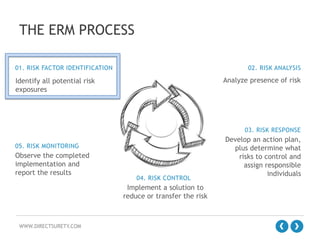
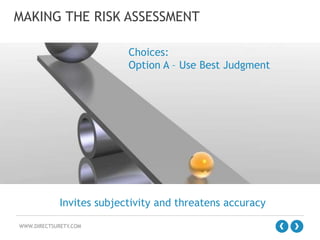
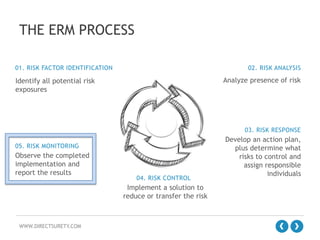
The document outlines the concept of Enterprise Risk Management (ERM), emphasizing its importance in identifying and managing risks that can negatively impact profitability and shareholder value in a construction context. It details the ERM process, which includes risk factor identification, analysis, response, control, and monitoring, along with benefits such as improved operational efficiencies and sound decision-making. Additionally, it highlights the evolution of risk management thinking and the necessity of integrating ERM into organizational culture for better financial and operational outcomes.