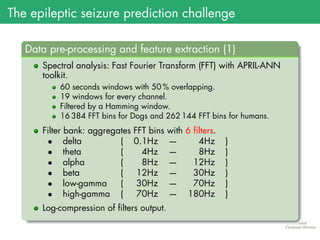
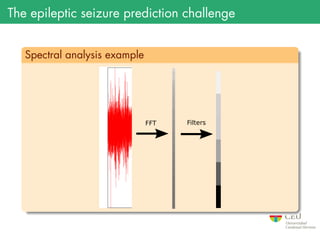
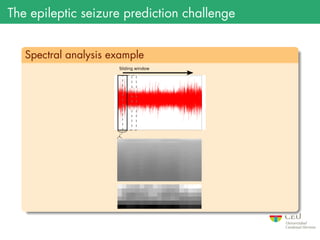
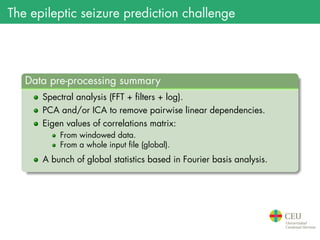
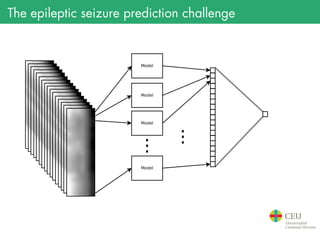
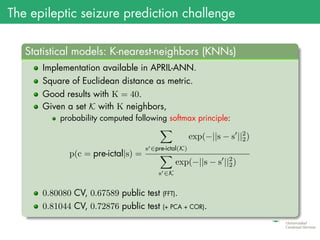
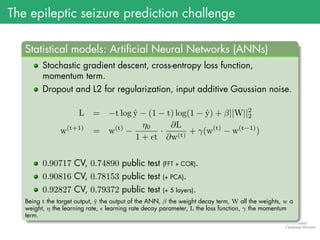
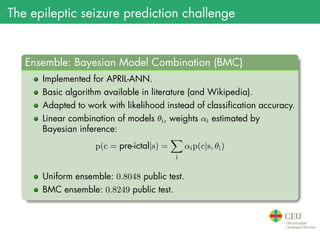
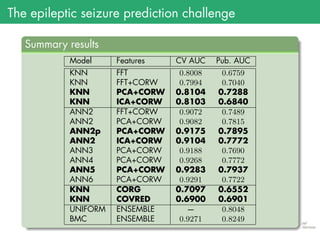
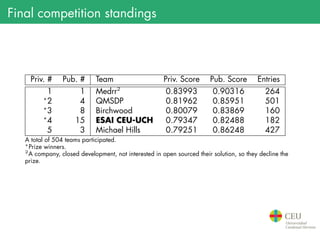
The document presents the details of the Epileptic Seizure Prediction Challenge organized by Kaggle, highlighting its goals, data structure, and approaches for classification of EEG recordings into pre-ictal and inter-ictal states. It reviews the methods for data preprocessing and feature extraction, as well as statistical models used, including k-nearest neighbors and artificial neural networks, and summarizes the competition results and model performances. Future work suggestions include developing a global model and exploring advanced neural network techniques.