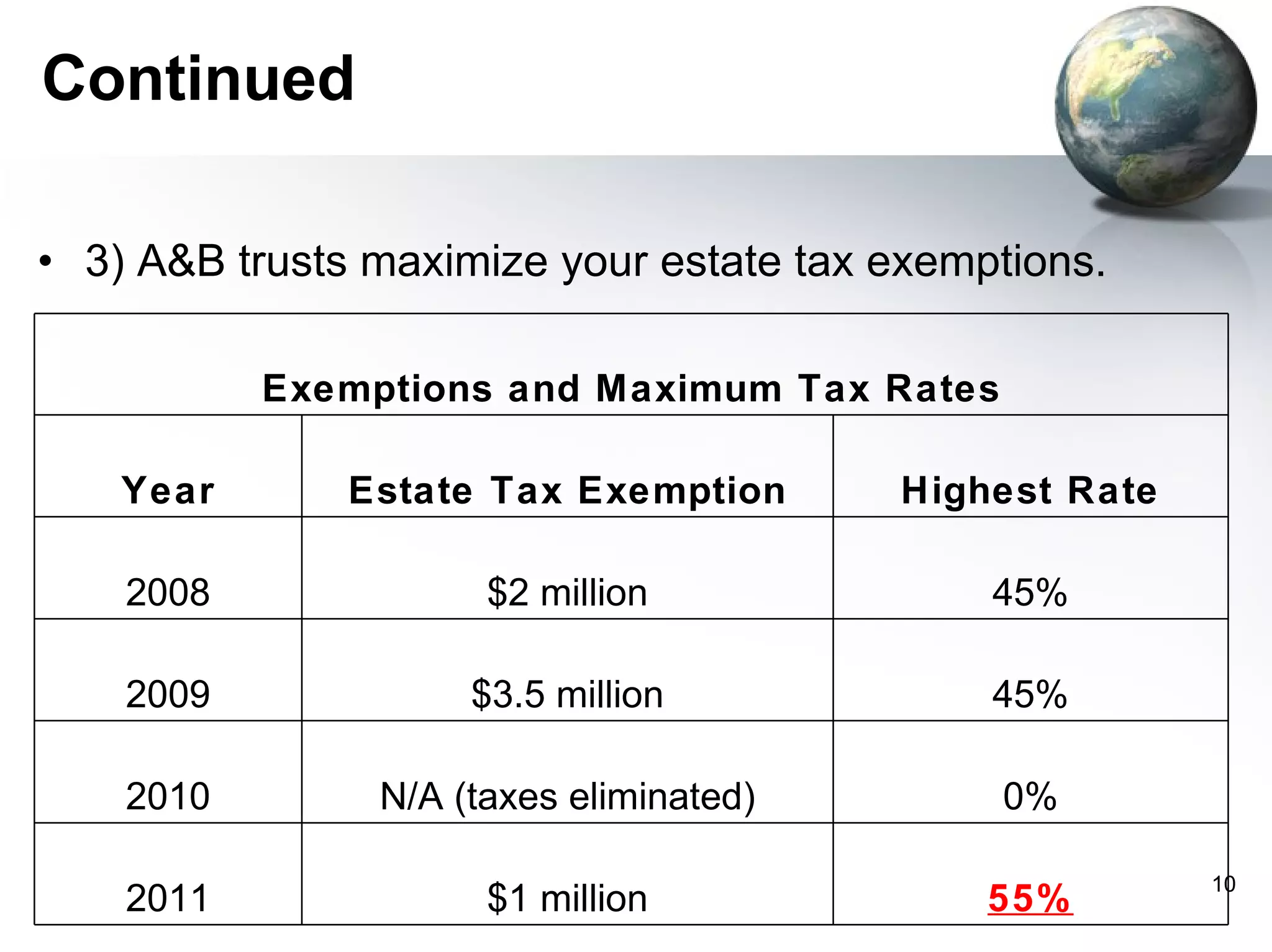
The document summarizes 5 basic estate planning tools: wills, living trusts, powers of attorney, family limited partnerships (FLPs), and irrevocable life insurance trusts (ILITs). It notes that most people do not have even basic estate plans like wills or powers of attorney in place. It stresses the importance of having the right tools, such as living trusts to avoid probate, ILITs to protect life insurance from estate taxes, and FLPs to facilitate wealth transfers and take advantage of valuation discounts when gifting assets.