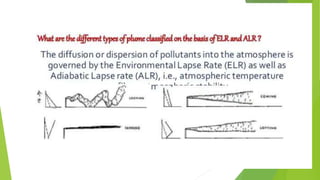
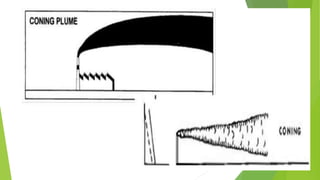
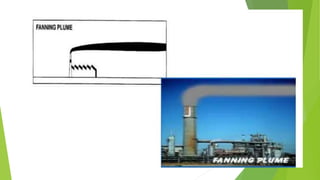
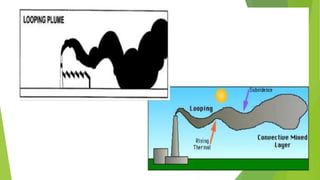
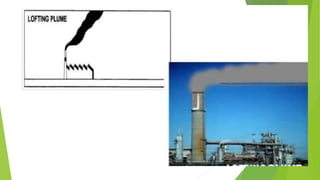
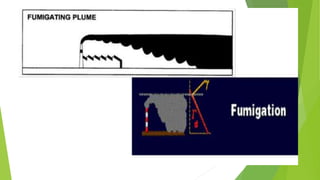
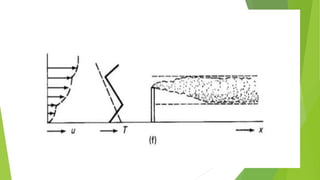
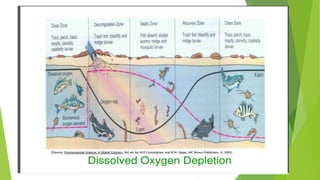
The document discusses limitations of the dissolved oxygen (DO) sag equation model for streams. It lists four main limitations:
1) The model assumes steady state conditions while streams have varying flows, velocities, geometries and temperatures over time.
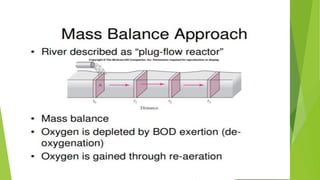
2) The model assumes plug flow while natural stream geometries are irregular with wide and narrow areas.
3) The model does not include the important role of algae in producing oxygen, which varies with sunlight.
4) The model only considers oxygen demand from suspended organisms, not from bottom-dwelling benthic organisms which account for significant oxygen demand, especially when organic material settles out.