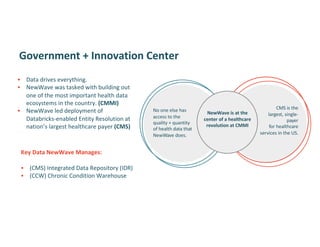
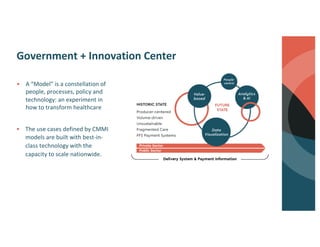
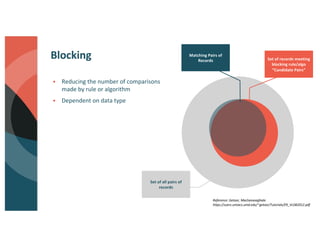
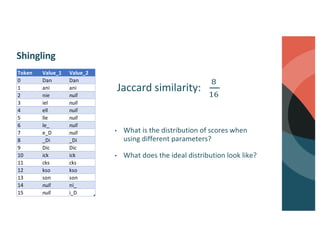
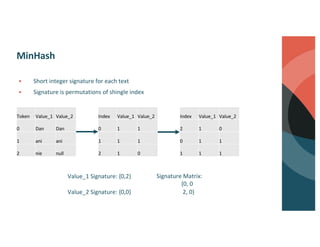
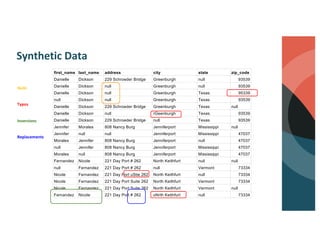
Brett Luskin presented on entity resolution using patient records at the CMS Innovation Center (CMMI). NewWave was tasked with building out one of the largest health data ecosystems in the country at CMMI. NewWave led the deployment of an entity resolution system using Databricks to link records across CMS's Integrated Data Repository and Chronic Condition Warehouse. Entity resolution involves tasks like deduplication, record linking, and canonicalization to determine if records refer to the same real-world entity. It presents significant scaling challenges due to the enormous number of possible record pairs to compare in large datasets. NewWave's system employs techniques like blocking, minhash locality-sensitive hashing, scoring, and graph-based clustering