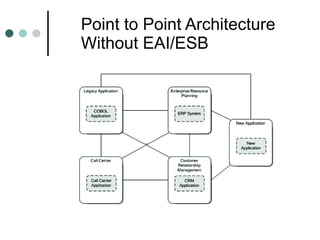
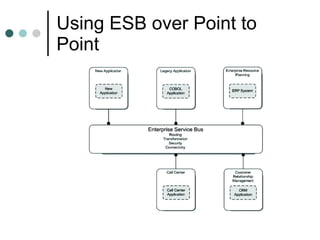
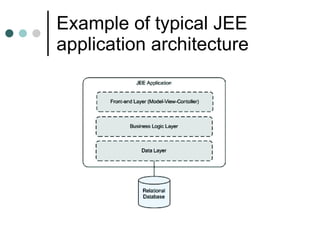
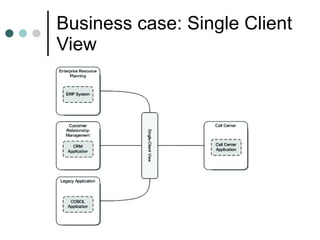
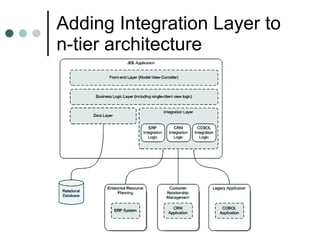
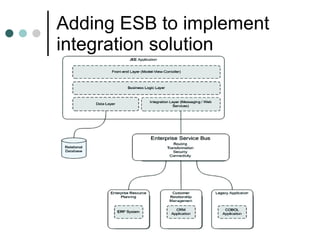
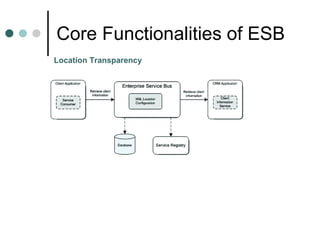
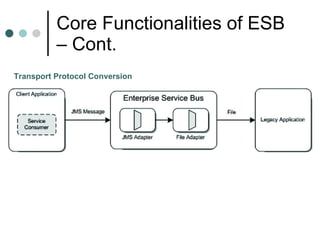
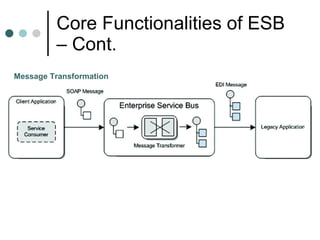
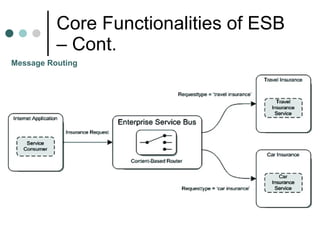
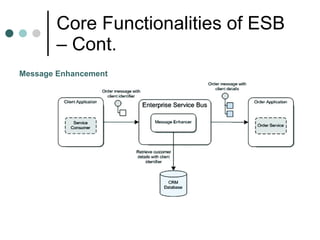
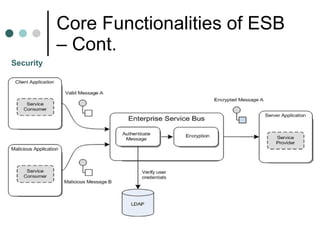
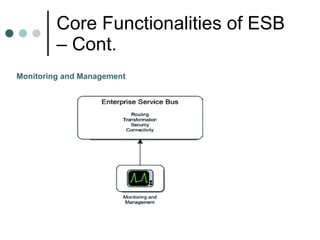
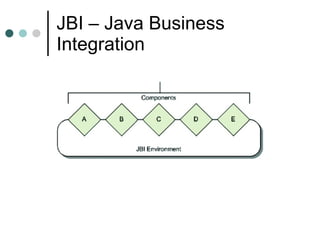
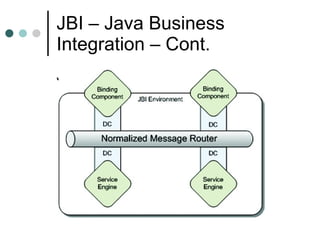
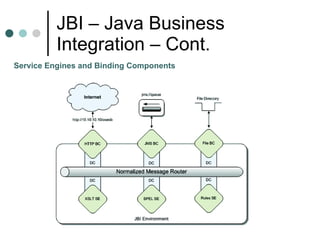
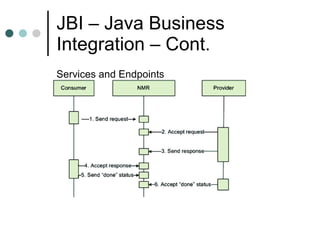
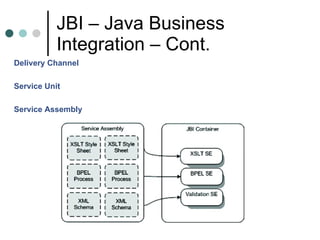
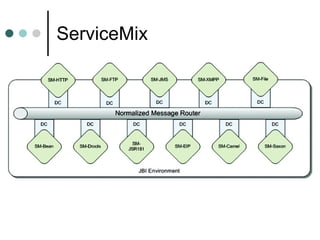
This document discusses the need for an enterprise service bus (ESB) and its core functionalities. An ESB is necessary to integrate heterogeneous applications and reduce costs associated with point-to-point integration. It provides location transparency, protocol conversion, message transformation, routing, enhancement, security, and monitoring capabilities. The document also describes Java Business Integration and how it uses a container, service engines, and other components to implement an ESB using services, endpoints, and a normalized message router. ServiceMix is presented as an open source ESB that can run as a standalone server or from a servlet engine.