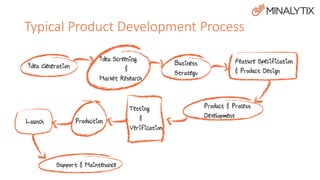
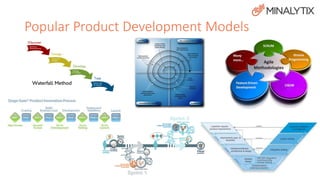
The document presents an overview of a product development session led by Dave Peres and Rob Patterson, focusing on the typical product development process and their experiences in software development for the mining industry. Key stages discussed include idea generation, product design, production, and maintenance, highlighting the importance of research, documentation, and customer collaboration. The session concludes with lessons learned from their experiences, emphasizing the significance of planning and structured processes to ensure successful product outcomes.