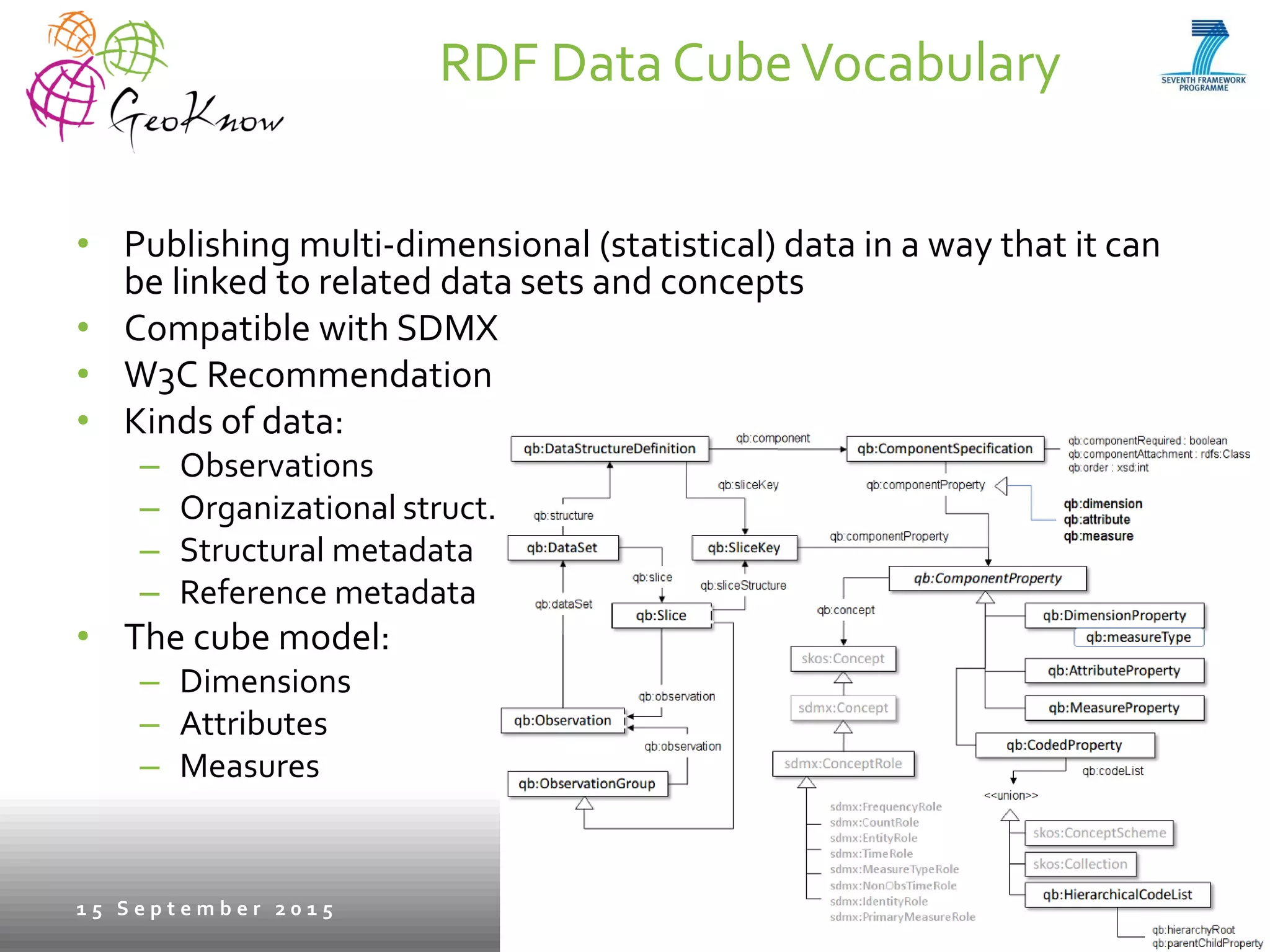
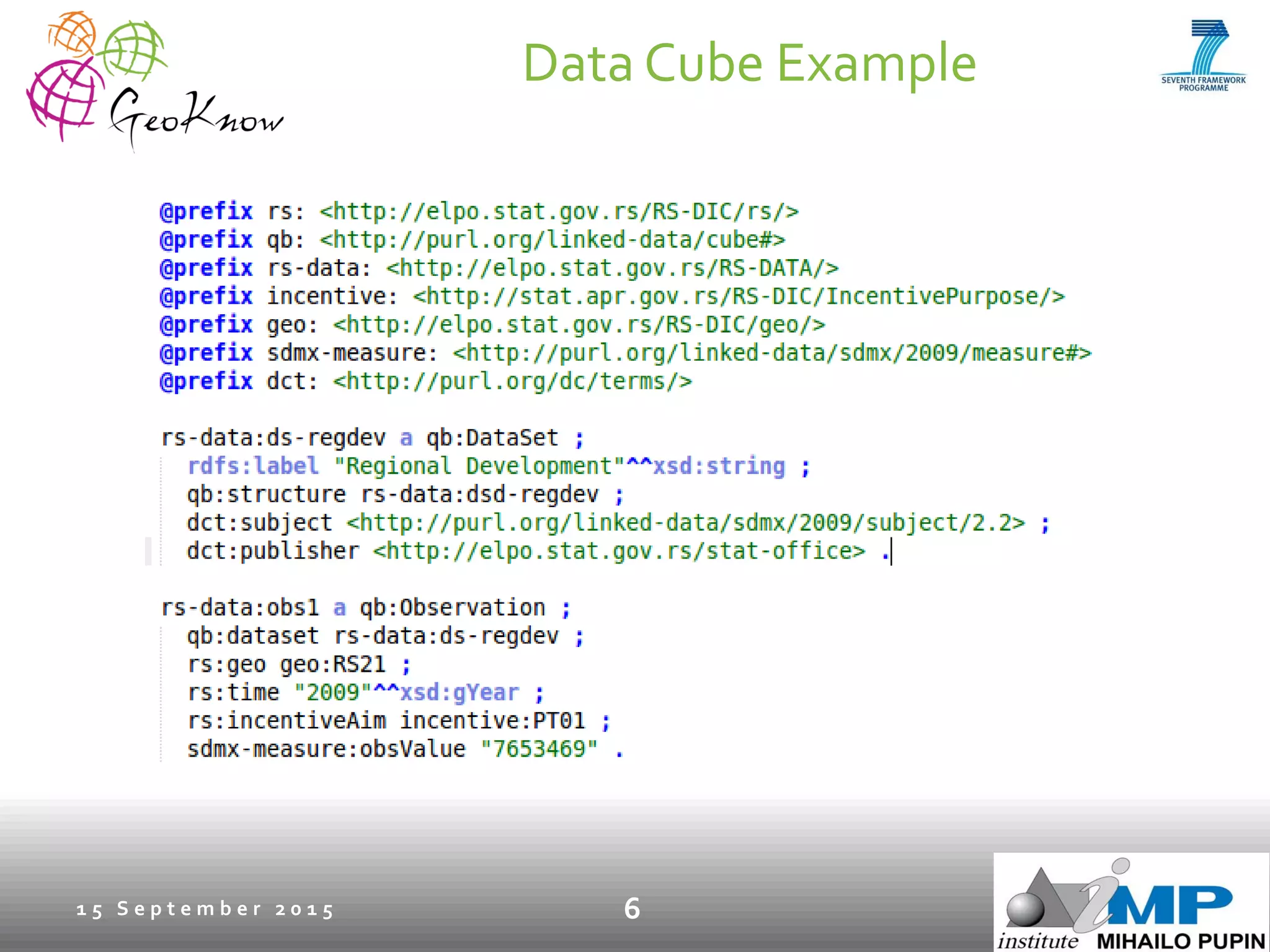
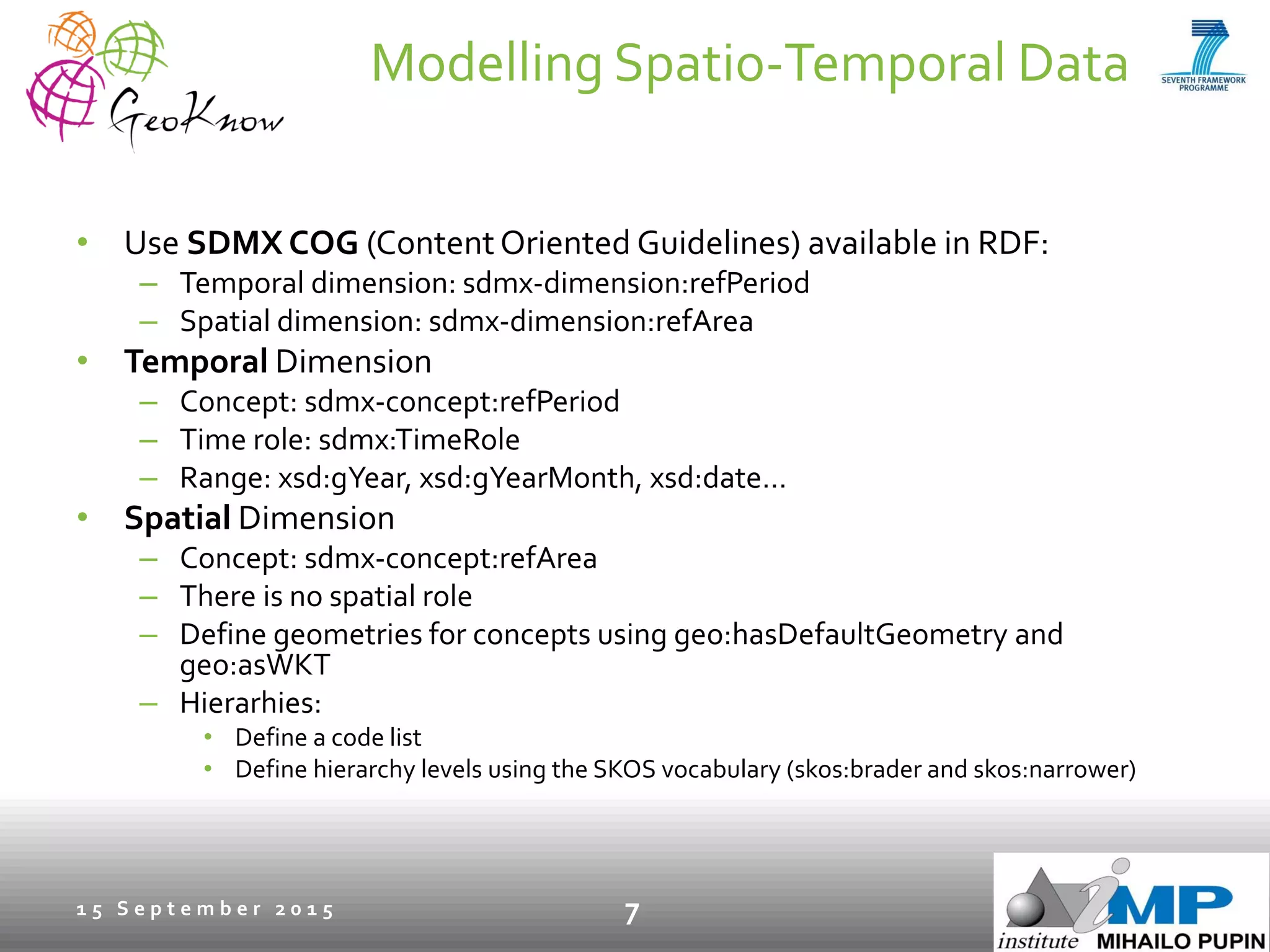
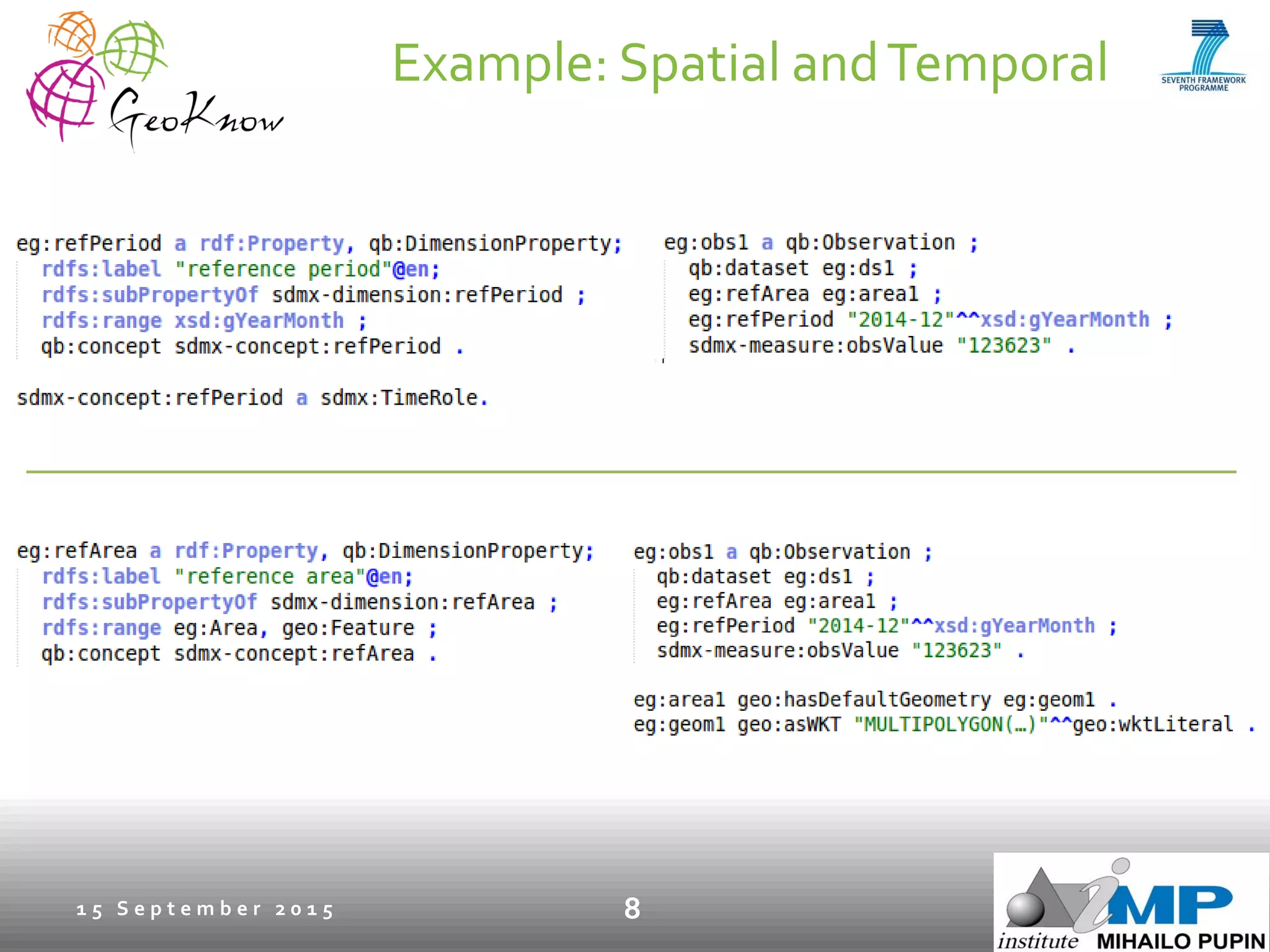
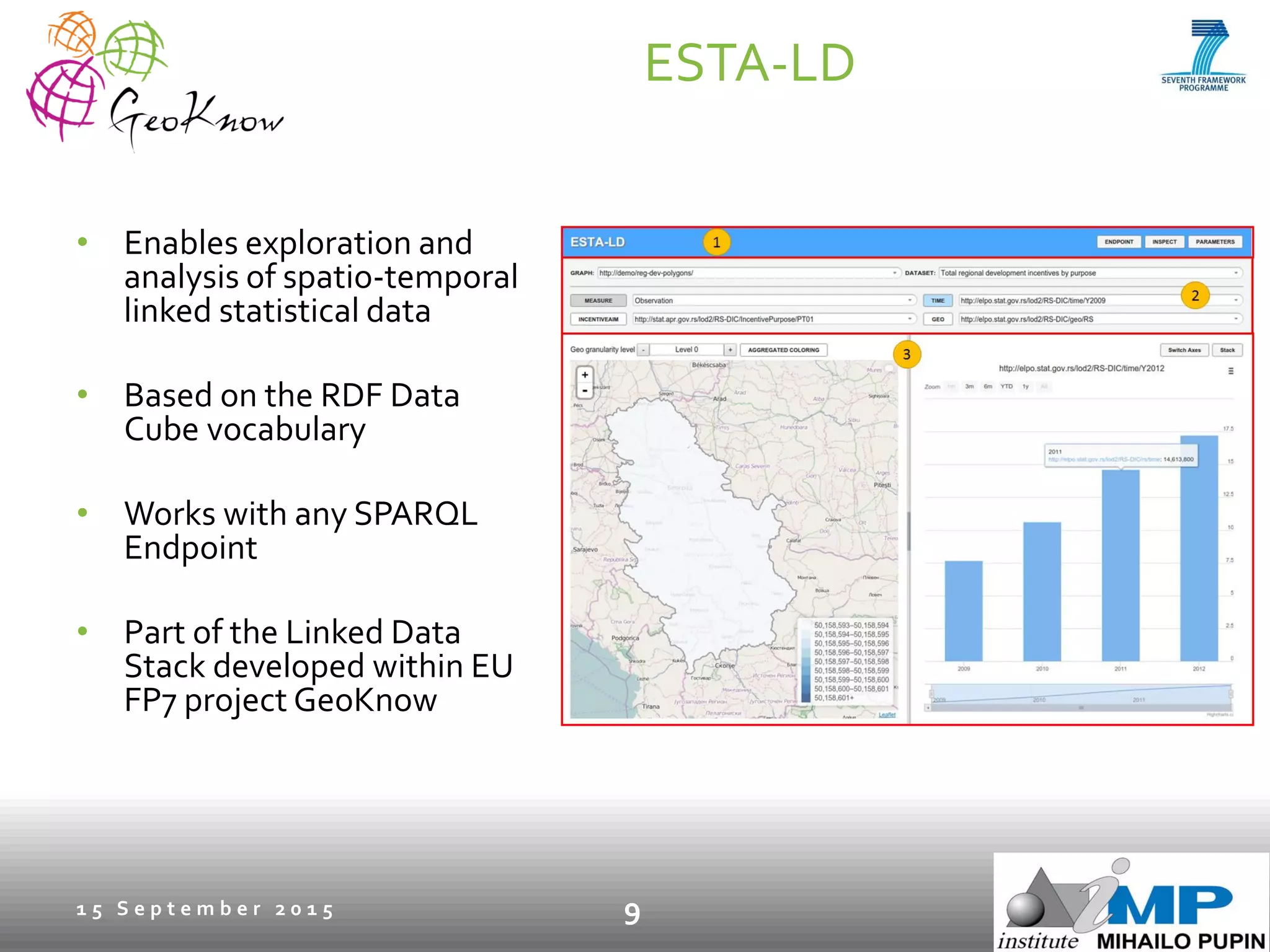
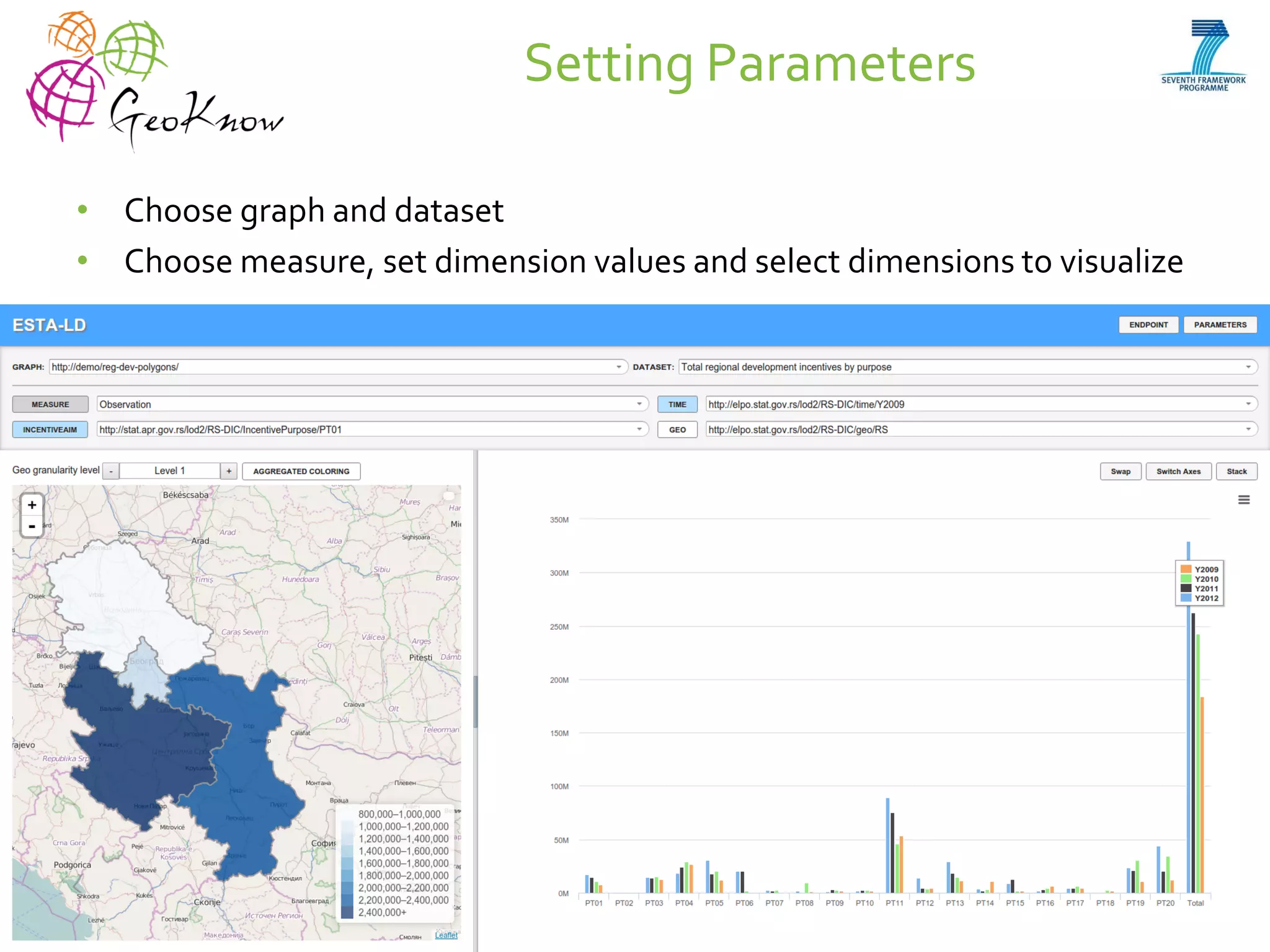
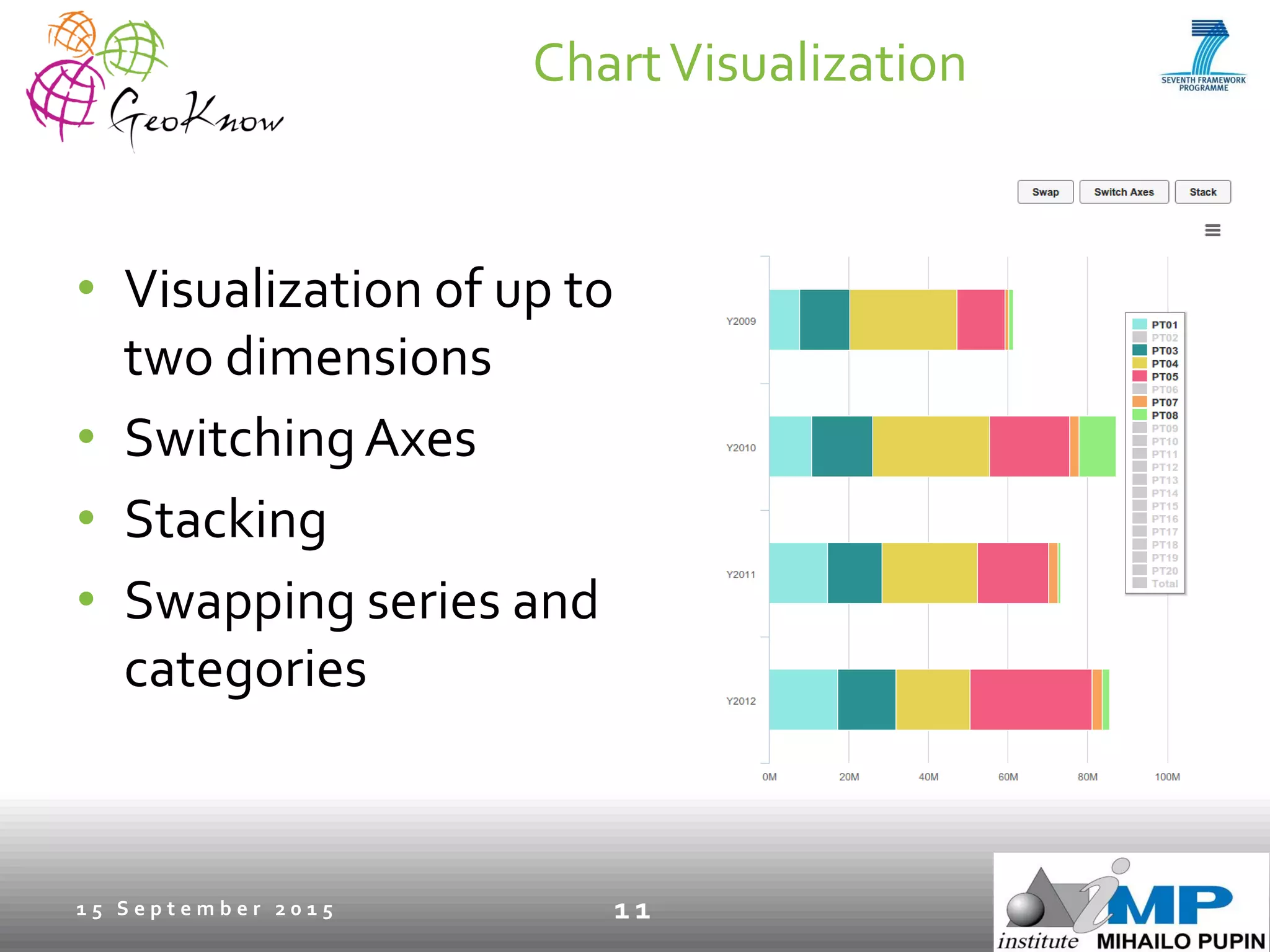
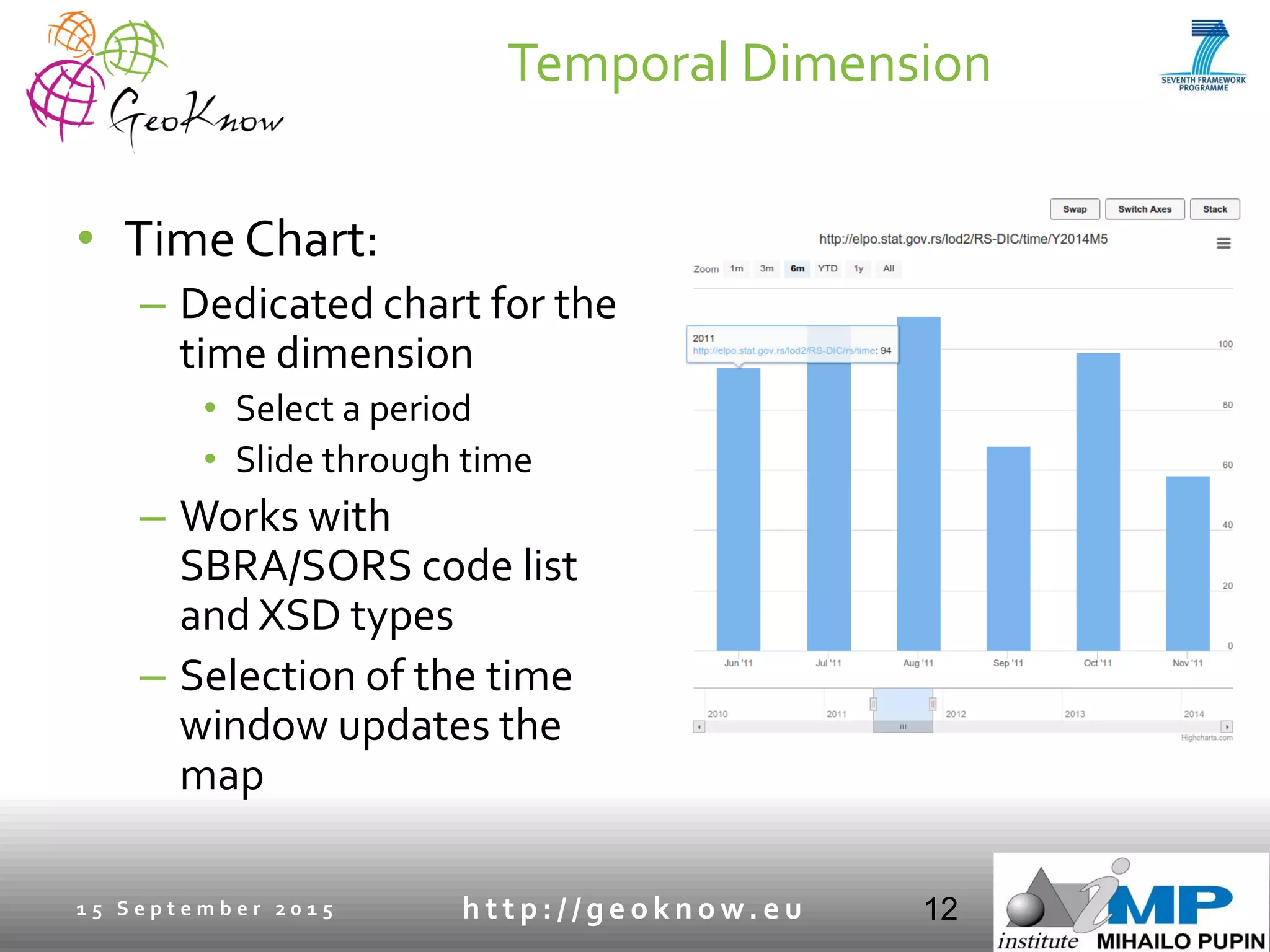
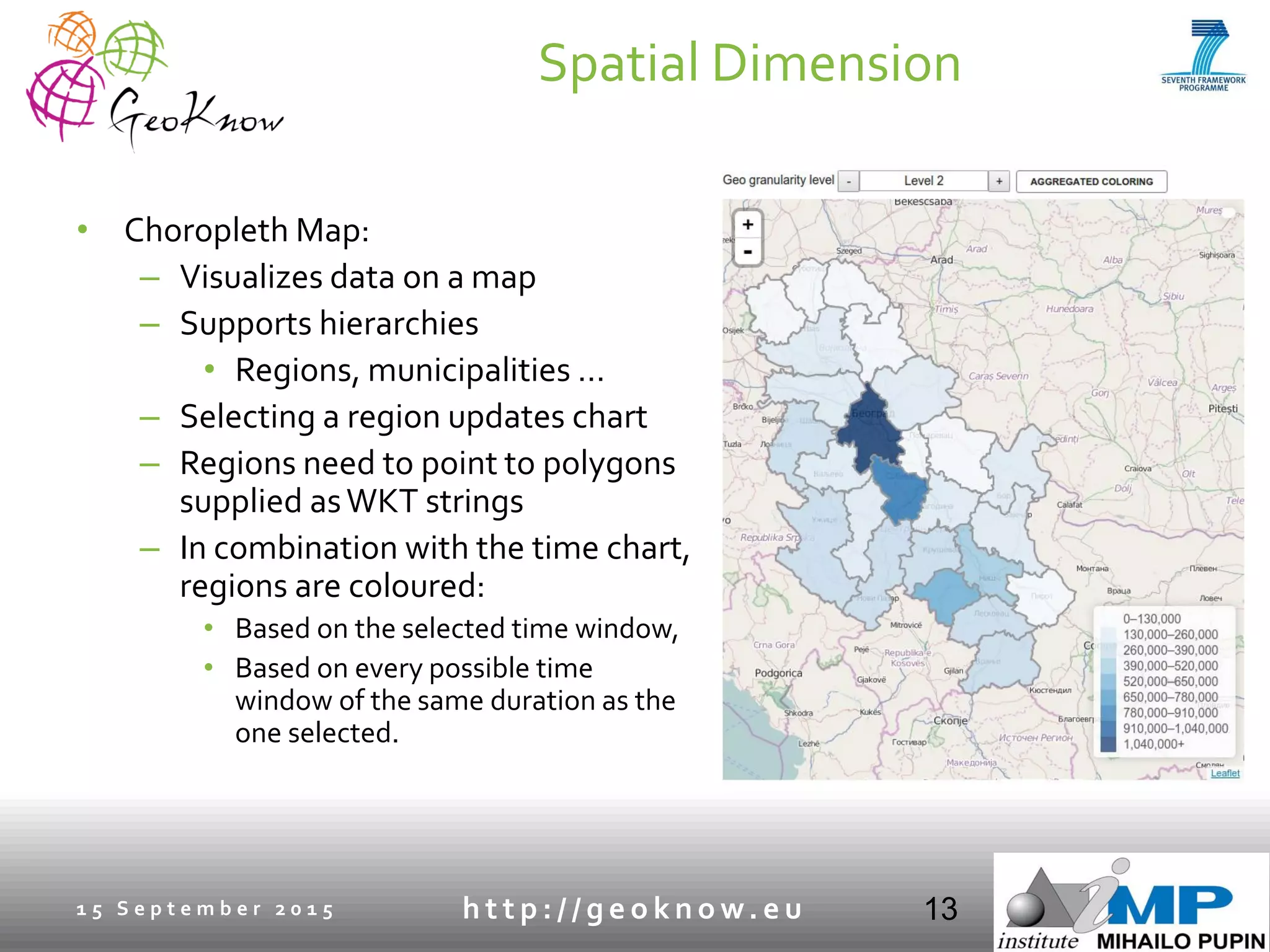
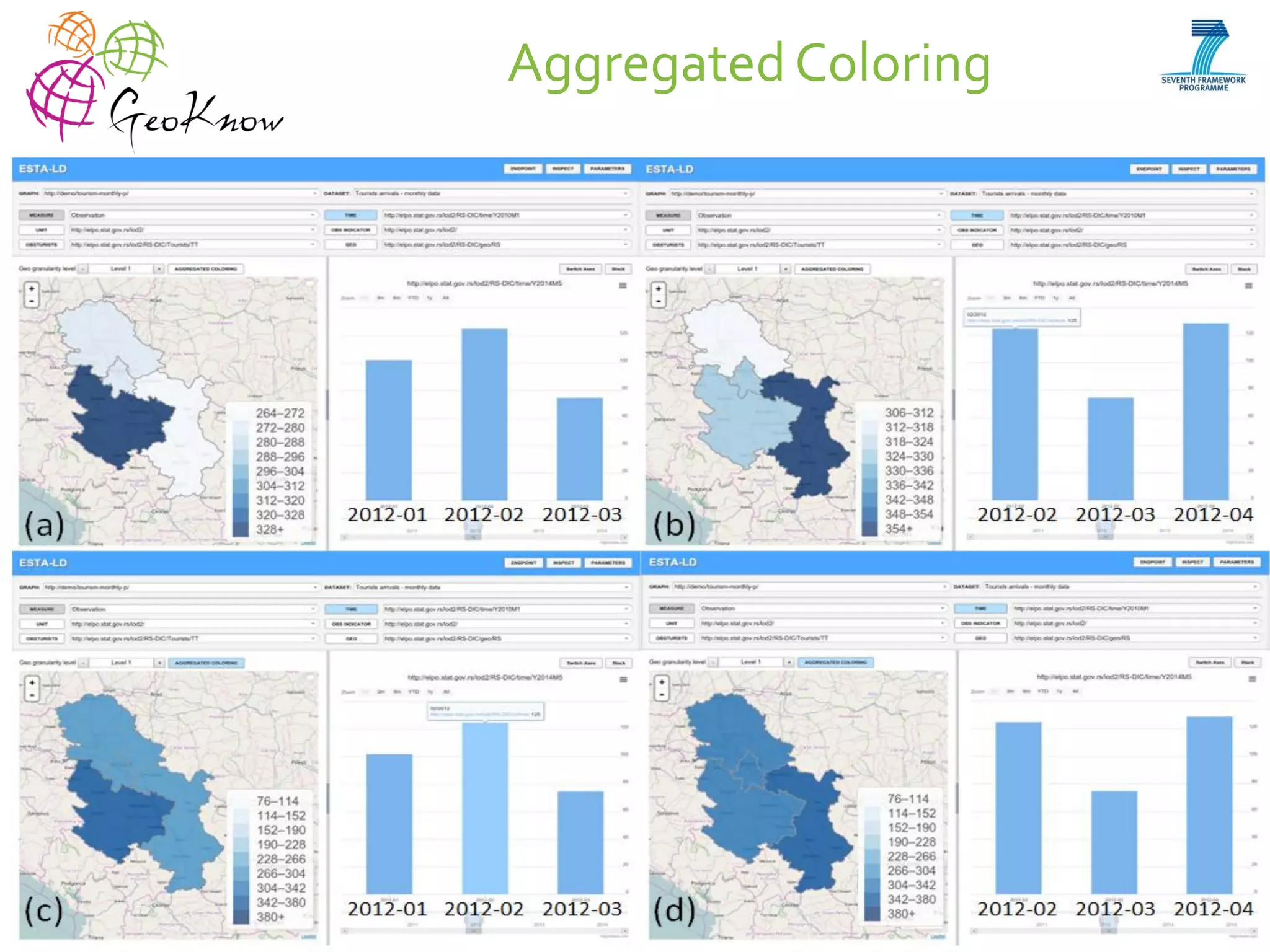
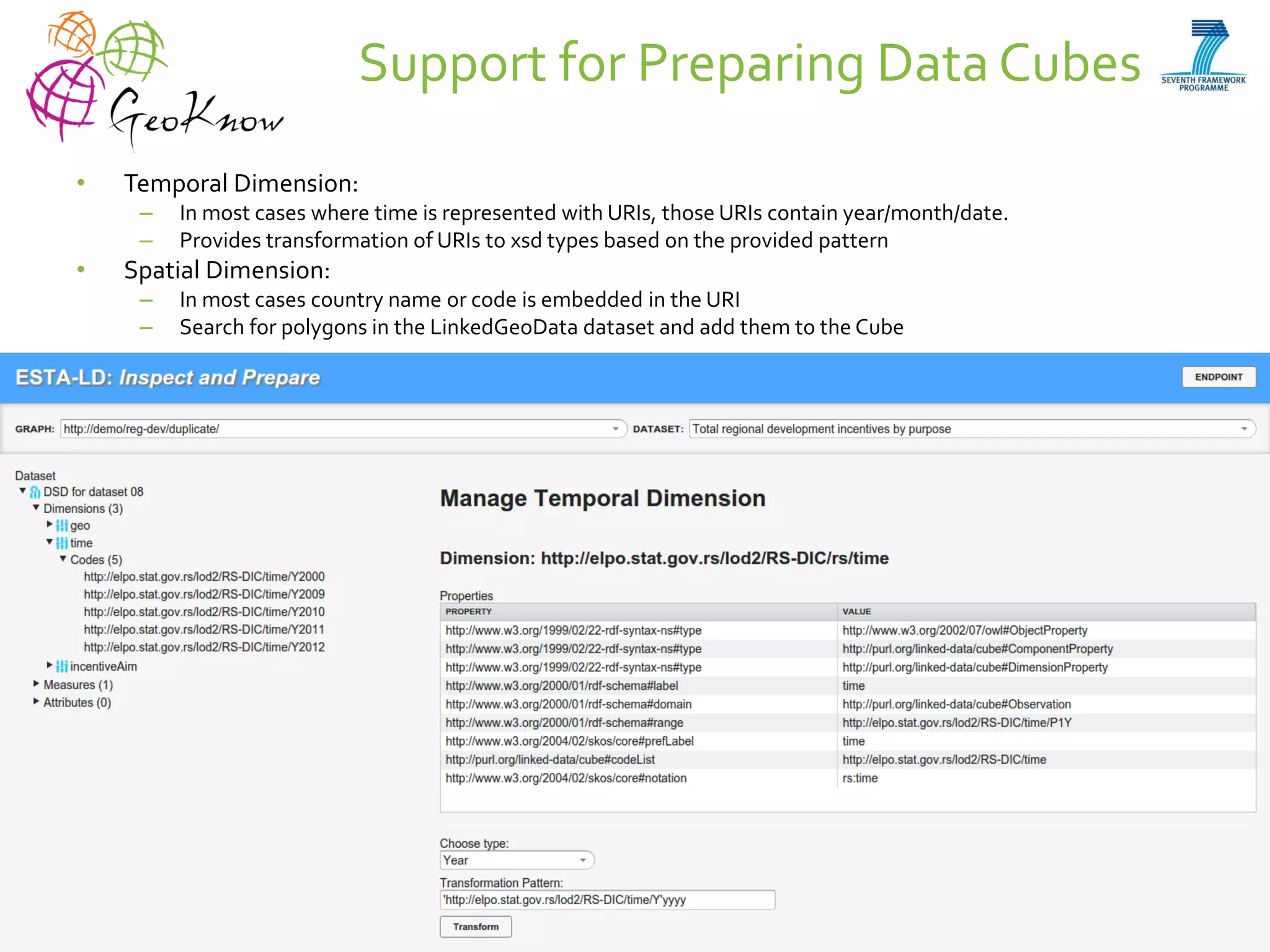
This document introduces ESTA-LD, a tool for exploring and analyzing spatio-temporal linked statistical data on the web. It summarizes ESTA-LD's key capabilities, which include visualizing statistical data on charts and maps, filtering and selecting dimensions like time and location, and aggregating data. The document also discusses how ESTA-LD models spatio-temporal data using the RDF Data Cube vocabulary and SDMX standards. Future work aims to expand ESTA-LD's chart types, analysis functions, and reduce data replication across datasets.