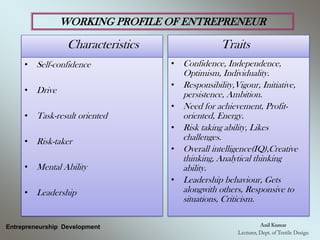
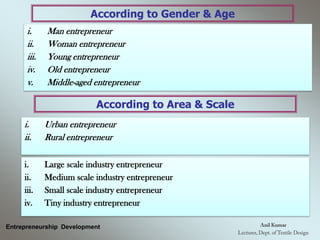
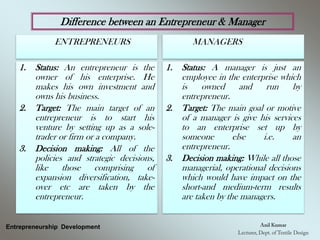
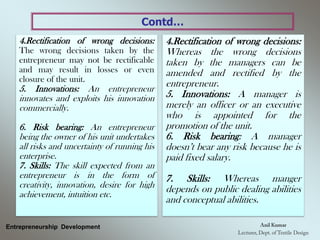
The document outlines the fundamental concepts and characteristics of entrepreneurship, detailing the profiles and distinctions between entrepreneurs and intrapreneurs. It classifies entrepreneurs based on various criteria, such as business type, technology, development stage, capital ownership, and gender/age, while also describing the essential functions and skills required for successful entrepreneurship. Furthermore, it emphasizes the differences between entrepreneurs and managers, highlighting their roles, decision-making processes, and risk-bearing responsibilities.