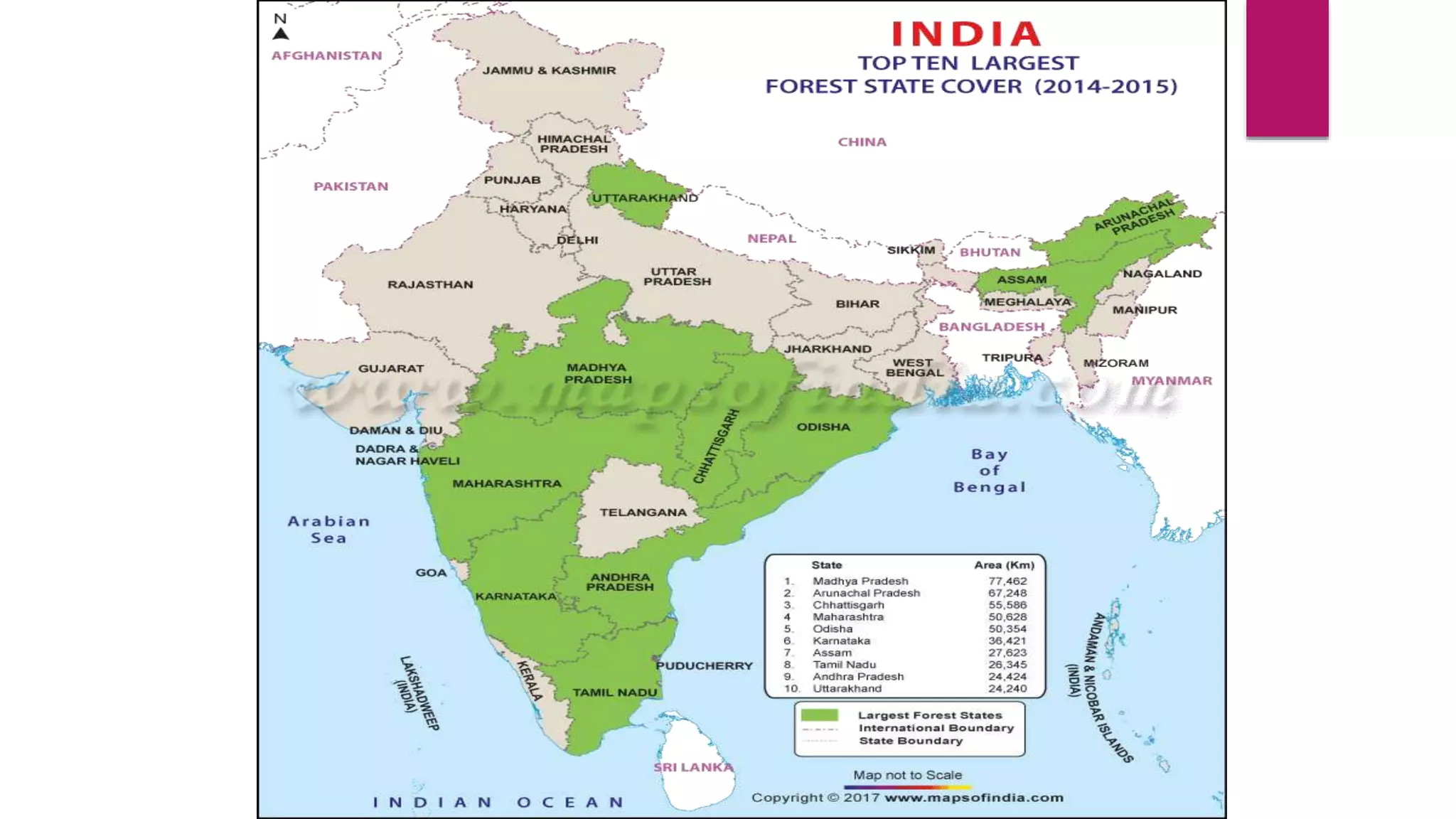
This document discusses deforestation, including its causes, impacts, and potential solutions. It notes that deforestation occurs when large areas of forest are cleared for non-forest uses such as agriculture, ranching, urban development, and mining. The main drivers of deforestation are agricultural expansion, logging for wood and fuel, urbanization and infrastructure development, and mining. Deforestation leads to environmental impacts like increased soil erosion, disrupted water cycles, reduced biodiversity, and climate change. Potential solutions discussed include corporations implementing anti-deforestation policies, governments enacting ambitious forest protection policies and supporting anti-deforestation organizations, and individuals reducing lifestyle contributions to deforestation.