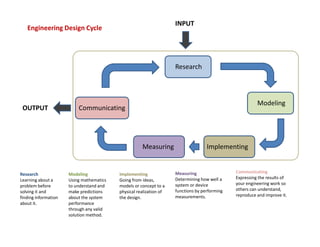
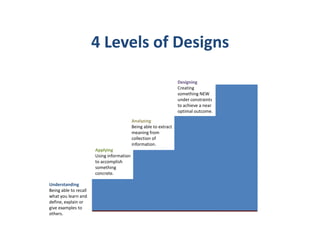
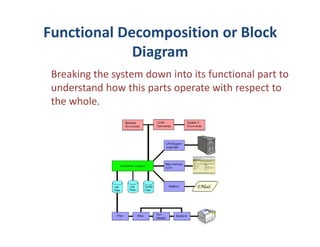
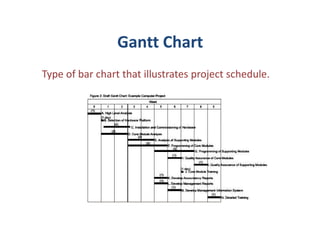
Engineering design is a process that applies science and math principles to optimally convert resources to meet a stated objective. It involves research, modeling, implementing, measuring, and communicating. The engineering design cycle includes input, research, modeling, implementing, measuring, and communicating output. Tools used in engineering design include functional decomposition or block diagrams to break down a system, Gantt charts for project scheduling, and a project manager to balance cost, schedule, and performance. Defining and specifying a project outlines precisely what is to be done under the constraints to achieve an optimal outcome.