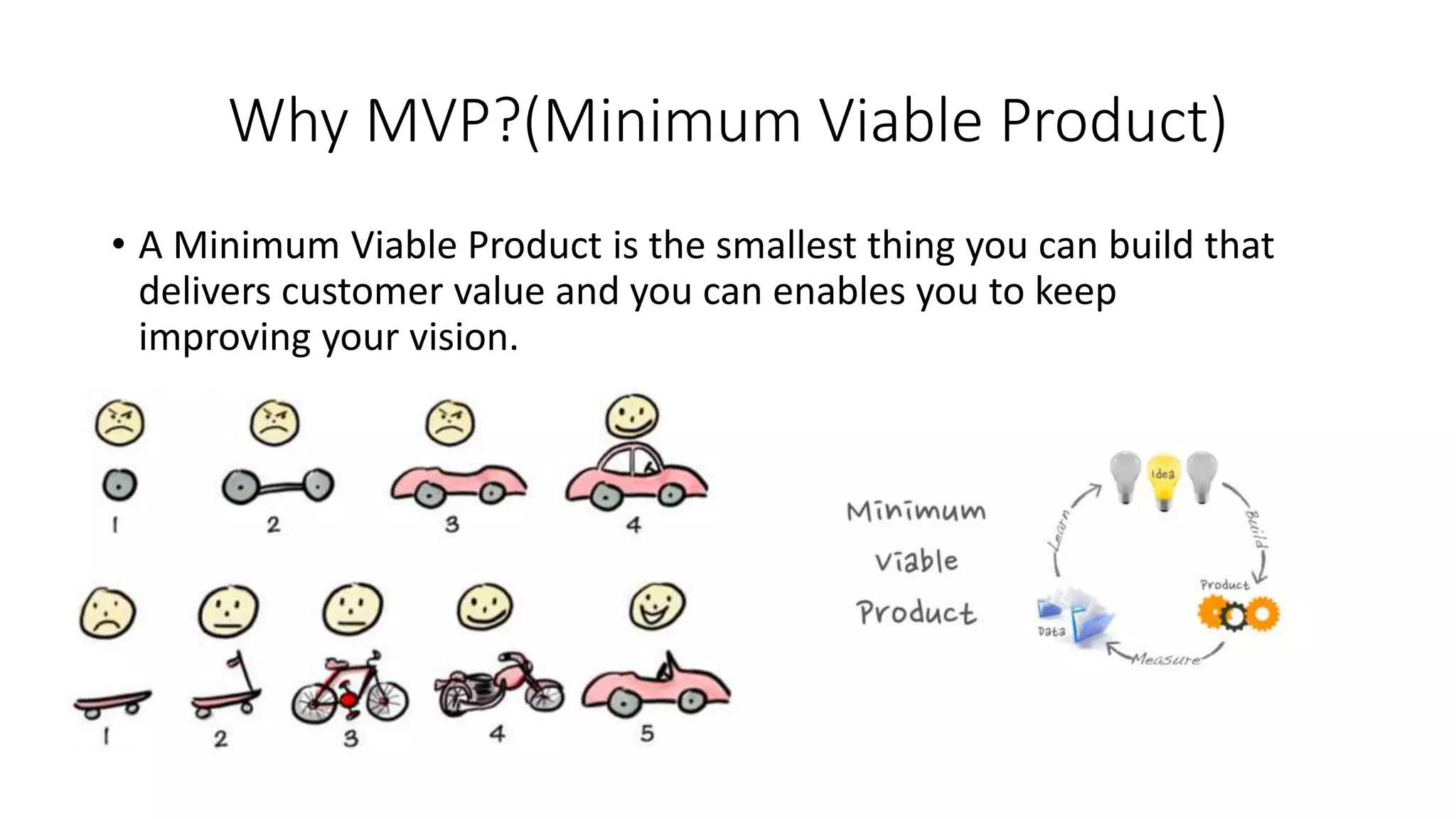
The document discusses entrepreneurship and provides information on why some people become entrepreneurs, challenges entrepreneurs may face, and key aspects of starting a business. It notes that while not everyone is suited to entrepreneurship due to risks like uncertainty, long hours, and potential failure, entrepreneurship allows one to pursue opportunities regardless of current resources. Successful entrepreneurs develop business models, acquire necessary human and other resources, and are responsible for business success or failure. The document also outlines common business model components like value propositions, key resources, customer segments, revenue streams, and provides examples of famous entrepreneurs.