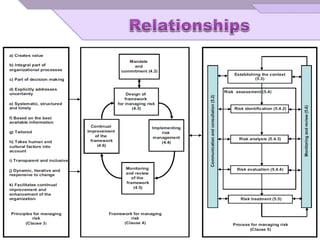
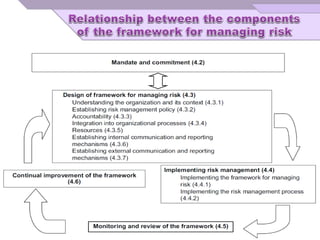
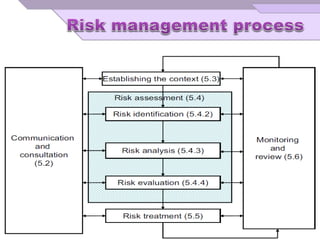
The document outlines principles and guidelines for risk management applicable to various organizations over their life cycle, emphasizing a systematic approach to managing risks. It covers essential components of risk management, including risk identification, analysis, evaluation, and treatment, while promoting accountability and integration within organizational processes. The effectiveness of risk management is highlighted as dependent on committed leadership, clear communication, and continuous improvement practices.







































































![ [1] ISO Guide 73:2009, Risk management —
Vocabulary
[2] IEC 31010, Risk management — Risk
assessment guidelines](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iso31000-170702074652/85/Iso-31000-Risk-management-Principles-and-guidelines-76-320.jpg)

