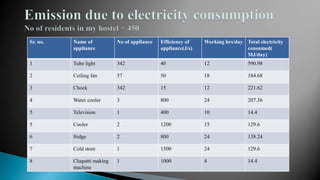
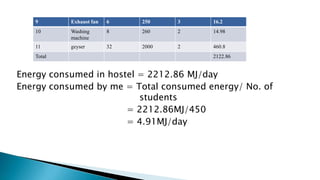
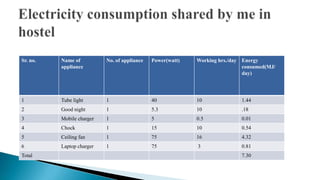
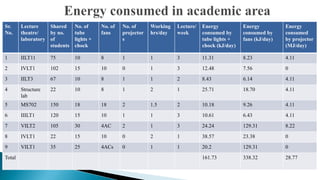
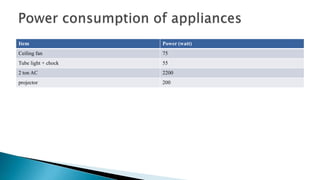
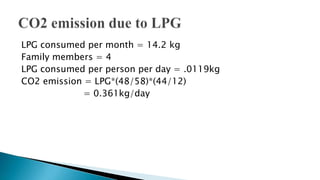
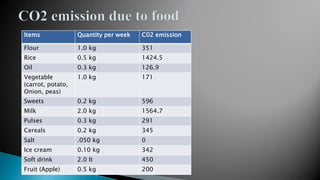
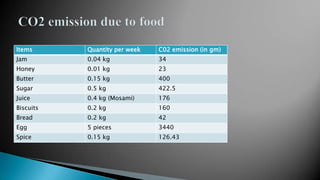
- A carbon footprint measures the total greenhouse gas emissions caused directly and indirectly by a person, organization, event or product. Carbon footprint quantification and reduction are key to preventing climate change through measures like enhancing energy efficiency and using green energy.
- Calculating one's carbon footprint involves estimating emissions from sources like fuel/electricity use, transportation, food consumption, and goods purchasing. The results can be used for environmental reporting, cost savings planning, and developing climate policies.
- Common methods to calculate carbon footprints include the Greenhouse Gas Protocol. Emissions scopes include direct sources like fuel combustion, indirect sources like purchased electricity, and optional sources like employee commuting.