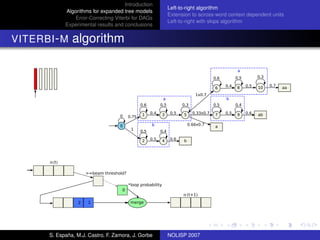
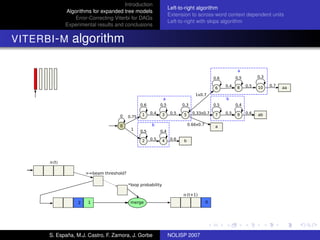
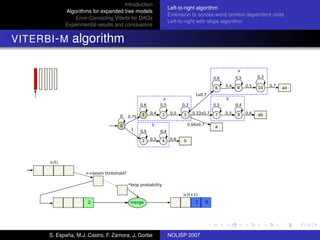
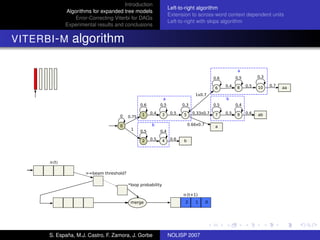
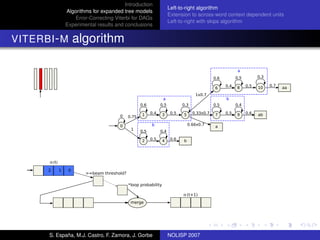
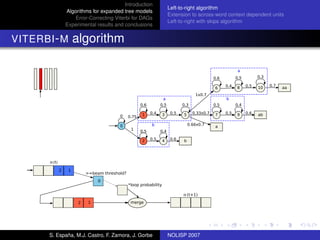
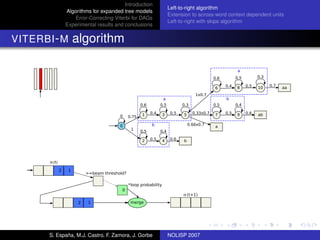
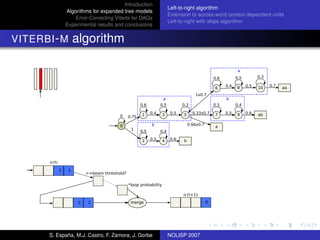
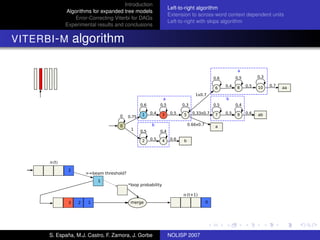
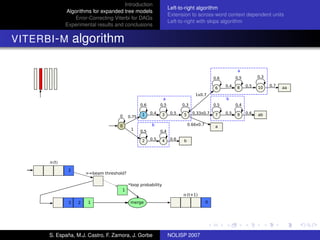
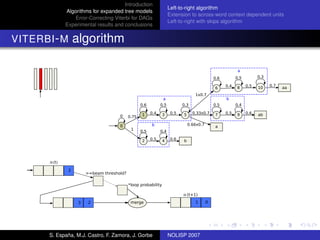
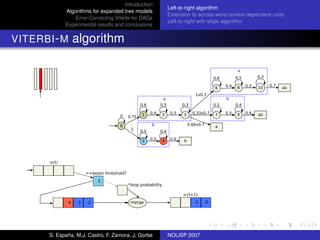
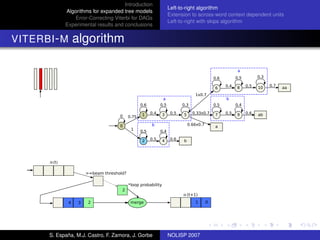
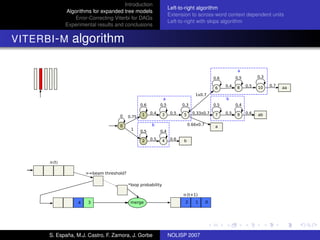
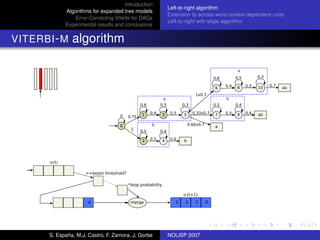
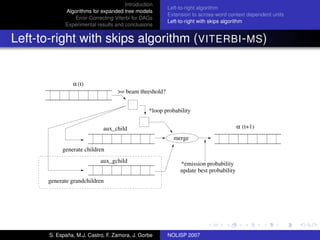
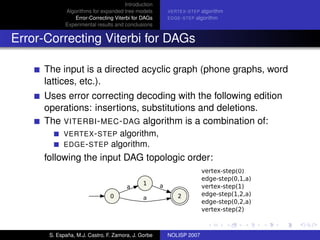
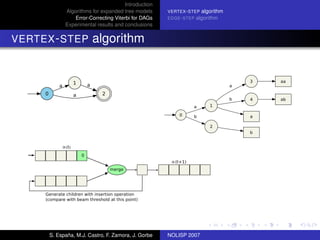
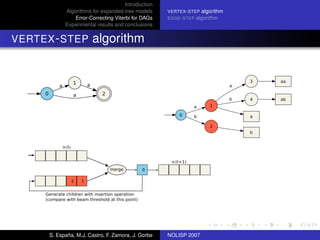
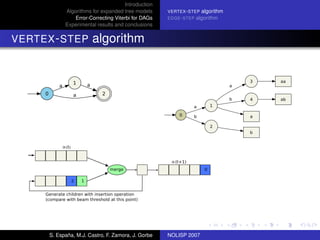
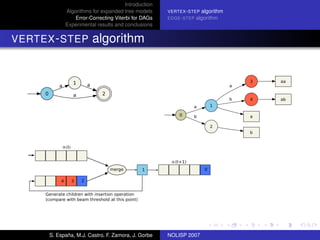
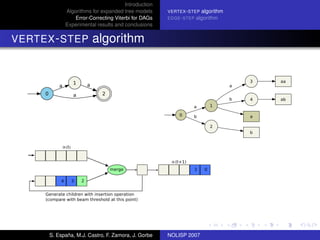
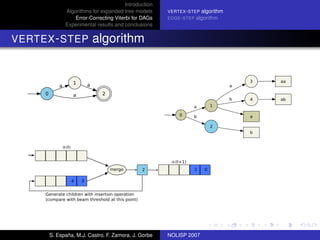
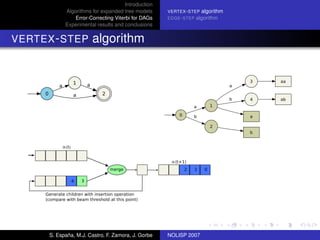
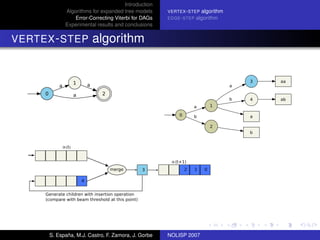
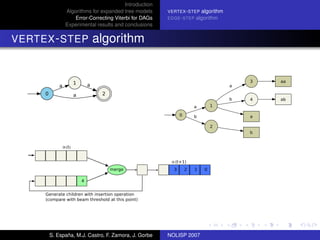
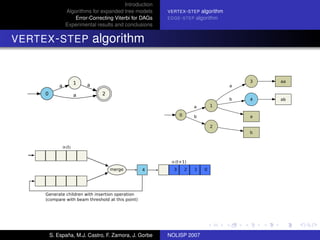
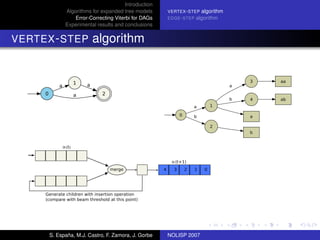
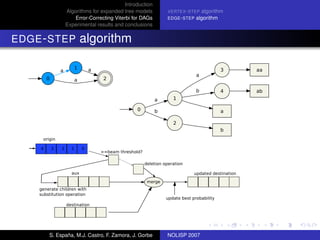
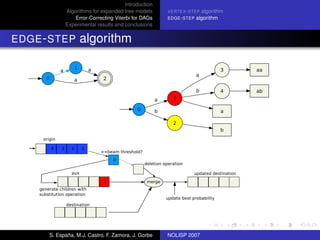
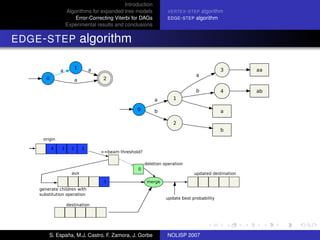
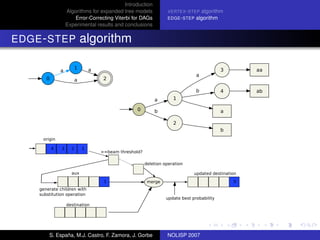
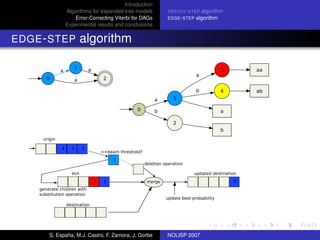
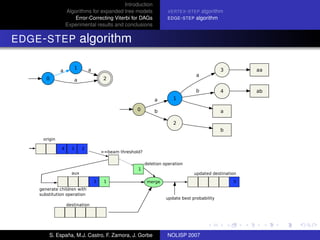
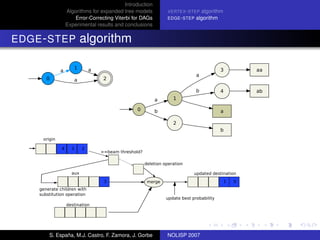
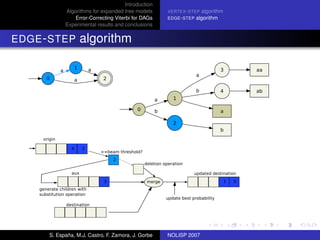
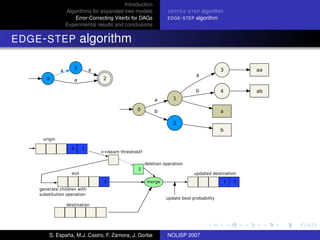
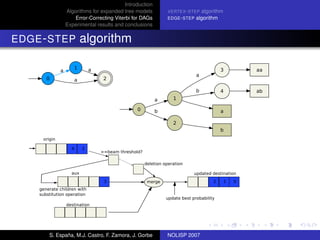
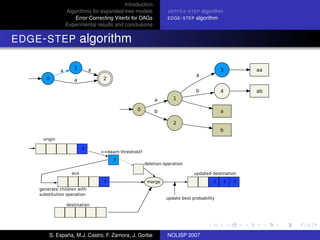
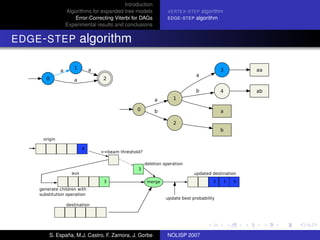
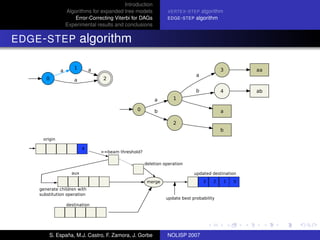
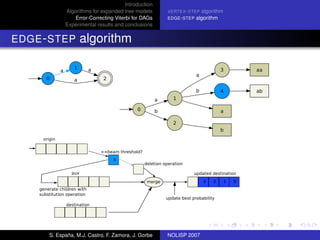
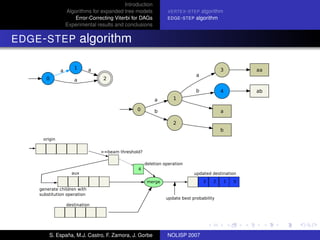
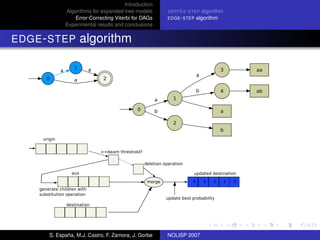
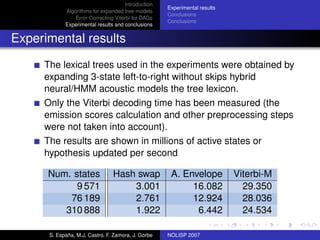
The document discusses algorithms for expanded tree models and error-correcting Viterbi methods for directed acyclic graphs (DAGs) in the context of automatic speech recognition (ASR). It highlights the efficiency of using lexical tree structures in Viterbi parsing, presents various specialized algorithms, and examines experimental results demonstrating their effectiveness. Key contributions include improved decoding techniques that enhance overall ASR system performance.