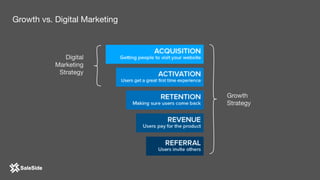
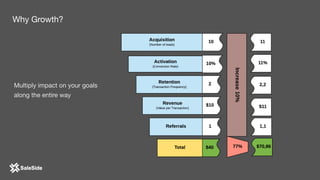
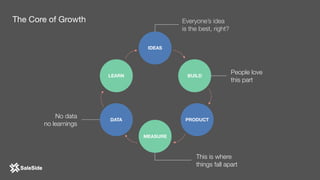
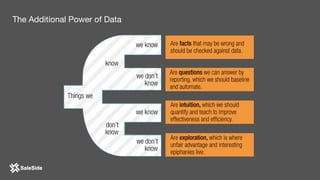
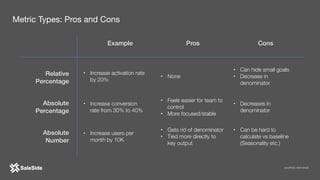
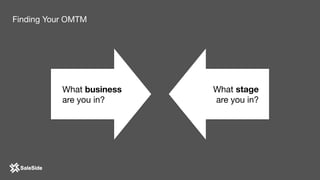
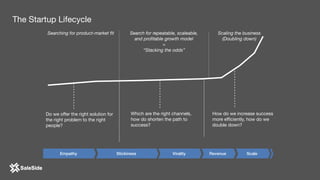
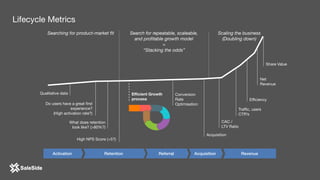
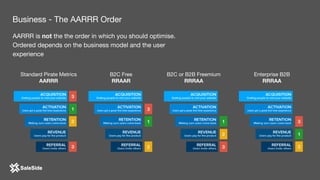
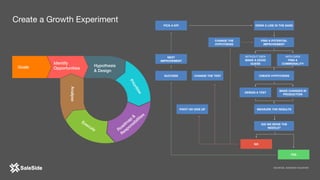
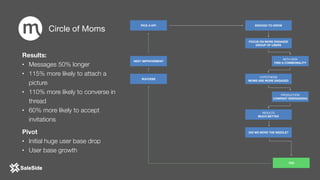
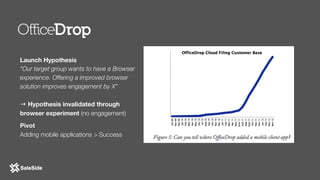
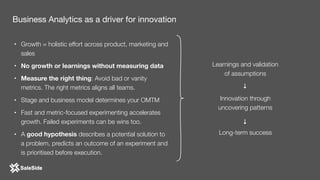
The document by Juliana Méndez outlines growth marketing strategies, emphasizing the importance of metrics in achieving business goals and driving growth. It discusses key concepts such as finding a North Star metric and One Metric That Matters (OMTM), goal setting, and conducting growth experiments while avoiding vanity metrics. Real-life case studies illustrate successful applications of these strategies, highlighting the value of data-driven decision-making in marketing.