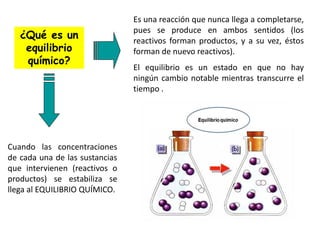
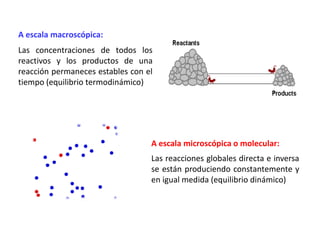
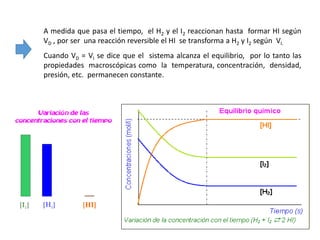
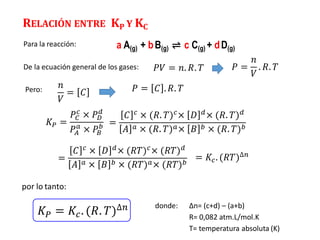
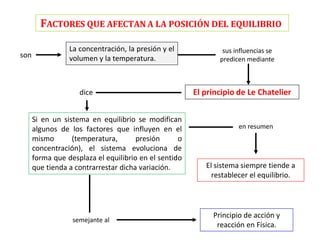
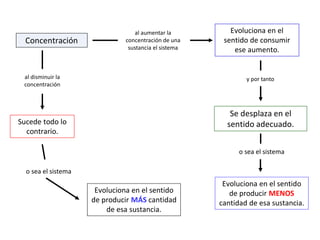
The document discusses chemical equilibrium. It states that in a chemical reaction, the rates of the forward and reverse reactions gradually decrease and increase, respectively, until they become equal, reaching a dynamic state where the concentrations of all species remain constant, known as chemical equilibrium. It then provides examples of chemical equations at equilibrium and definitions of key terms like the equilibrium constant Kc and how it relates to the law of mass action and reaction quotients.






![Aplicación de la ley de acción de masas
El producto de las concentraciones de los productos dividido por
el producto de las concentraciones de sus reactivos es su valor
siempre constante (mientras no varié la temperatura)
𝑎𝐴 + 𝑏𝐵 ⇆ 𝑐𝐶 + 𝑑𝐷 𝐾𝑐 =
[𝐶]𝑐[𝐷]𝑑
[𝐴]𝑎[𝐵]𝑏
La concentración molar o molaridad (M)
de una sustancia se calcula dividiendo el
número de moles de soluto entre el
volumen deseado de la solución,
expresados en litros (L)
𝑀 =
𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝑑𝑒 𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑜
𝑉 𝐿 𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑐𝑖ó𝑛
=
𝑛
𝑉](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sesion06-equilibrioquimico-210313065123/85/Equilibrio-quimico-13-320.jpg)



![Constante de equilibrio (Kc)
[ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ]
c d
c a b
C D
K
A B
𝑎𝐴 + 𝑏𝐵 ⇆ 𝑐𝐶 + 𝑑𝐷
En una reacción cualquiera:
La constante Kc tomará el valor:
para concentraciones en el equilibrio
La constante Kc cambia con la temperatura
¡ATENCIÓN!: Sólo se incluyen las especies gaseosas y/o en disolución. Las
especies en estado sólido o líquido tienen concentración constante y por
tanto, se integran en la constante de equilibrio.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sesion06-equilibrioquimico-210313065123/85/Equilibrio-quimico-17-320.jpg)
![Expresar la constante de equilibrio para la siguiente reacción:
EJEMPLO 02:
𝐼2(𝑔) + 𝐻2(𝑔) ⇆ 2𝐻𝐼(𝑔)
Solución:
𝐾𝑐 =
[𝐻𝐼]2
𝐻2 𝐼2
El valor de Kc dada su expresión, depende de cómo se ajuste la reacción.
Es decir, si la reacción anterior la hubiéramos ajustado como:
½ H2(g) + ½ I2(g) ⇆ HI(g)
la constante valdría la raíz cuadrada de la anterior.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sesion06-equilibrioquimico-210313065123/85/Equilibrio-quimico-18-320.jpg)
![Tengamos el equilibrio:
2SO2(g) + O2(g) ⇆ 2SO3(g)
Se hacen cinco experimentos en los que se introducen diferentes concentraciones
iniciales de ambos reactivos (SO2 y O2). Se produce la reacción y una vez alcanzado el
equilibrio se miden las concentraciones tanto de reactivos como de productos
observándose los siguientes datos:
Concentraciones iniciales
(mol/L)
Concentraciones en
equilibrio (mol/L)
[SO2] [O2] [SO3] [SO2] [O2] [SO3] Kc
Exp 1 0,20 0,20 — 0,030 0,155 0,170 279,2
Exp 2 0,15 0,40 — 0,014 0,332 0,135 280,7
Exp 3 — — 0,20 0,053 0,026 0,143 280,0
Exp 4 — — 0,70 0,132 0,066 0,568 280,5
Exp 5 0,15 0,40 0,25 0,037 0,343 0,363 280,6
EJEMPLO 03:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sesion06-equilibrioquimico-210313065123/85/Equilibrio-quimico-19-320.jpg)
![Solución:
Concentraciones iniciales
(mol/L)
Concentraciones en
equilibrio (mol/L)
[SO2] [O2] [SO3] [SO2] [O2] [SO3] Kc
Exp 1 0,20 0,20 — 0,030 0,155 0,170 279,2
Exp 2 0,15 0,40 — 0,014 0,332 0,135 280,7
Exp 3 — — 0,20 0,053 0,026 0,143 280,0
Exp 4 — — 0,70 0,132 0,066 0,568 280,5
Exp 5 0,15 0,40 0,25 0,037 0,343 0,363 280,6
2
3
2
2 2
[ ]
[ ] [ ]
C
SO
K
SO O
En la reacción anterior:
Kc se obtiene aplicando la expresión:
2SO2(g) + O2(g) ⇆ 2SO3(g)
y como se ve es prácticamente constante.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sesion06-equilibrioquimico-210313065123/85/Equilibrio-quimico-20-320.jpg)
![Escribir las expresiones de Kc para los siguientes equilibrios químicos:
EJEMPLO 04:
𝐵𝑟2(𝑔) + 𝐻2(𝑔) ⇆ 𝐻𝐵𝑟(𝑔)
Solución:
𝑁𝑂(𝑔) + 𝐶𝑙2(𝑔) ⇆ 𝑁𝑂𝐶𝑙(𝑔)
2𝑆𝑂2(𝑔) + 𝑂2(𝑔) ⇆ 𝑆𝑂3(𝑔)
𝑁2𝑂4(𝑔) ⇆ 𝑁𝑂2(𝑔)
𝑎)
𝑏)
𝑐)
𝑑)
𝐾𝑐 =
[𝐻𝐵𝑟]2
𝐻2 𝐵𝑟2
𝐵𝑟2(𝑔) + 𝐻2(𝑔) ⇆ 2𝐻𝐵𝑟(𝑔)
𝐾𝑐 =
[𝑁𝑂𝐶𝑙]2
𝑁𝑂 2 𝐶𝑙2
2𝑁𝑂(𝑔) + 𝐶𝑙2(𝑔) ⇆ 2𝑁𝑂𝐶𝑙(𝑔)
2𝑆𝑂2(𝑔) + 𝑂2(𝑔) ⇆ 2𝑆𝑂3(𝑔) 𝐾𝑐 =
[𝑆𝑂3]2
𝑆𝑂2
2 𝑂2
𝑁2𝑂4(𝑔) ⇆ 2𝑁𝑂2(𝑔) 𝐾𝑐 =
[𝑁𝑂2]2
𝑁2𝑂4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sesion06-equilibrioquimico-210313065123/85/Equilibrio-quimico-21-320.jpg)


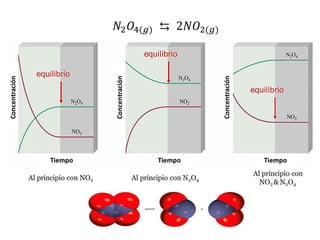
![TIPOS DE EQUILIBRIO
1N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇌ 2NH3(g)
CaCO3(s) + calor ⇌ CaO(s) + CO2(g)
EQUILIBRIO HOMOGÉNEO
Son aquellos sistemas donde los reactantes y productos se encuentran en una misma
fase o en un mismo estado físico
Ejemplo:
𝐾𝑐 =
[𝑁𝐻3]2
𝑁2 𝐻2
3
EQUILIBRIO HETEROGÉNEO
Son sistemas donde las sustancias se encuentran en más de una fase o más de un
estado físico.
Ejemplo:
𝐾𝑐 = 𝐶𝑂2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sesion06-equilibrioquimico-210313065123/85/Equilibrio-quimico-25-320.jpg)
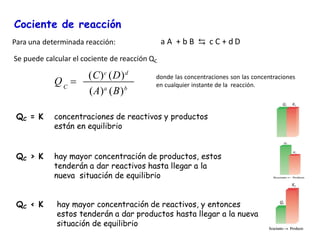


![Consideremos la reacción: H2 (g) + I2 (g) ⇄ 2 HI (g)
Cuando se alcanza el equilibrio
eq
2
2
2
c
I
H
HI
=
K
=
Q
… Si se añade hidrógeno:
a) Aumenta [H2], mientras que [I2] y [HI] permanecen constante; Q disminuye dejando
de ser igual a Kc, rompiéndose el equilibrio químico.
c) El equilibrio se desplaza hacia la derecha:
H2 (g) + I2 (g) → 2 HI (g)
b) De acuerdo con el principio de Le Châtelier, el sistema reacciona en el sentido de
contrarrestar el aumento de la concentración de H2, consumiendo parte del H2
añadido, al reaccionar con el I2, produciendo más HI.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sesion06-equilibrioquimico-210313065123/85/Equilibrio-quimico-31-320.jpg)

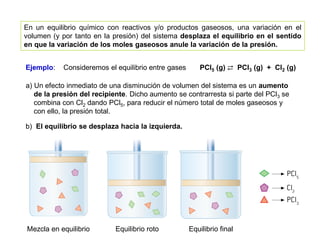


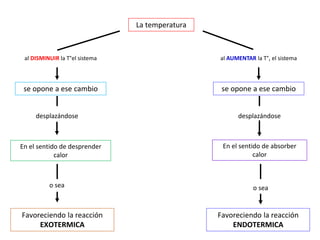


![ Es muy importante en la industria el saber qué condiciones favorecen el
desplazamiento de un equilibrio hacia la formación de un producto, pues
se conseguirá un mayor rendimiento, en dicho proceso.
En la síntesis de Haber en la formación de amoniaco
[N2(g) + 3 H2(g) ⇄ 2 NH3(g)]
exotérmica, la formación de amoniaco está favorecida por altas presiones y
por una baja temperatura. Por ello esta reacción se lleva a cabo a altísima
presión y a una temperatura relativamente baja, aunque no puede ser muy
baja para que la reacción no sea muy lenta. Hay que mantener un equilibrio
entre rendimiento y tiempo de reacción.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sesion06-equilibrioquimico-210313065123/85/Equilibrio-quimico-40-320.jpg)

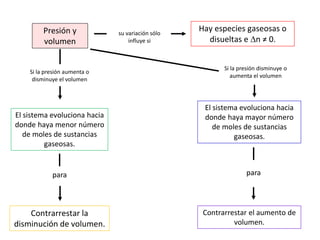
![VARIACIONES EN EL EQUILIBRIO
[reactivos] ↑
[reactivos] ↓
[productos] ↑
[productos] ↓
T ↑ (exotérmicas)
T ↑ (endotérmicas)
T ↓ (exotérmicas)
T ↓ (endotérmicas)
p ↑ Hacia donde menos nº moles de gases
p ↓ Hacia donde más nº moles de gases](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sesion06-equilibrioquimico-210313065123/85/Equilibrio-quimico-42-320.jpg)






![EFECTO DE LA MASA
Cuando existe una variación de reactantes o productos
𝑎𝐴 + 𝑏𝐵 ⇆ 𝑐𝐶 + 𝑑𝐷 𝑄 =
[𝐶]𝑐
[𝐷]𝑑
[𝐴]𝑎[𝐵]𝑏
𝐾𝑐 =
[𝐶]𝑐
[𝐷]𝑑
[𝐴]𝑎[𝐵]𝑏
𝑠𝑒 𝑑𝑎 𝑐𝑢𝑎𝑛𝑑𝑜 𝑣1 = 𝑣2
𝑛𝑜 𝑣𝑎𝑟í𝑎𝑛
𝑆𝑖:
𝑄 < 𝐾 → 𝑙𝑎 𝑟𝑒𝑎𝑐𝑐𝑖ó𝑛 𝑠𝑒 𝑑𝑒𝑠𝑝𝑙𝑎𝑧𝑎 ℎ𝑎𝑐𝑖𝑎 𝑙𝑎 𝑑𝑒𝑟𝑒𝑐ℎ𝑎 (→)
𝑄 = 𝐾 → 𝑠𝑒 ℎ𝑎 𝑙𝑙𝑒𝑔𝑎𝑑𝑜 𝑎 𝑢𝑛 𝑒𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑑𝑜 𝑑𝑒 𝑒𝑞𝑢𝑖𝑙𝑖𝑏𝑟𝑖𝑜
𝑄 > 𝐾 → 𝑙𝑎 𝑟𝑒𝑎𝑐𝑐𝑖ó𝑛 𝑠𝑒 𝑑𝑒𝑠𝑝𝑙𝑎𝑧𝑎 ℎ𝑎𝑐𝑖𝑎 𝑙𝑎 𝑖𝑧𝑞𝑢𝑖𝑒𝑟𝑑𝑎 (←)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sesion06-equilibrioquimico-210313065123/85/Equilibrio-quimico-52-320.jpg)

![FUERZA IÓNICA
Es igual a la semisuma de la concentración de iones al cuadrado
𝑁𝑎2𝑆𝑂4 ⇆ 2𝑁𝑎(𝑎𝑐)
+
+ 𝑆𝑂4(𝑎𝑐)
2−
[𝑁𝑎+
] = 2 0,2 = 0,4 𝑀
𝐹𝑖 =
1
2
. 𝑍1
2
+ . 𝑍2
2
+ . 𝑍3
2
…
EJEMPLO 09: ¿Cuál es la fuerza iónica de una solución de Na2SO4 0,2 M?
Solución:
[𝑆𝑂4
2−
] = 1 0,2 = 0,2 𝑀
[ ]𝑁𝑎2𝑆𝑂4
= 0,2 𝑀
𝐹𝑖 =
1
2
𝑁𝑎+ . 𝑍𝑁𝑎+
2
+ 𝑆𝑂4
2−
. 𝑍𝑆𝑂4
2−
2
𝐹𝑖 =
1
2
0,4 . (1)2
+ 0,2 . (2)2
𝐹𝑖 = 0,06 𝑀](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sesion06-equilibrioquimico-210313065123/85/Equilibrio-quimico-54-320.jpg)
![𝐴𝑙2(𝑆𝑂4)3 ⇆ 2𝐴𝑙(𝑎𝑐)
3+
+ 3𝑆𝑂4(𝑎𝑐)
2−
[𝐴𝑙3+] = 2 0,1 = 0,2 𝑀
EJEMPLO 10: ¿Cuál es la fuerza iónica de una solución de NaCl 0,1 M y Al2(SO4)3 0,1 M?
Solución:
[𝑆𝑂4
2−
] = 3 0,1 = 0,3 𝑀
[ ]𝑁𝑎𝐶𝑙= 0,1 𝑀
𝐹𝑖 =
1
2
0,1 . (1)2
+ 0,1 . (1)2
+ 0,2 . (3)2
+ 0,3 . (2)2
𝐹𝑖 = 1,6 𝑀
𝑁𝑎𝐶𝑙 ⇆ 𝑁𝑎(𝑎𝑐)
+
+ 𝐶𝑙(𝑎𝑐)
−
[𝑁𝑎+] = 1(0,1) = 0,1 𝑀
[𝐶𝑙−
] = 1(0,1) = 0,1 𝑀
[ ]𝐴𝑙2(𝑆𝑂4)3
= 0,1 𝑀
𝐹𝑖 =
1
2
𝑁𝑎+
. 𝑍𝑁𝑎+
2
+ 𝐶𝑙−
. 𝑍𝐶𝑙−
2
+ 𝐴𝑙3+
. 𝑍𝐴𝑙3+
2
+ 𝑆𝑂4
2−
. 𝑍𝑆𝑂4
2−
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sesion06-equilibrioquimico-210313065123/85/Equilibrio-quimico-55-320.jpg)
![[ ]𝑒𝑓𝑒𝑐𝑡𝑖𝑣𝑎= 𝐴𝑐𝑡𝑖𝑣𝑖𝑑𝑎𝑑 < [ ]𝑟𝑒𝑎𝑙
𝐴𝑐𝑡𝑖𝑣𝑖𝑑𝑎𝑑 = . 𝛾
A: actividad
: coeficiente de actividad
Depende de la fuerza iónica
la fuerza iónica influye
en la actividad
Si el coeficiente de actividad () es igual a 1, entonces no hay perturbación de electrolitos.
El coeficiente de actividad depende de la fuerza iónica
𝐻2𝐶𝑂3 + 𝐻2𝑂 ⇆ 𝐻3𝑂+
+ 𝐻𝐶𝑂3
−
10𝐾𝑂𝐻 → 10𝐾+
+ 10𝑂𝐻−
10𝑁𝐻4𝑂𝐻 → 2𝑁𝐻4
+
+ 1𝑂𝐻− ELECTROLITOS
La actividad de un ión depende de su coeficiente de actividad ()
𝐴 = 𝛾. 𝐹𝑖 =
1
2
. 𝑍1
2
+ . 𝑍2
2
+ .𝑍3
2
…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sesion06-equilibrioquimico-210313065123/85/Equilibrio-quimico-56-320.jpg)
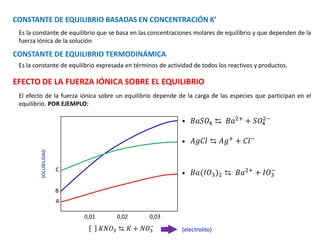
![Entre menor sea la concentración del electrolito,
las constantes basadas en concentración tienden
a su valor termodinámico
𝐾𝑎 =
𝐻3𝑂+
𝐶𝐻3𝐶𝑂𝑂−
𝐶𝐻3𝐶𝑂𝑂𝐻
Ka = 1,75x10-5
Kps = 1x10-10
Kw = 1,10x10-14
A
B
C
10-6 10-4 10-2 10-1
CONSTANTE
DE
EQUILIBRIO
BASADA
EN
CONCENTRACIÓN
K
equ.
[
]
[ ]molar NaCl
𝐻2𝑂 ⇆ 𝐻+ + 𝑂𝐻−
2𝐻2𝑂 ⇆ 𝐻3𝑂+ + 𝑂𝐻−
𝐾𝑊 = 𝐻3𝑂+ 𝑂𝐻−
𝐵𝑎𝑆𝑂4 ⇆ 𝐵𝑎2+ + 𝑆𝑂4
2−
𝐾𝑃𝑆 = 𝐵𝑎2+ 𝑆𝑂4
2−
𝐶𝐻3𝐶𝑂𝑂𝐻 + 𝐻2𝑂 ⇆ 𝐻3𝑂+
+ 𝐶𝐻3𝐶𝑂𝑂−
EFECTO DE LA CONCENTRACIÓN DE LOS ELECTROLITOS SOBRE LA
CONSTANTE DE EQUILIBRIO BASADAS EN CONCENTRACIÓN
A)
B)
C)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sesion06-equilibrioquimico-210313065123/85/Equilibrio-quimico-57-320.jpg)
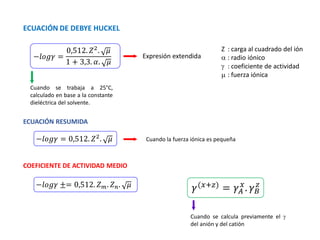
![Fi : fuerza iónica
: coeficiente de actividad
𝛾 ≅ 1
−𝑙𝑜𝑔𝛾 = 0,512. 𝑍2
. 𝜇
COEFICIENTE DE ACTIVIDAD
𝐹𝑖 = 0
𝑖ó𝑛 − 𝑖ó𝑛
𝑖ó𝑛−𝑑𝑖𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑣𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑒
𝛾 > 1
𝛾 < 1
𝛾 = 1
𝐹1 ≠ 0
𝐹𝑖 ≠ 0
𝐹𝑖 = 0
LEY LIMITANTE DE DEBYE HUCKEL
Si existe influencia del electrolito → A [ ]
Si no existe influencia del electrolito → A = [ ]
𝜇 ∶ 𝑓𝑢𝑒𝑟𝑧𝑎 𝑖ó𝑛𝑖𝑐𝑎
0,512
Este valor se utiliza cuando se
trabaja en medio acuoso y
depende de la temperatura y de
la constante dieléctrica](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sesion06-equilibrioquimico-210313065123/85/Equilibrio-quimico-59-320.jpg)
![EJEMPLO 11: Calcular el coeficiente de actividad para el carbonato de sodio 0,1 M
Solución:
[𝐶𝑂3
2−
] = 1 0,1 = 0,1 𝑀
𝐹𝑖 =
1
2
0,2 . (1)2+ 0,1 . (2)2
𝐹𝑖 = 0,3 𝑀
𝑁𝑎2𝐶𝑂3 ⇆ 2𝑁𝑎(𝑎𝑐)
+
+ 𝐶𝑂3
2− [𝑁𝑎+
] = 2(0,1) = 0,2 𝑀
[ ]𝑁𝑎2𝐶𝑂3
= 0,1 𝑀
𝐹𝑖 =
1
2
𝑁𝑎+
. 𝑍𝑁𝑎+
2
+ 𝐶𝑂3
2−
. 𝑍𝐶𝑂3
2−
2
−𝑙𝑜𝑔𝛾 ±= 0,512. 𝑍𝑚. 𝑍𝑛. 𝜇
−𝑙𝑜𝑔𝛾±𝑁𝑎2𝐶𝑂3
= 0,512. (1). (2). 0,3
−𝑙𝑜𝑔𝛾±𝑁𝑎2𝐶𝑂3
= 0,5608 𝛾𝑁𝑎2𝐶𝑂3
= 3,63](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sesion06-equilibrioquimico-210313065123/85/Equilibrio-quimico-61-320.jpg)
![Es una expresión que relaciona las concentraciones en equilibrio de varias especies
en una solución con la concentración analítica de los distintos solutos
BALANCE DE MASA
El balance de masa relaciona las concentraciones en equilibrio de los diferentes solutos
Entonces el balance de masa es:
𝑁𝑎𝐶𝑙 0,1 𝑀
0,1 𝑀 𝑁𝑎+
0,1 𝑀 𝐶𝑙−
𝑁𝑎𝐶𝑙 ⇆ 𝑁𝑎+ + 𝐶𝑙−
𝐻2𝑂 ⇆ 𝐻+
+ 𝑂𝐻−
𝐵𝑀 → [𝑁𝑎+
] = [𝐶𝑙−
]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sesion06-equilibrioquimico-210313065123/85/Equilibrio-quimico-62-320.jpg)
![EJEMPLO 12: Hacer el balance de masa de una solución de sulfato de sodio
Solución:
[𝑆𝑂4
2−
] = ½ 𝑁𝑎+
𝑁𝑎2𝑆𝑂4 ⇆ 2𝑁𝑎(𝑎𝑐)
+
+ 𝑆𝑂4(𝑎𝑐)
2−
[𝑁𝑎+] = 2 [𝑆𝑂4
2−
]
𝐵𝑀
EJEMPLO 13: Hacer el balance de masa de una solución de sulfato de sodio 0,1 M
Solución:
[𝑆𝑂4
2−
] = 1 0,1 = 0,1 𝑀
𝑁𝑎2𝑆𝑂4 ⇆ 2𝑁𝑎(𝑎𝑐)
+
+ 𝑆𝑂4(𝑎𝑐)
2−
[𝑁𝑎+
] = 2 0,1 = 0,2 𝑀
𝐵𝑀
𝑆𝑂4
2−
+ 𝐻2𝑂 ⇆ 𝐻𝑆𝑂4
−
+ 𝑂𝐻−
𝐻2𝑂 ⇆ 𝐻+
+ 𝑂𝐻−
[𝑆𝑂4
2−
] = 0,1 𝑀
[𝑆𝑂4
2−
] + 𝐻𝑆𝑂4
−
= 0,1 𝑀
BM, en el caso que no se conociera la
concentración de la solución](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sesion06-equilibrioquimico-210313065123/85/Equilibrio-quimico-63-320.jpg)
![Es aquella en la cual la concentración de las cargas positivas de una disolución debe
ser igual a la concentración total de las cargas negativas.
BALANCE DE CARGA
moles / L (carga +) = moles / L (carga -)
[ ] [ ]
EJEMPLO 14: Hacer el balance de carga de una solución de CaCl2 0,2 M y Na2SO4 0,1 M
Solución:
𝐶𝑎𝐶𝑙2 ⇆ 𝐶𝑎2+
+ 𝐶𝑙−
2[𝐶𝑎2+
] + 1 𝑁𝑎+
+ 𝐻3𝑂+
= 1 𝐶𝑙−
+ 2 𝑆𝑂4
2−
+ [𝑂𝐻−
]
𝐵C
𝐶𝑙−
𝐶𝑎2+ 𝑁𝑎+
𝑆𝑂4
2−
𝑂𝐻− 𝐻3𝑂+
Reemplazando valores:
2 0,2 + 1(0,2) + 1 × 10−7 = 1(0,4) + 2(0,1) + 1 × 10−7
𝑁𝑎2𝑆𝑂4 ⇆ 2𝑁𝑎+
+ 𝑆𝑂4
2−
[𝐶𝑎2+
] = 0,2 𝑀 [𝐶𝑙−
] = 0,4 𝑀
[𝑁𝑎+
] = 0,2 𝑀 [𝑆𝑂4
2−
]=0,1 M
𝐶𝑎2+
𝐶𝑙−
𝑁𝑎+
𝑆𝑂4
2−
;
;
0 = 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sesion06-equilibrioquimico-210313065123/85/Equilibrio-quimico-64-320.jpg)


