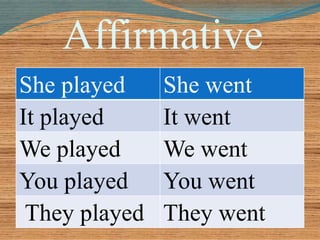
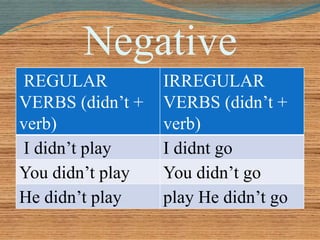
The document discusses the use of the past simple tense in English to talk about completed actions in the past. It provides rules for forming the past simple of regular and irregular verbs in affirmative, negative and interrogative sentences. Examples are given to illustrate using the past simple to talk about a single completed action, a series of actions, durations in the past, past habits, past facts and the importance of when-clauses. Adverb placement and active/passive voice are also briefly covered.