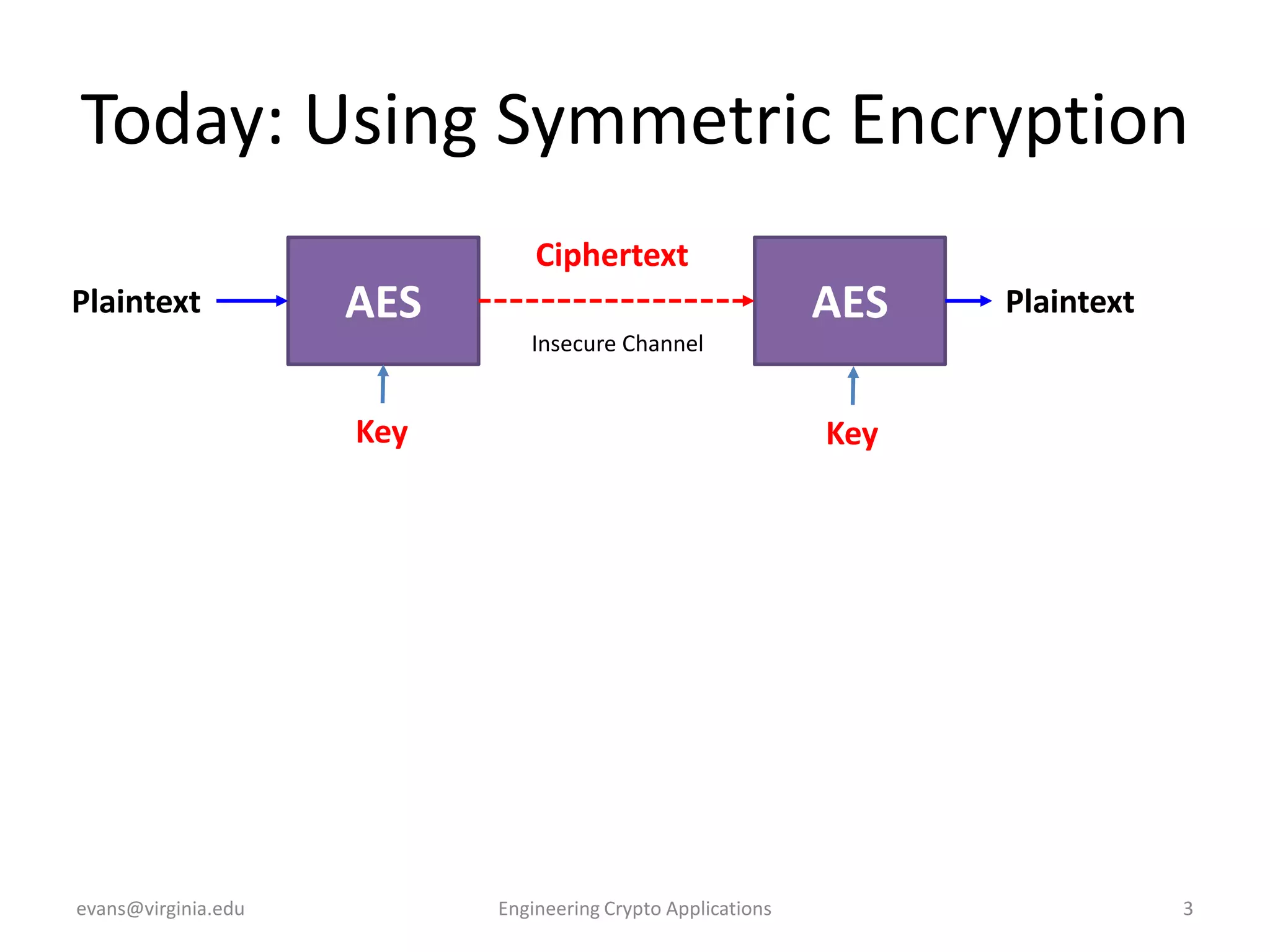
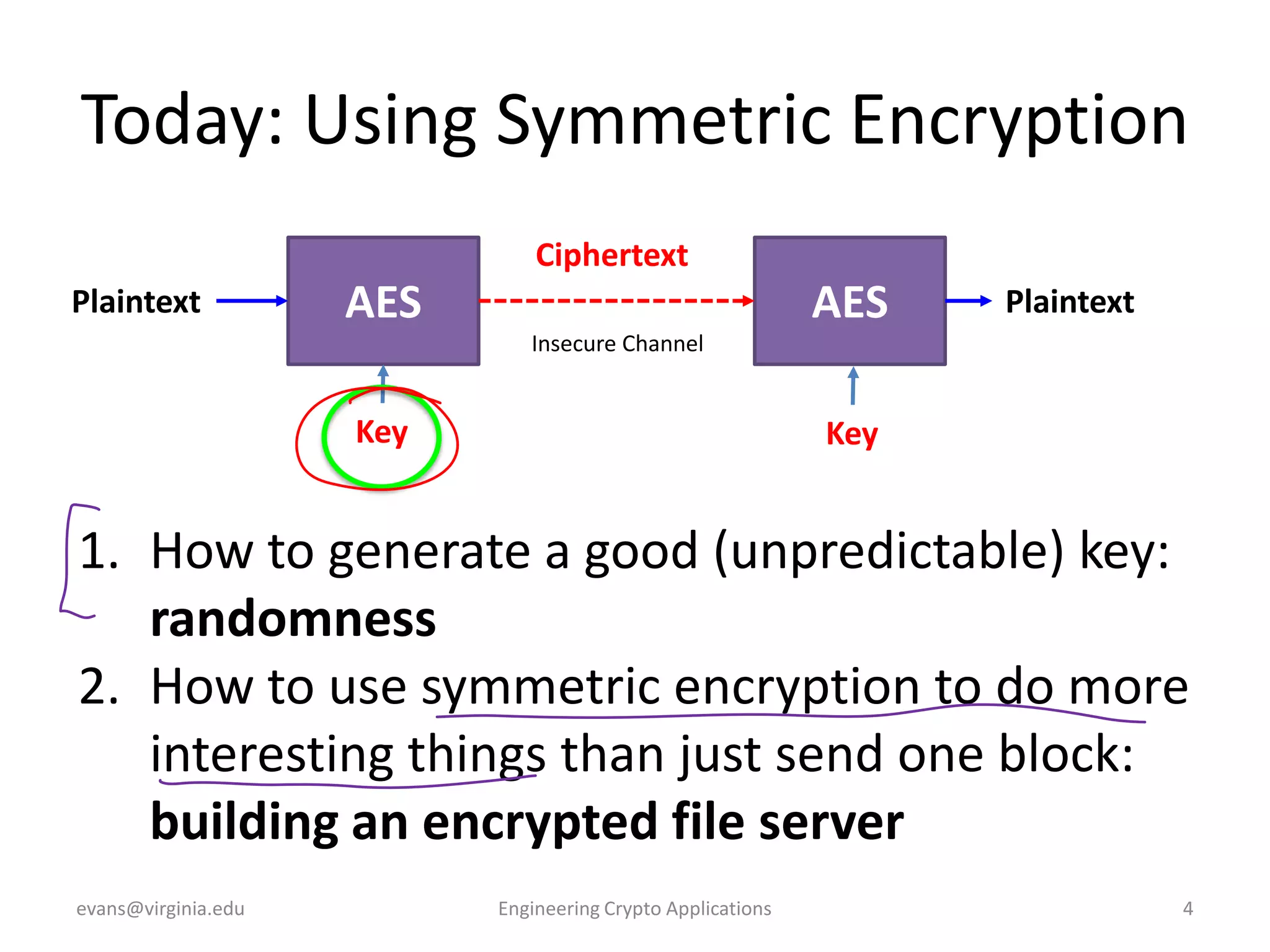
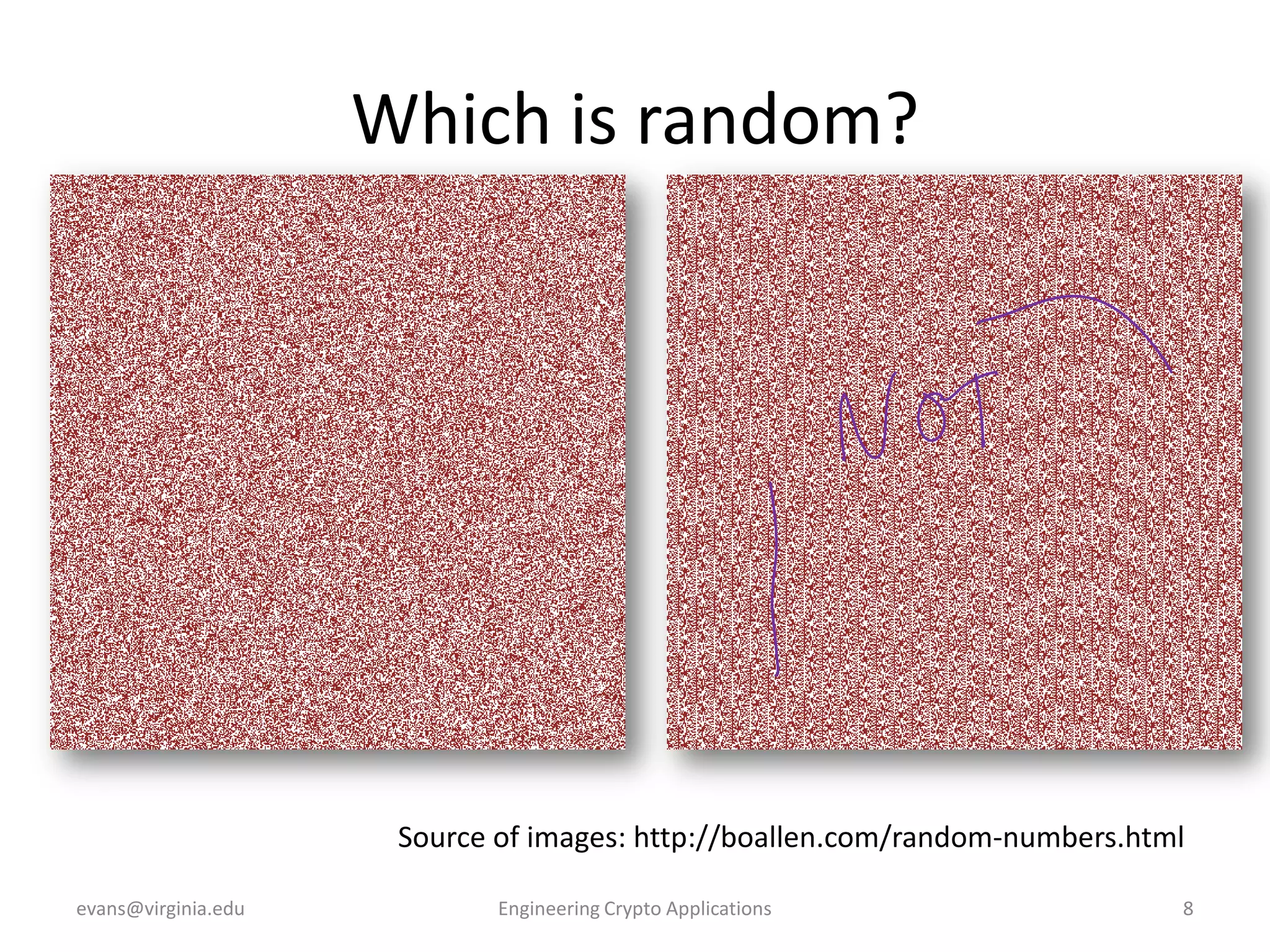
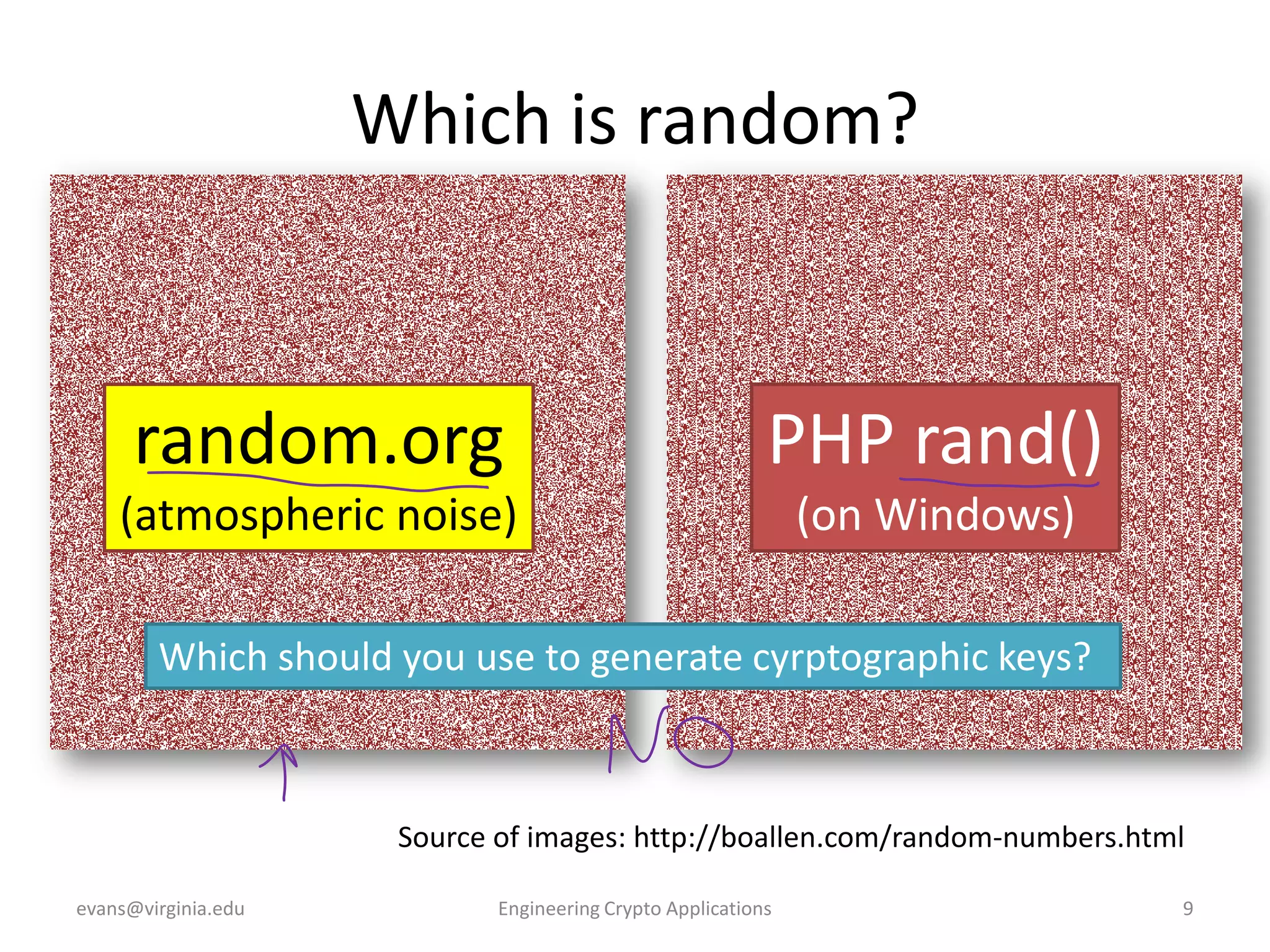
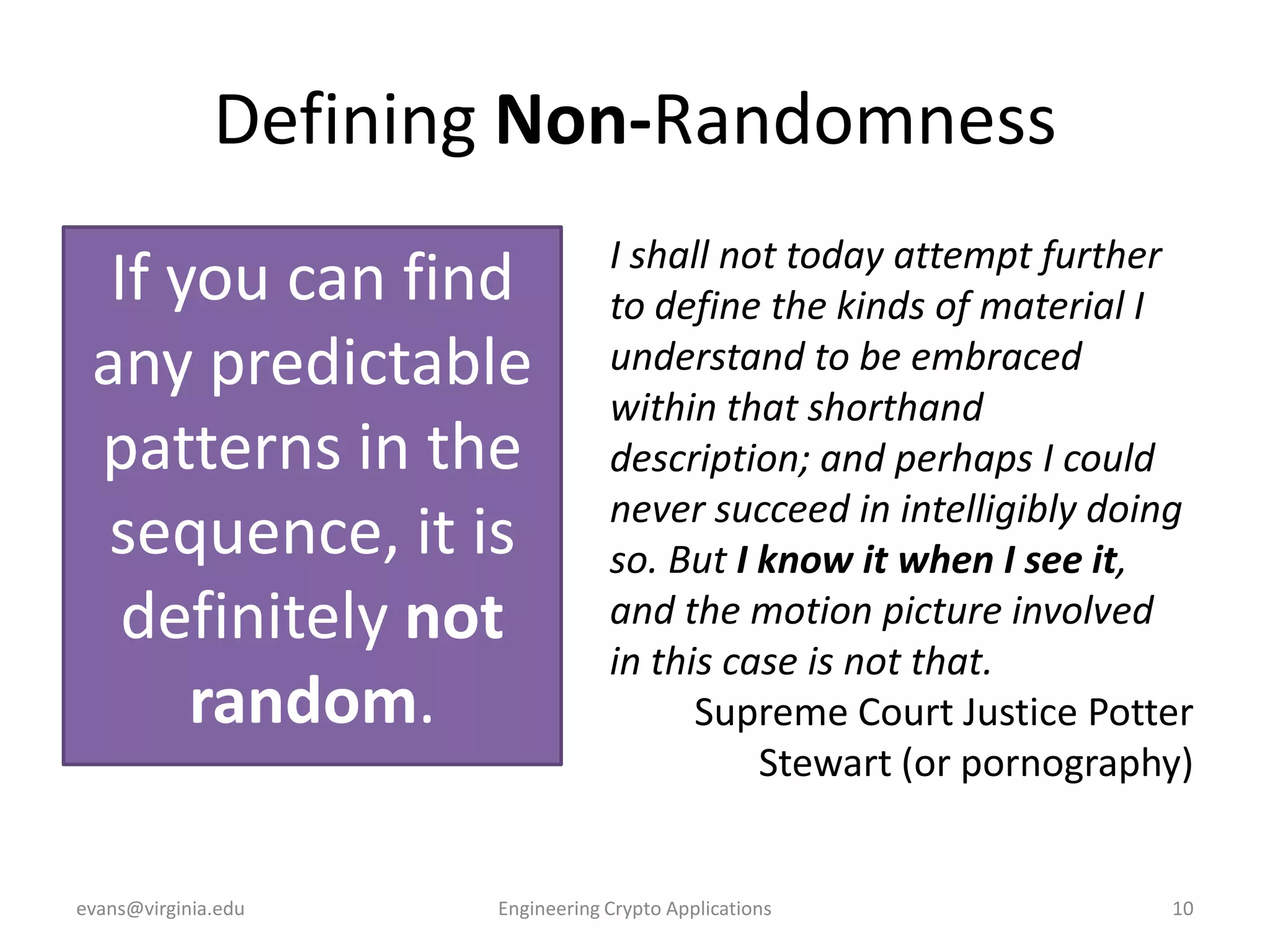
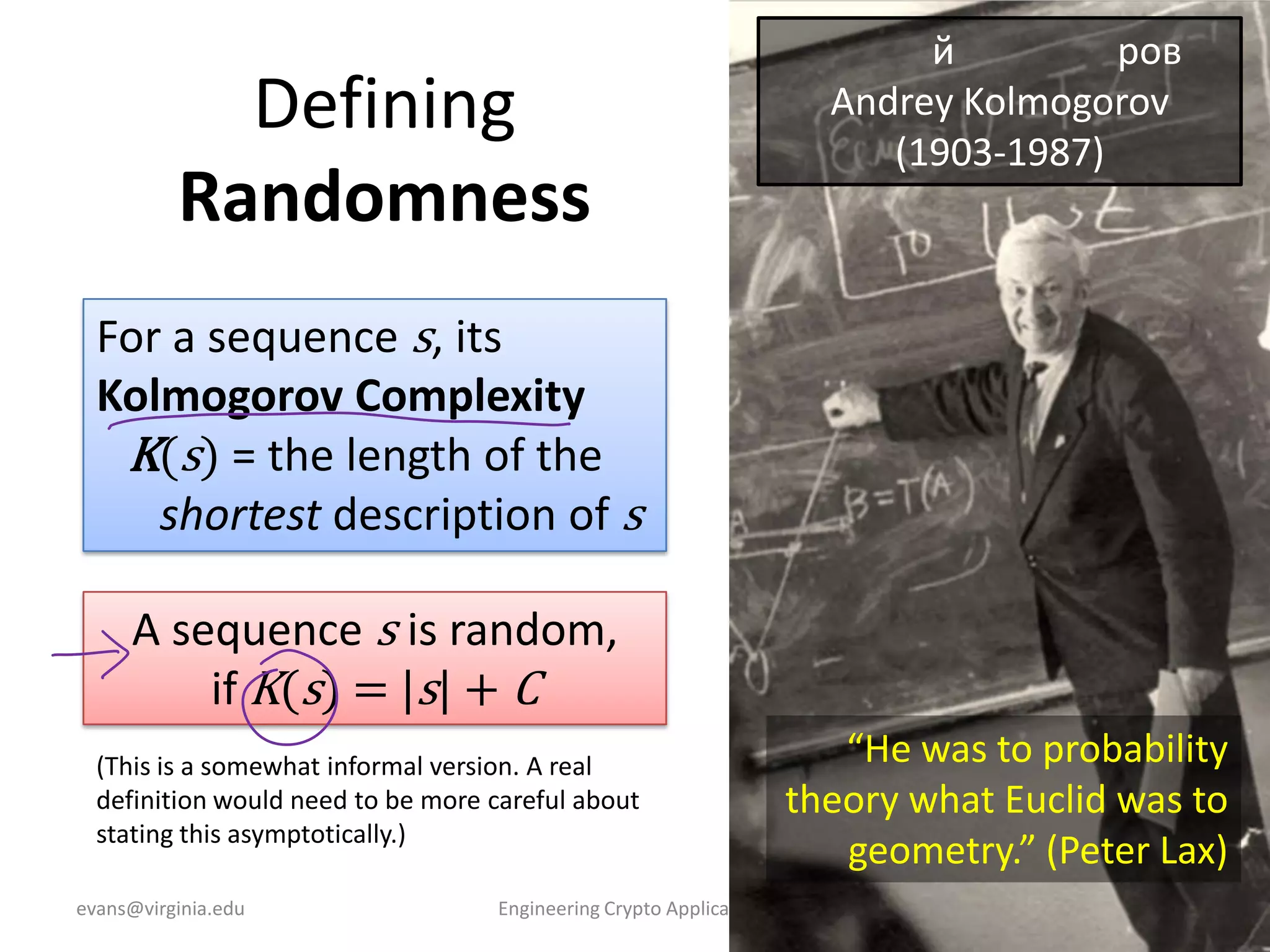
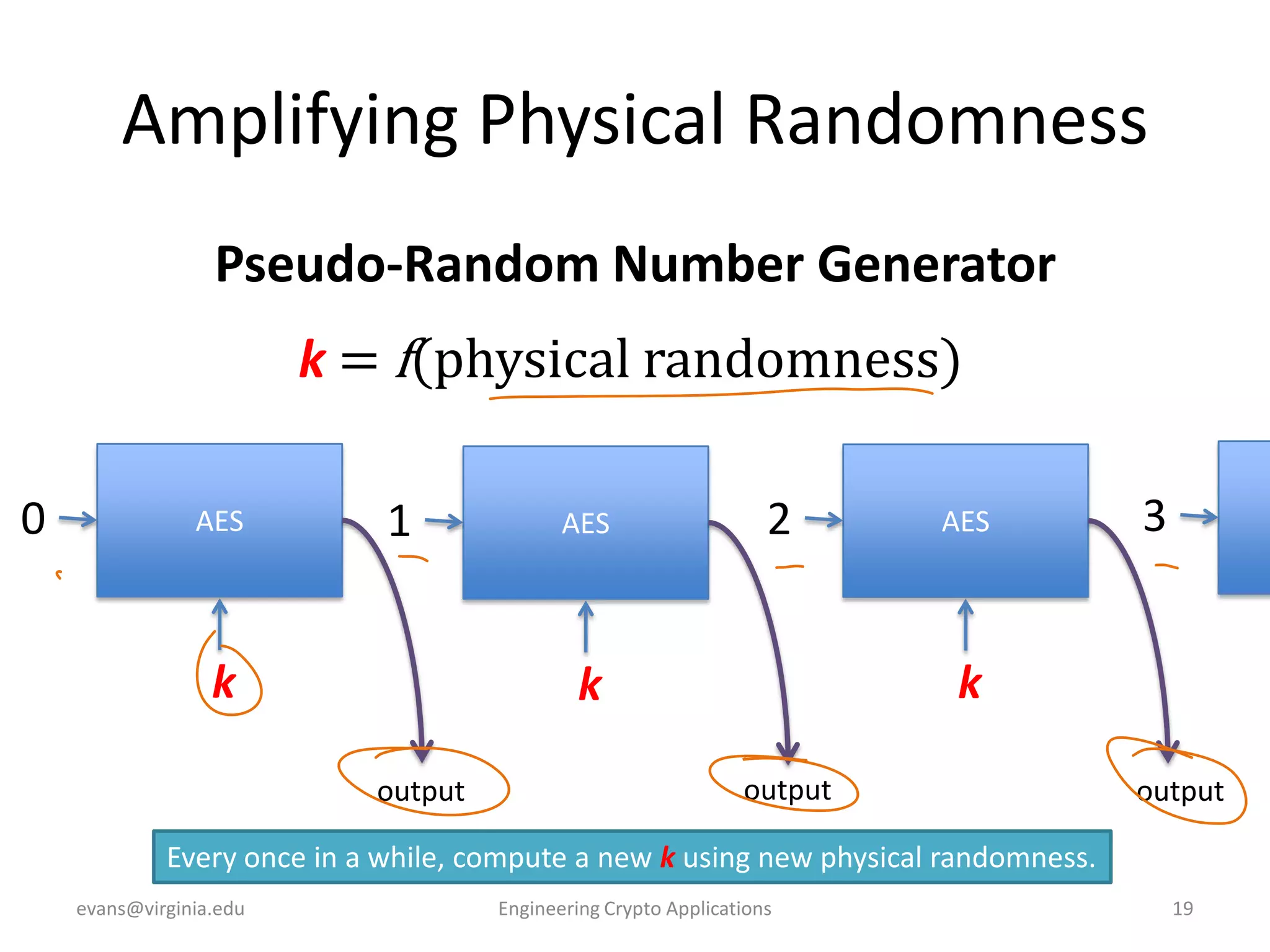
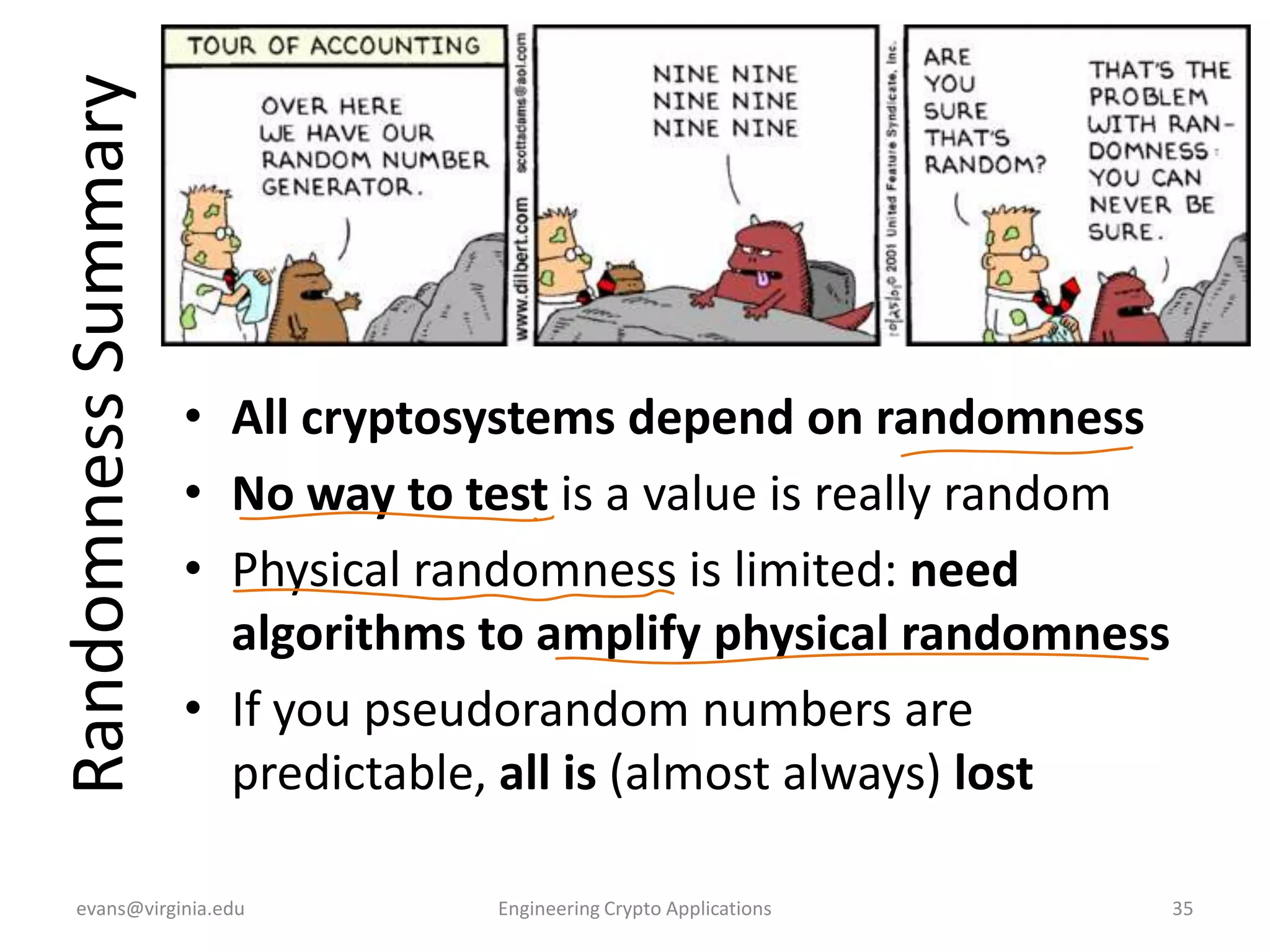
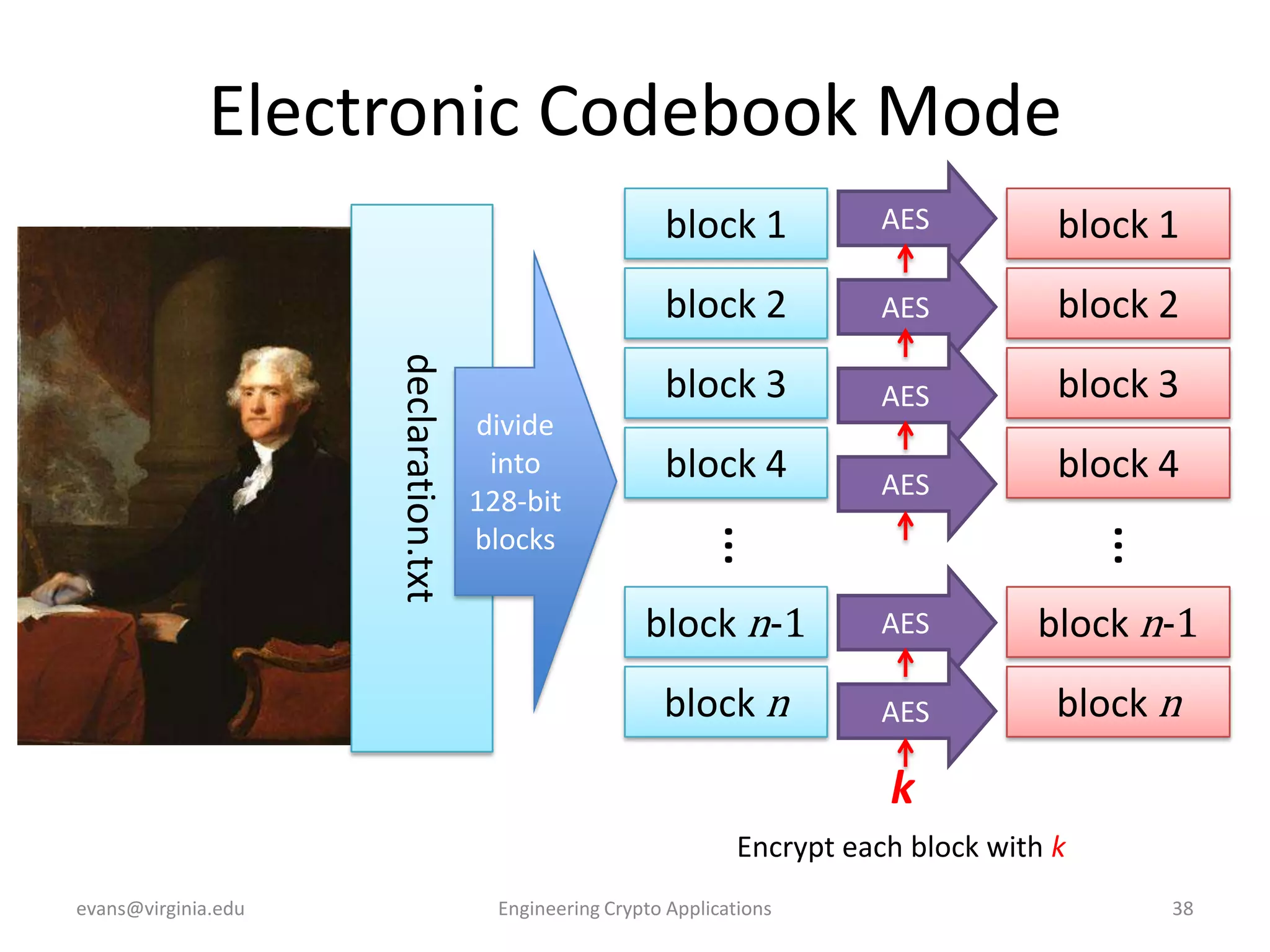
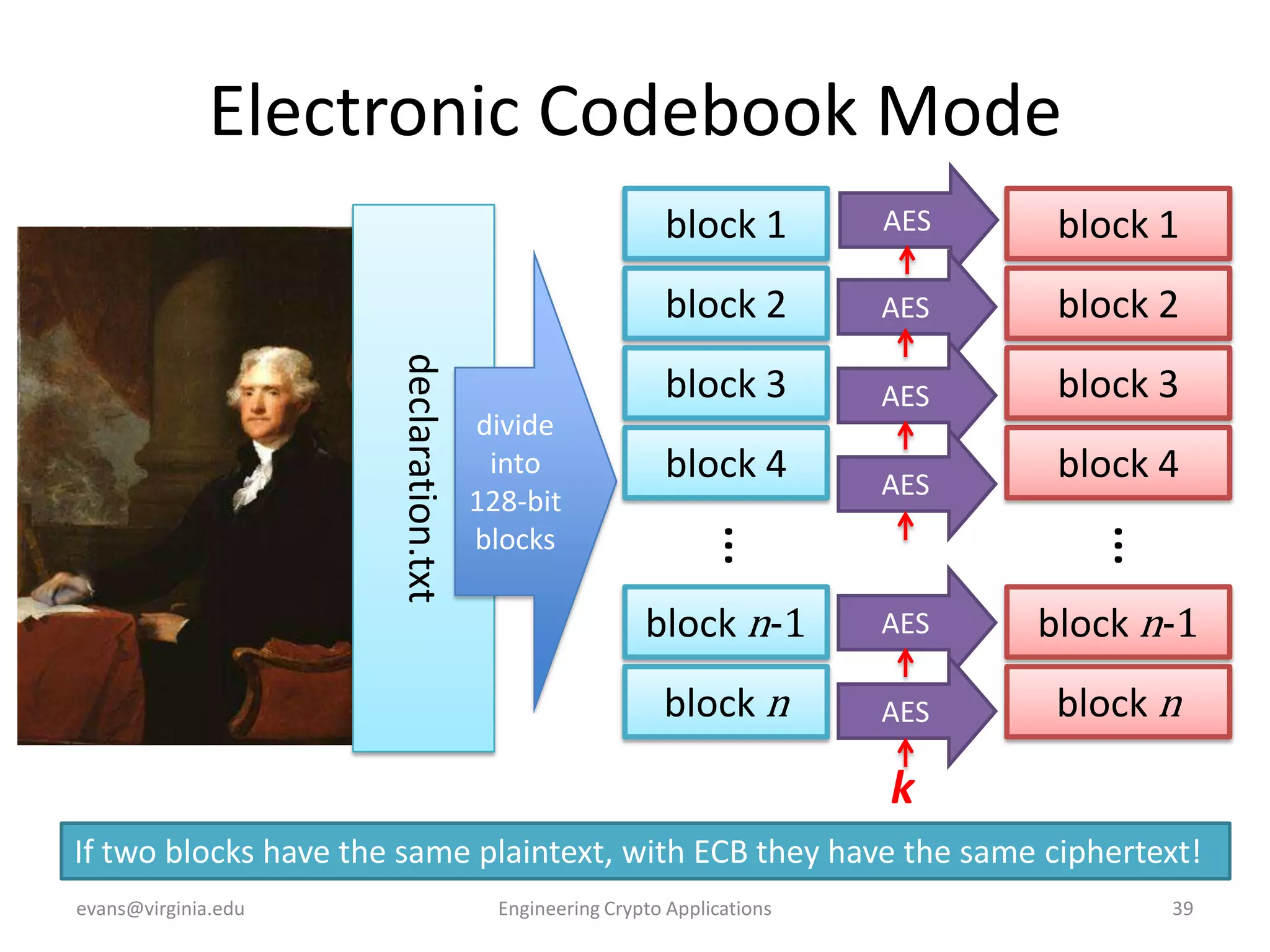
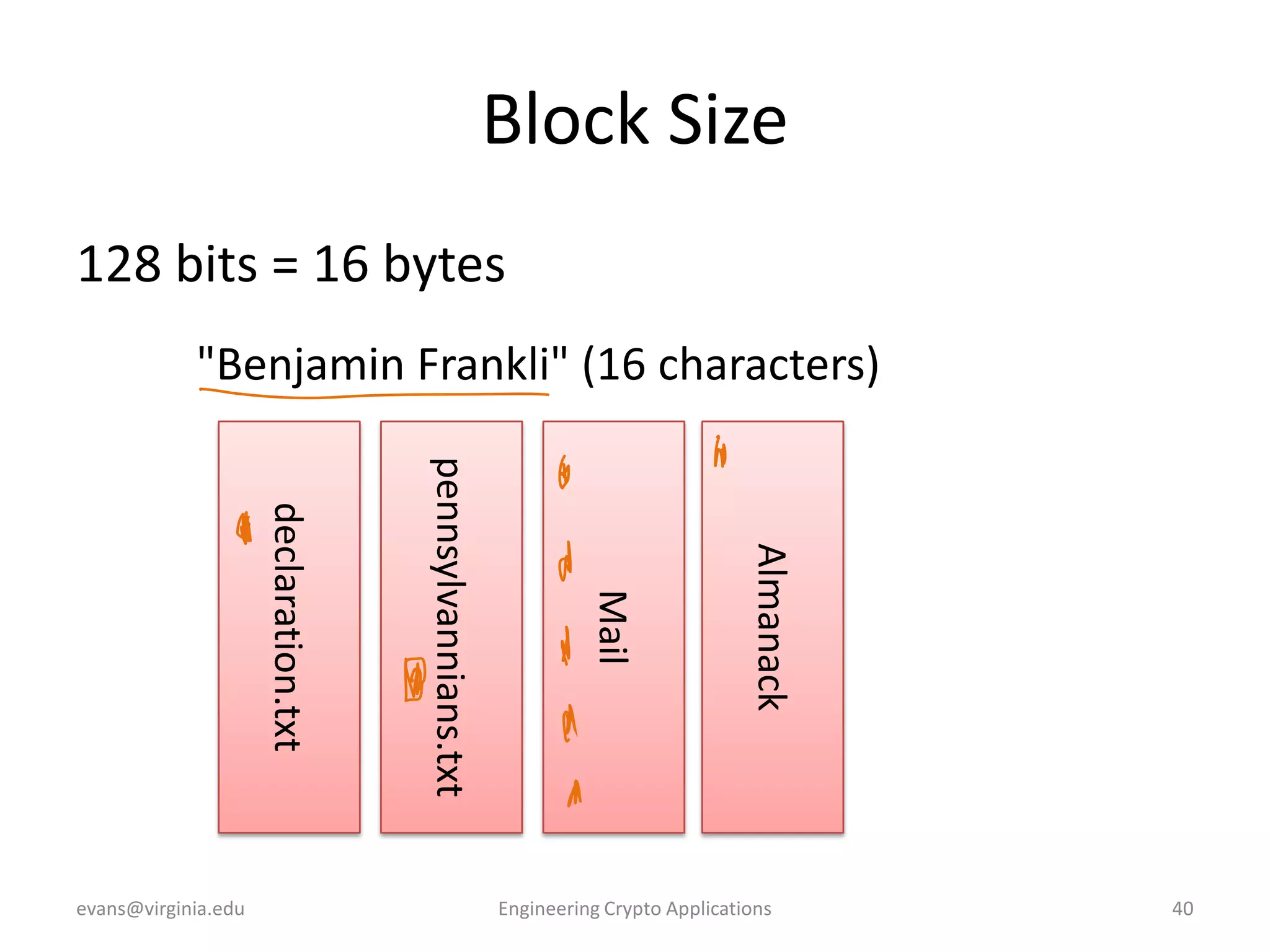
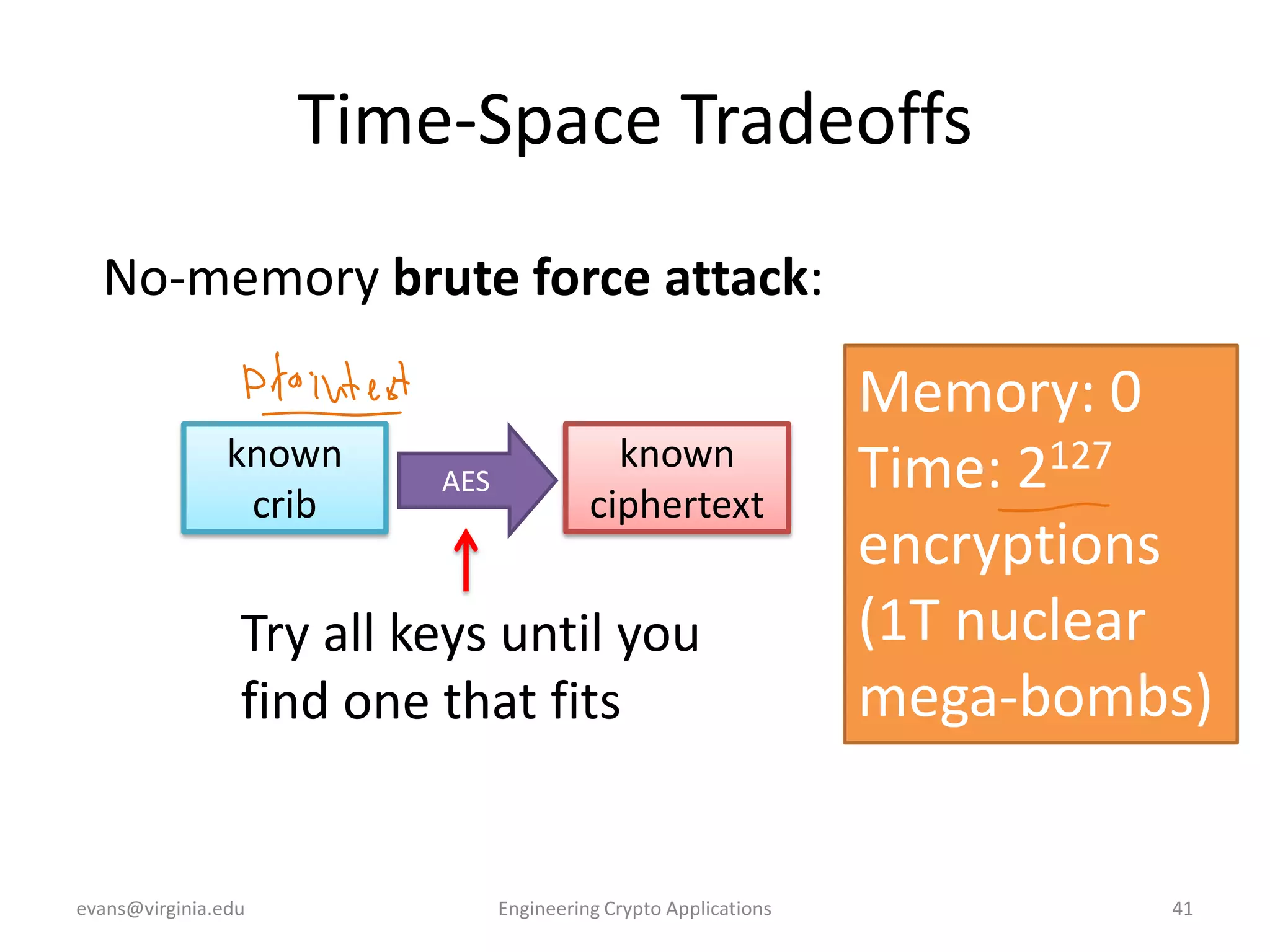
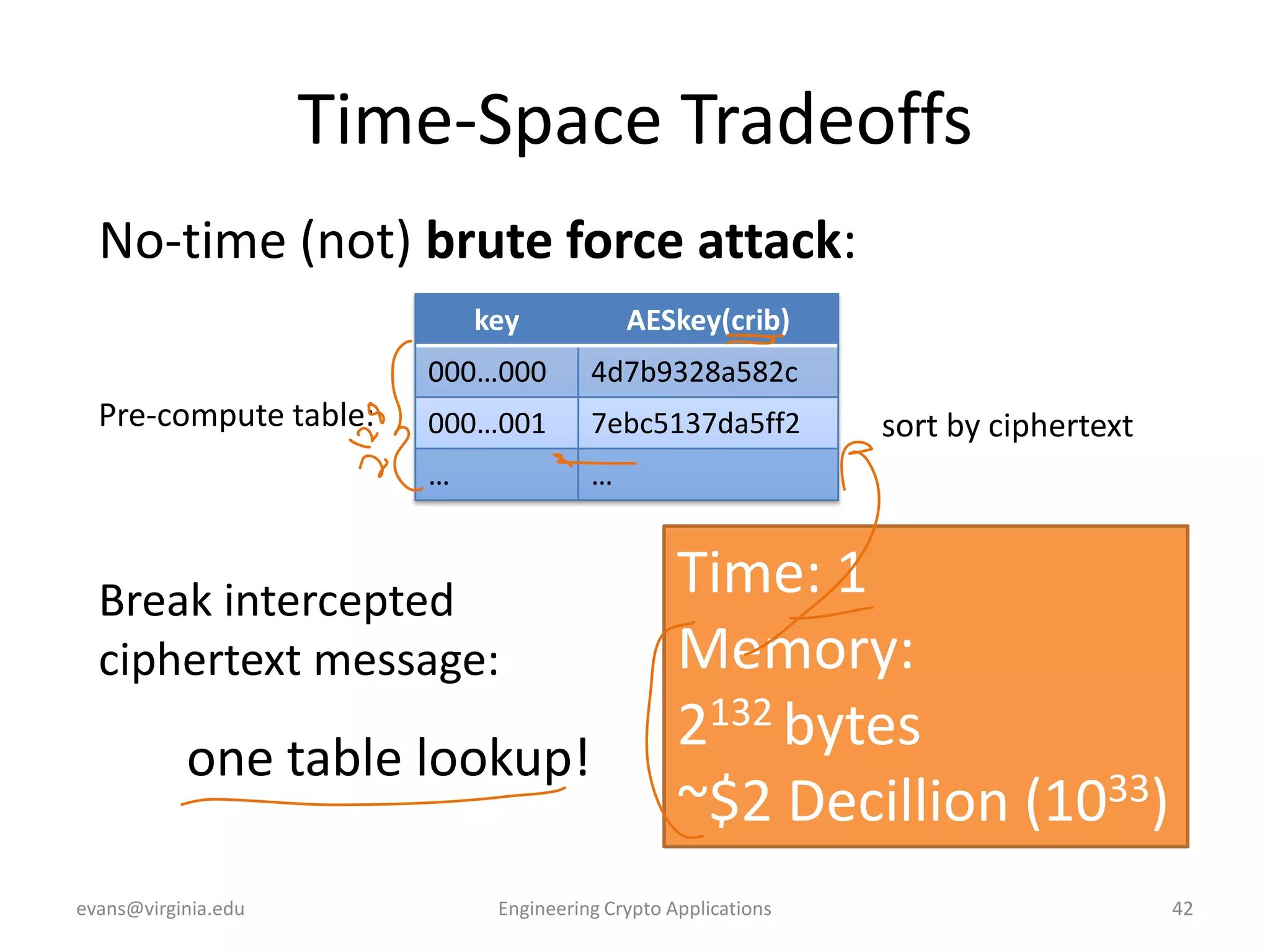
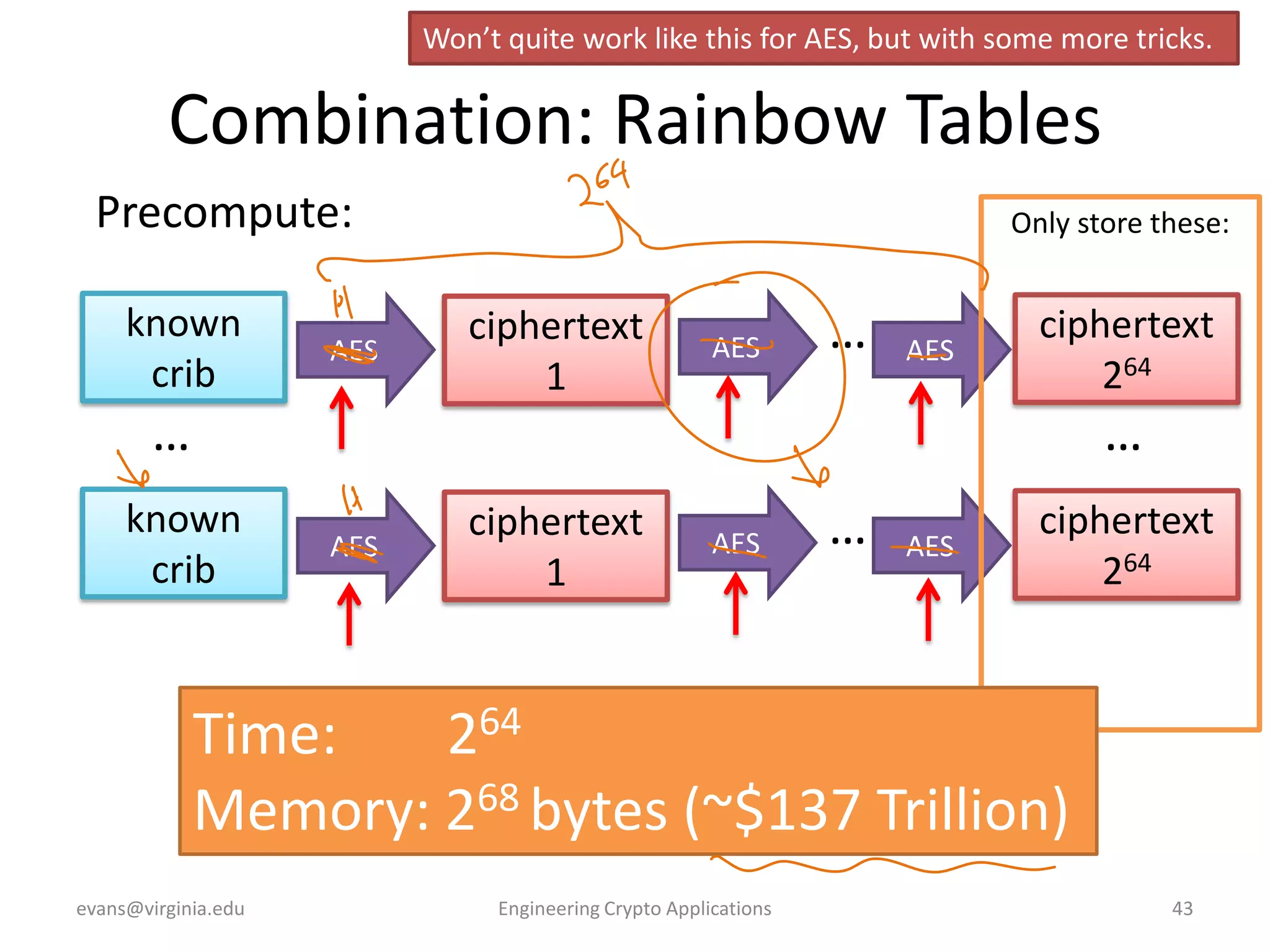
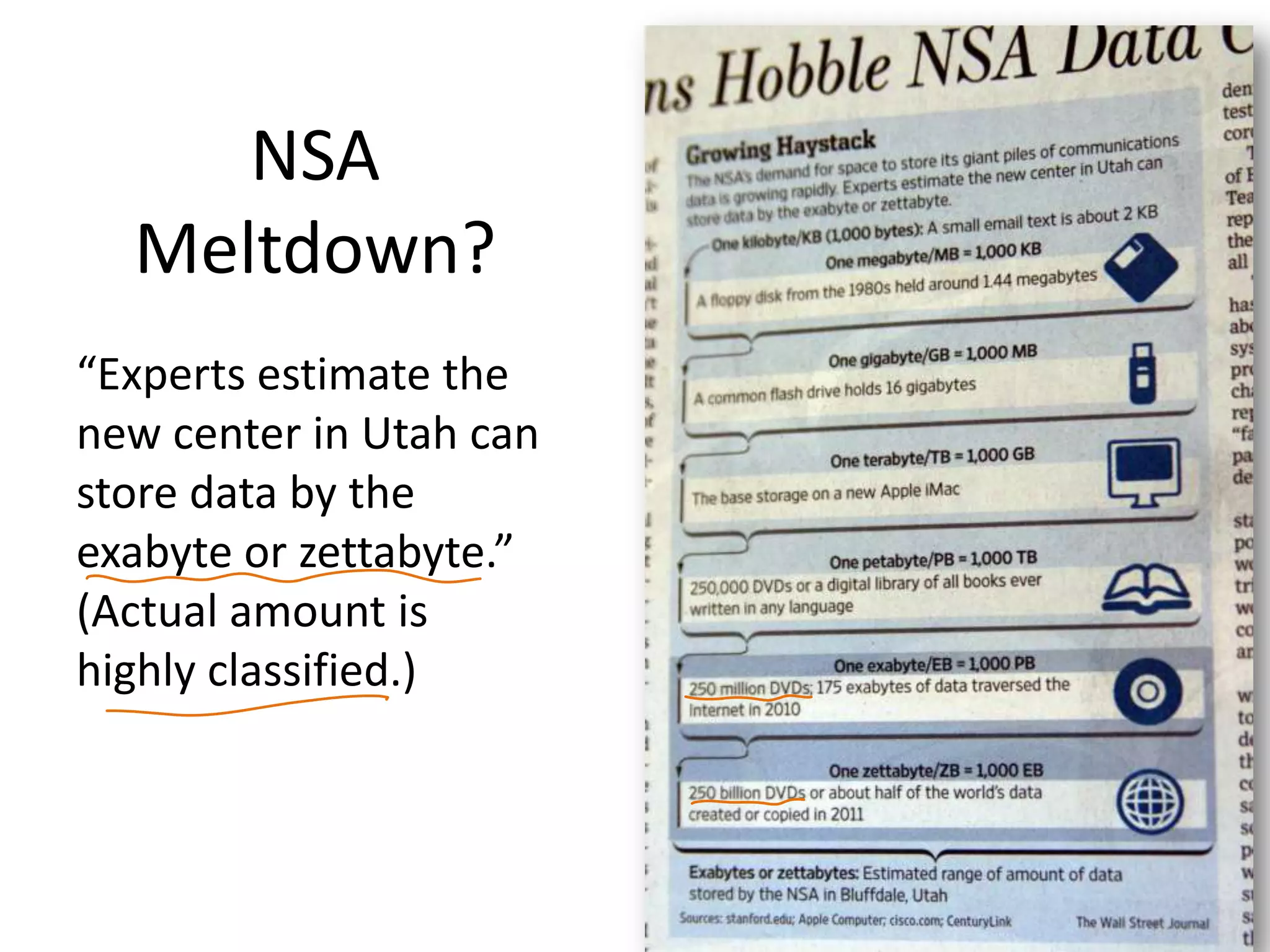
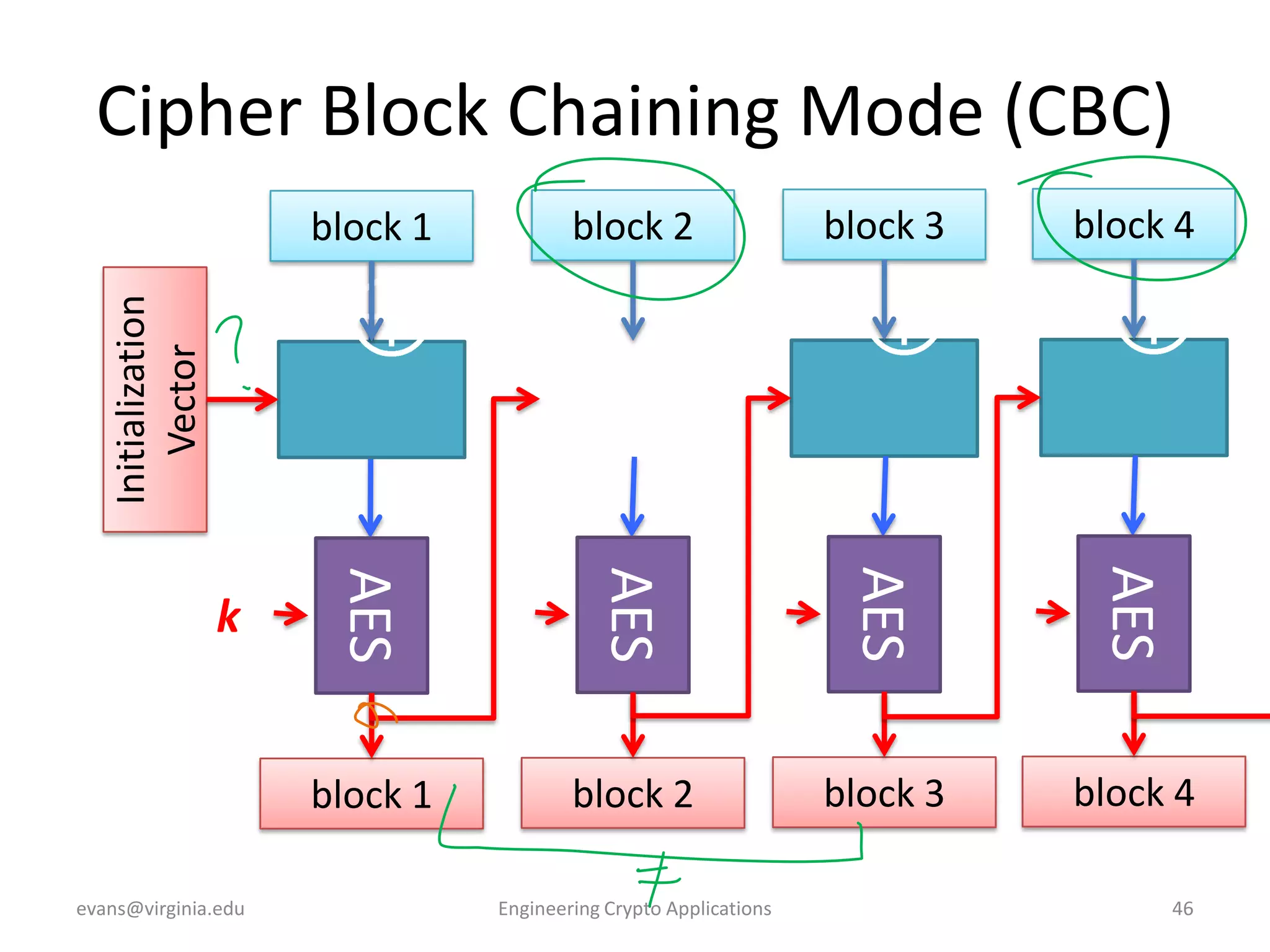
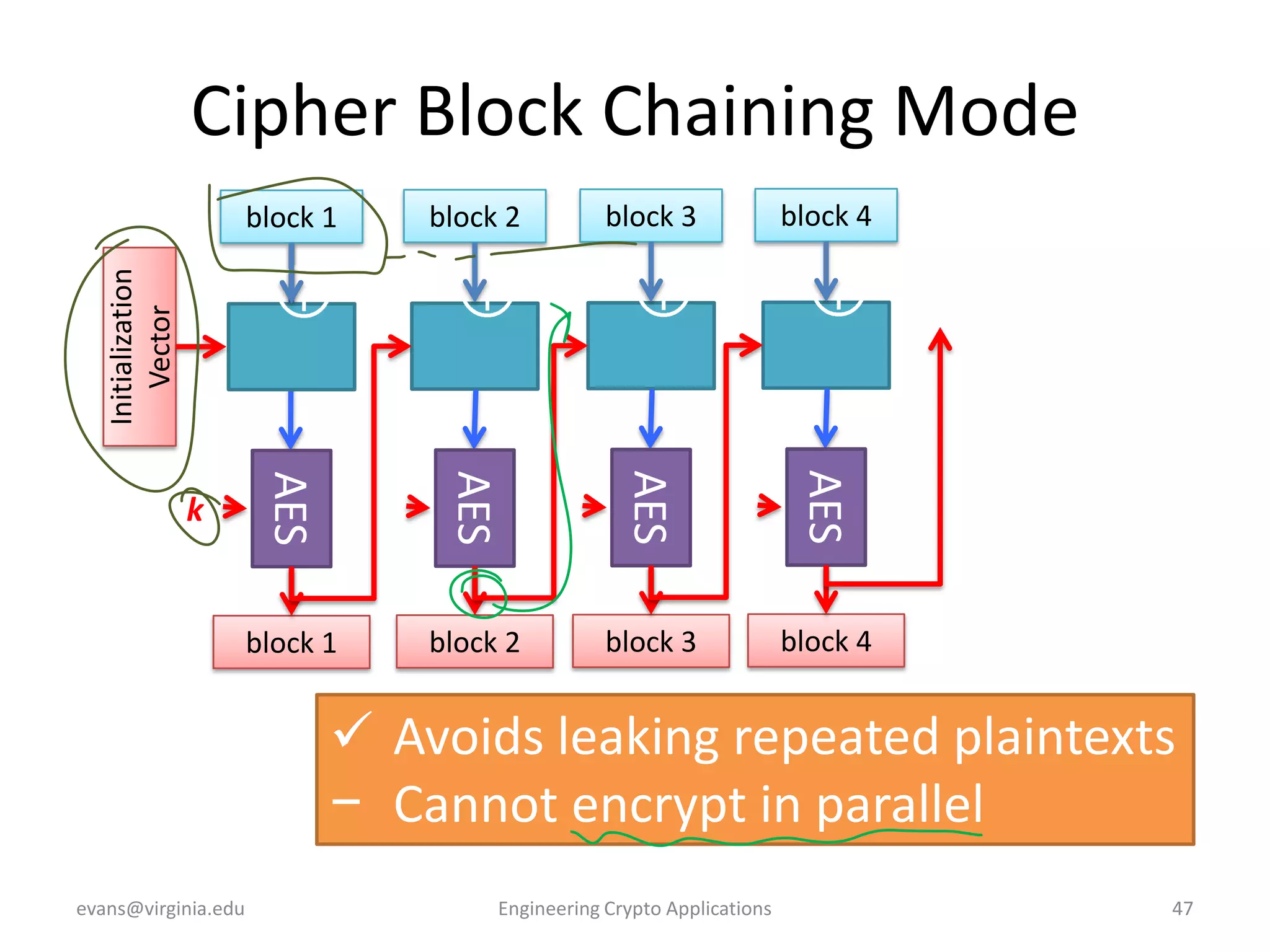
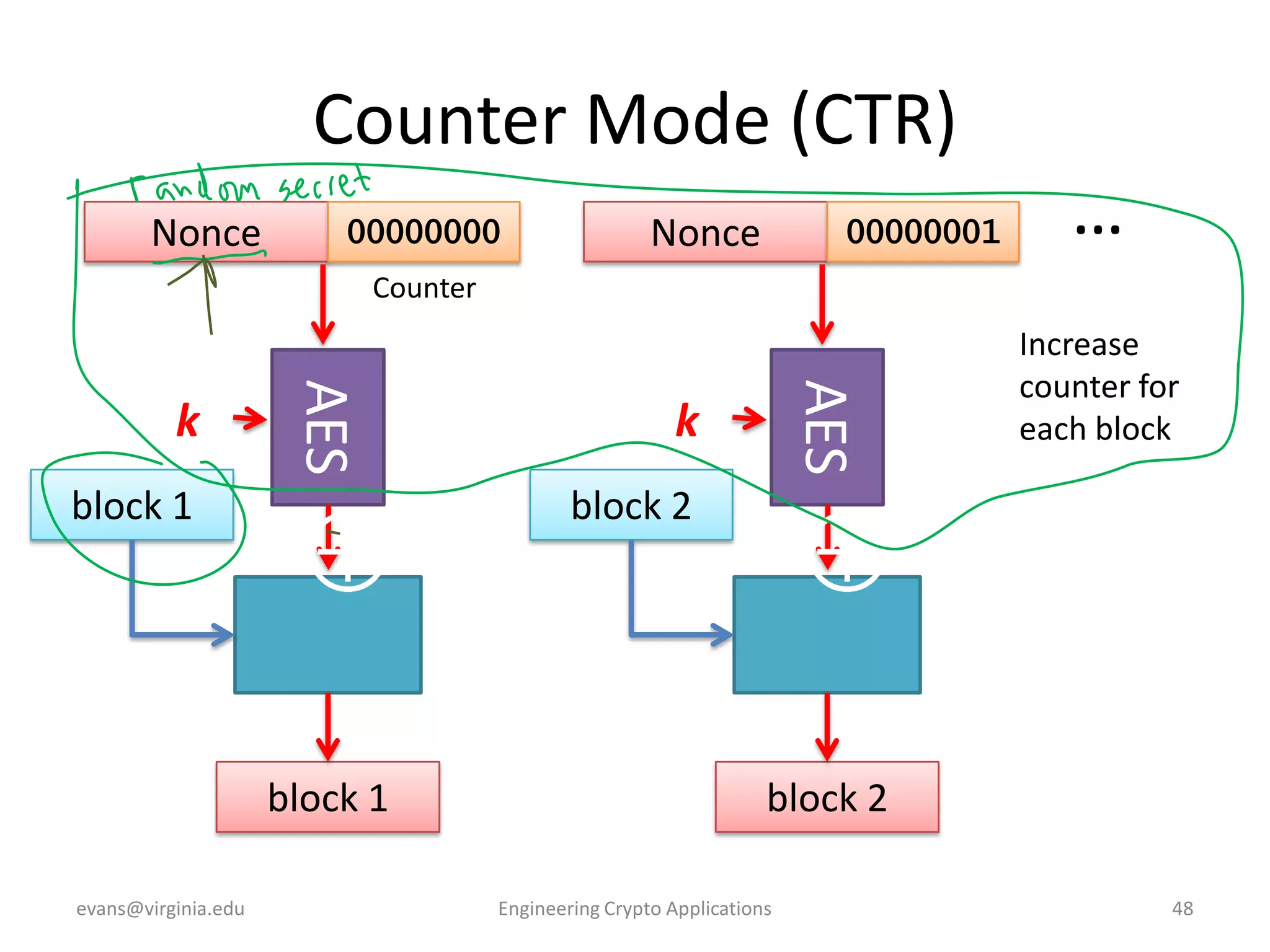
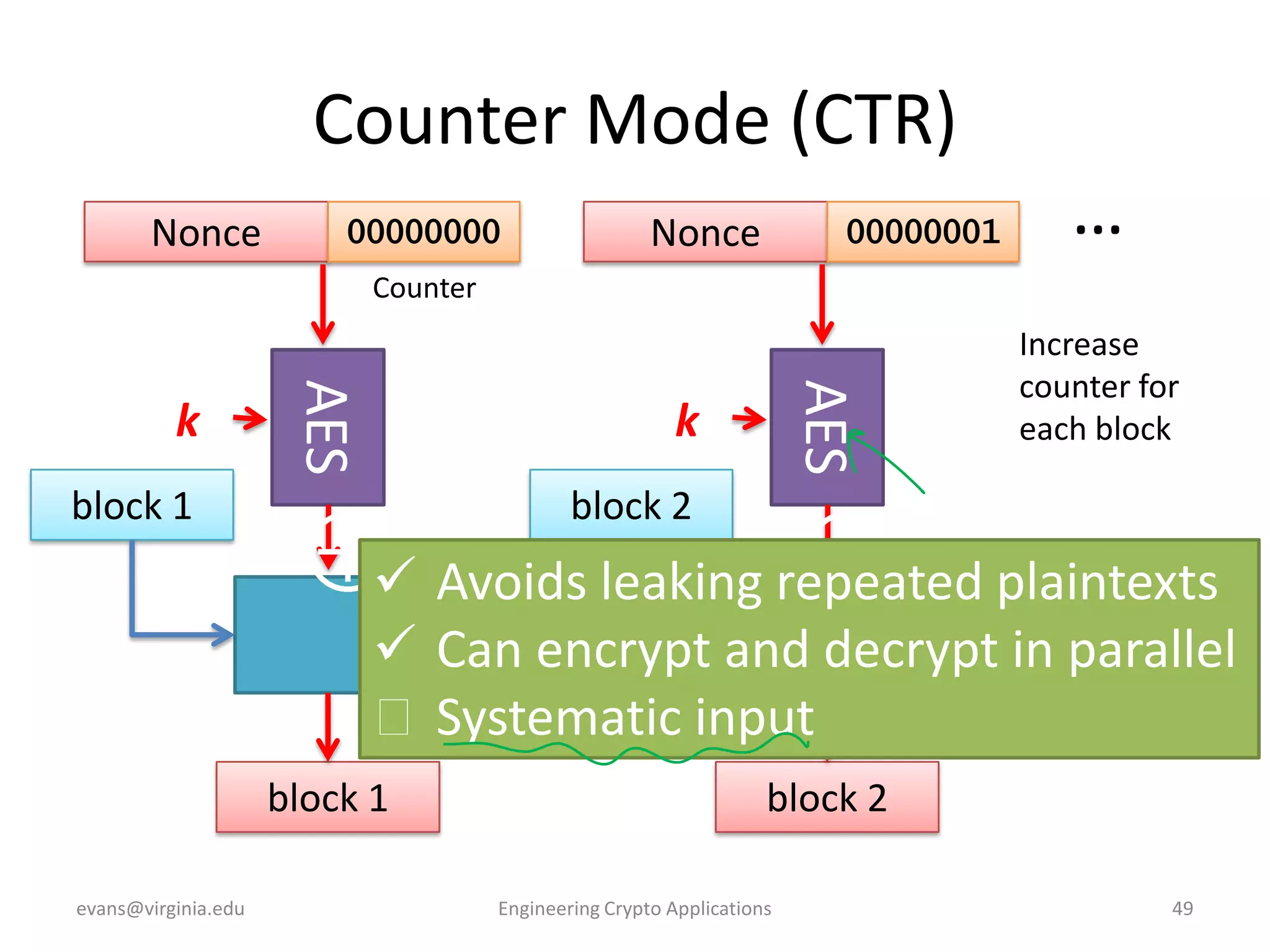
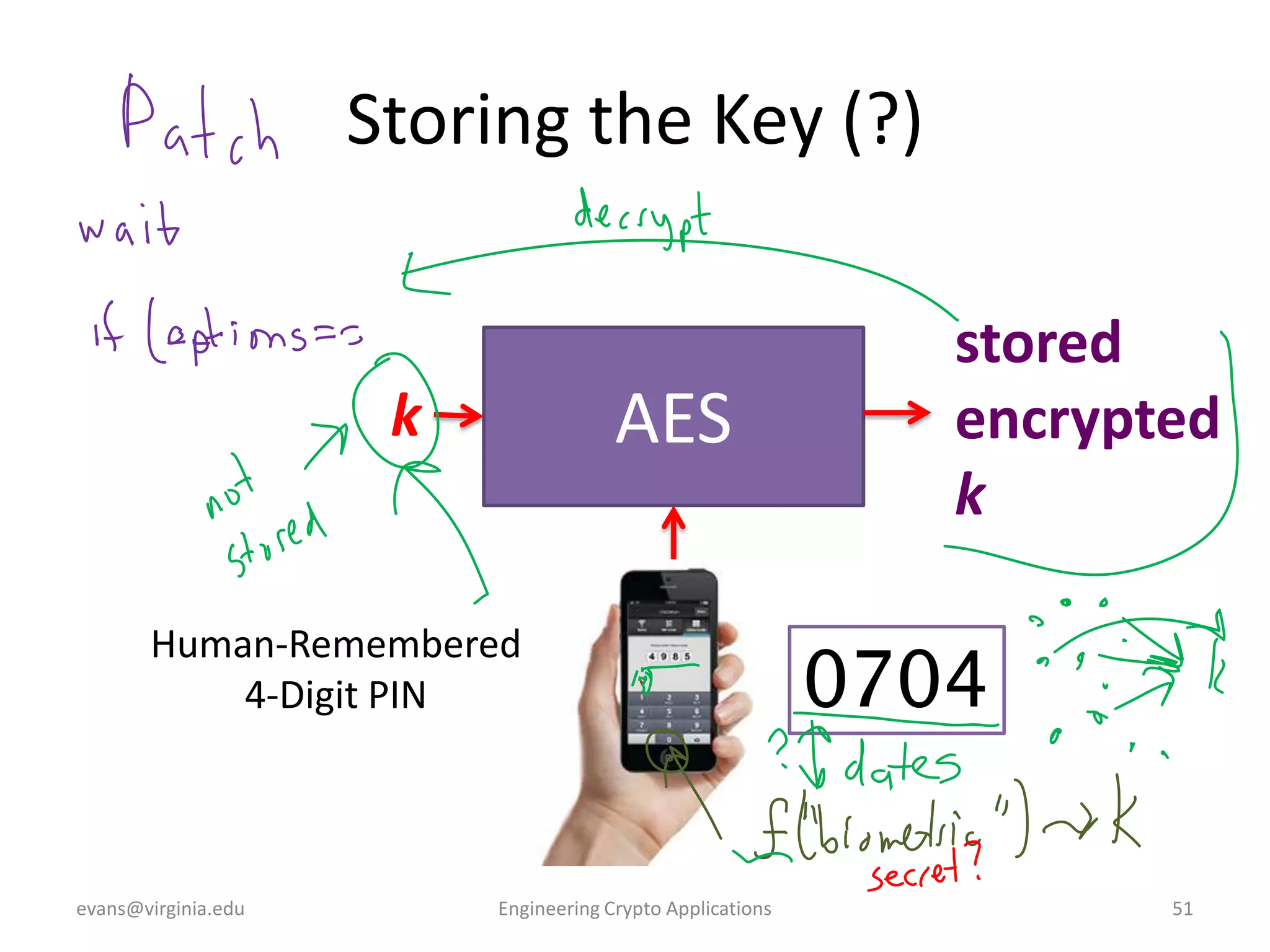
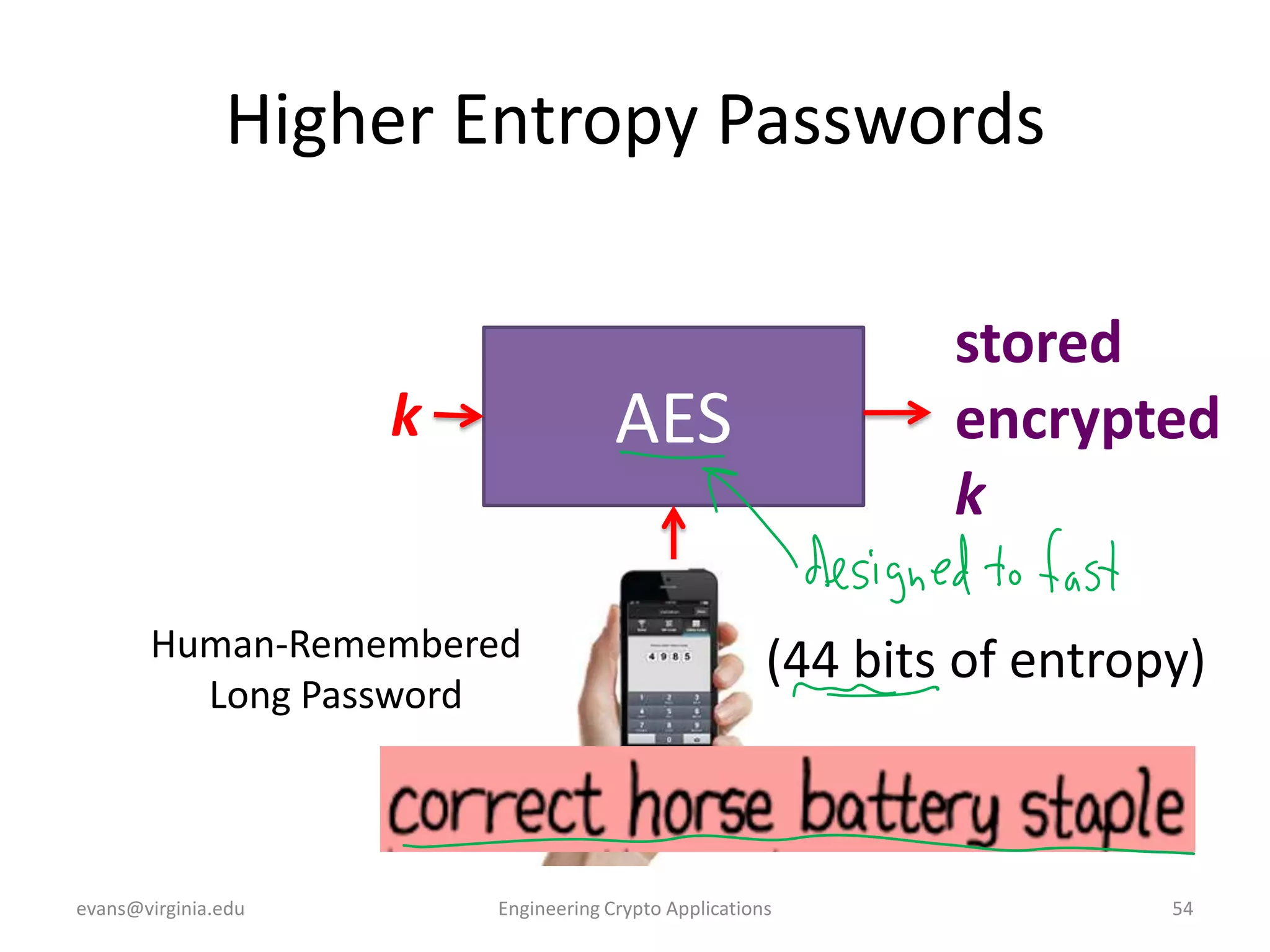
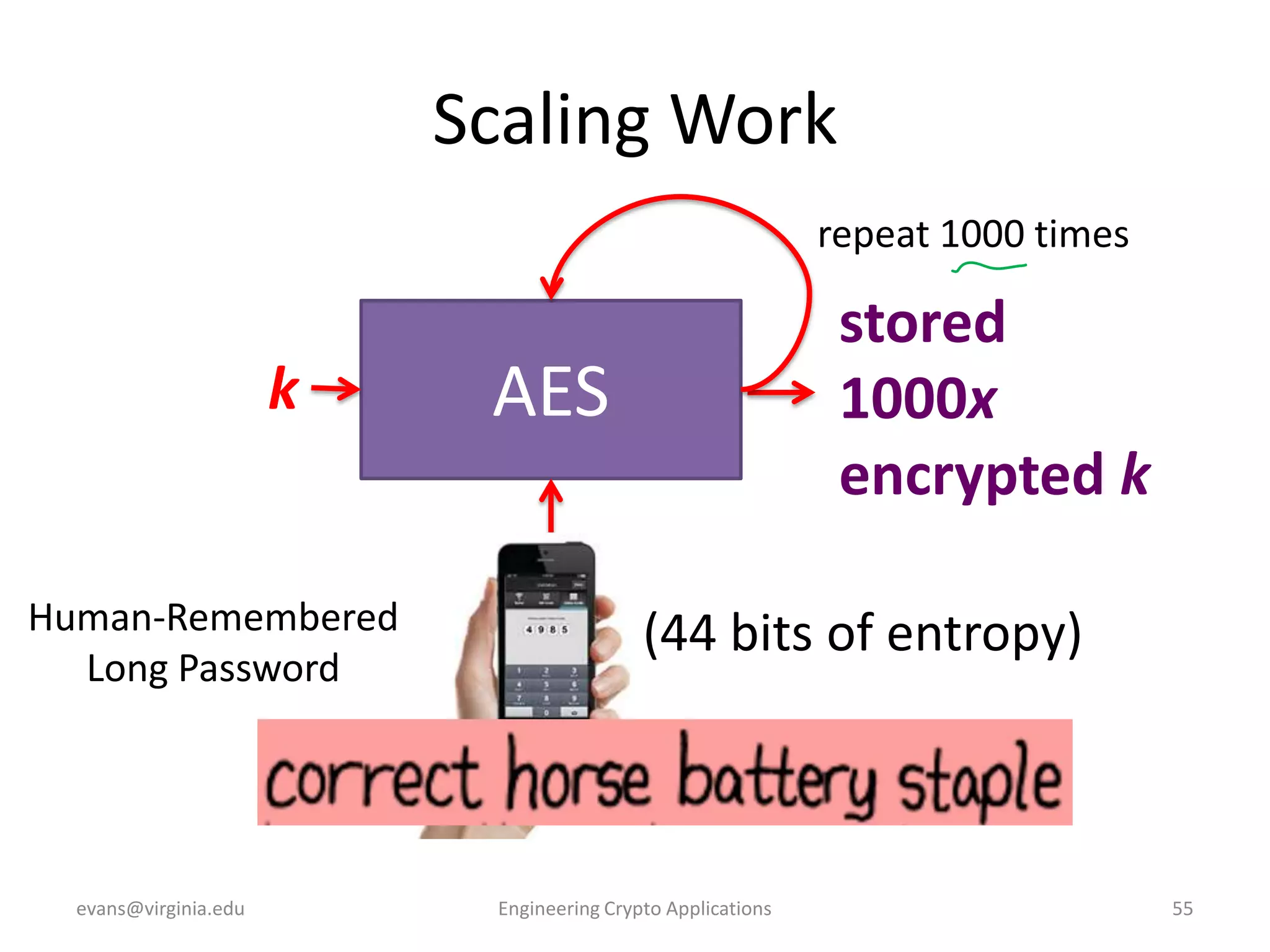
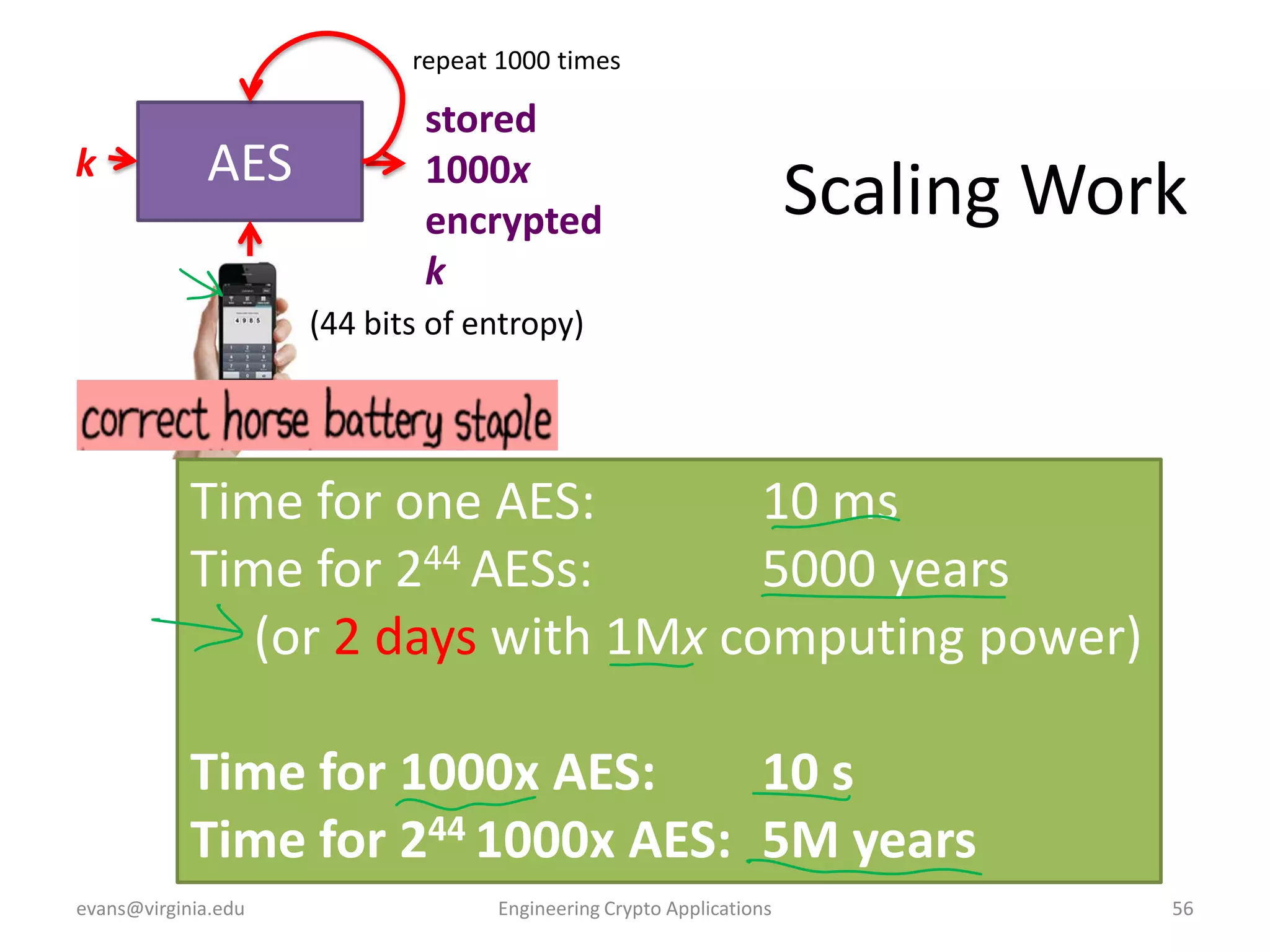
This document discusses using symmetric encryption for applications beyond simple transmission of encrypted messages. It covers generating cryptographically secure random keys, using block cipher modes like CBC and CTR to encrypt files, and securely storing encryption keys and initialization vectors. Generating true randomness is impossible, so physical sources must be amplified with cryptographic pseudorandom number generators. Commonly used block cipher modes like ECB leak information, while CBC and CTR avoid this if properly implemented with random or changing nonces/IVs. Storing keys securely, such as encrypting them with a password-derived key, is also important for practical encrypted storage systems.






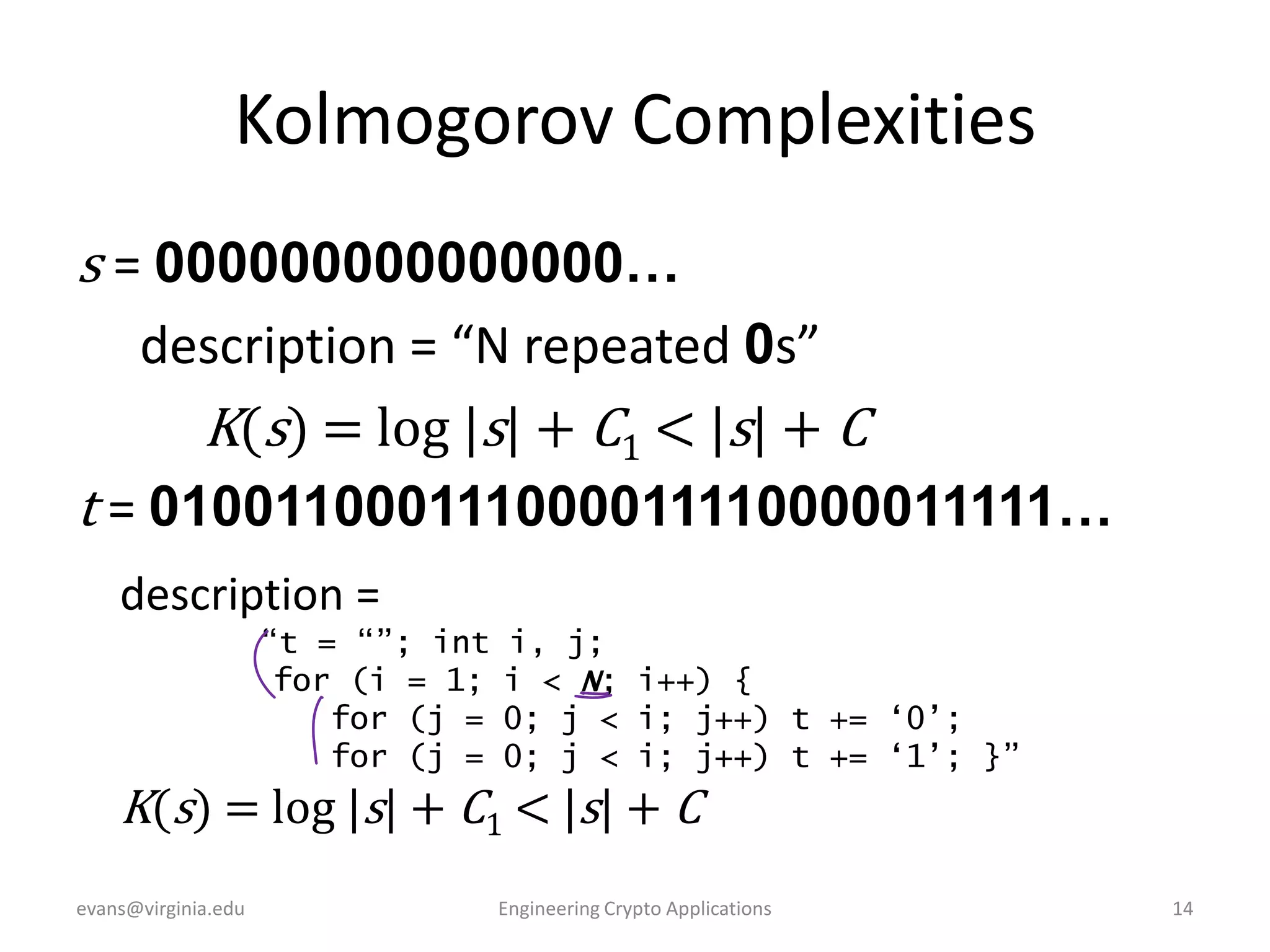
![Kolmogorov Complexities
r=010110000111101100001110111010000000011101
100000001110110110010111110011011110010000011
100000011101110000000111010100100010100000101
000010011101110111111110011000101…
"from Crypto.Random import random
def random_sequence(n):
return map(lambda x: random.choice([0, 1]), range(n)) "
and
state of random module (and any entropy added during
generation)
Hmmm…maybe answer from earlier slide was wrong!
evans@virginia.edu
Engineering Crypto Applications
15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day2-used-131016123610-phpapp01/75/Engineering-Cryptographic-Applications-Using-and-Misusing-Symmetric-Ciphers-16-2048.jpg)
















![Early Password Schemes
UserID
benf
Password
flyakite
samadams beer
tj
Monti07cello04
…
Login: tj
Password: wahoo
Failed login.
Guess again.
…
authentication check:
guess == users[userID].password
evans@virginia.edu
Engineering Crypto Applications
60](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day2-used-131016123610-phpapp01/75/Engineering-Cryptographic-Applications-Using-and-Misusing-Symmetric-Ciphers-61-2048.jpg)
![Early Password Schemes
UserID
Password
benf
samadams
tj
…
FAIL Login: tj
Password: wahoo
beer
someone who gets
Failed login.
Guess again.
Monti07cello04
password file learns
…
all passwords
flyakite
authentication check:
guess == users[userID].password
evans@virginia.edu
Engineering Crypto Applications
61](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day2-used-131016123610-phpapp01/75/Engineering-Cryptographic-Applications-Using-and-Misusing-Symmetric-Ciphers-62-2048.jpg)
![Encrypted Passwords Scheme
UserID
benf
Password
AESK(flyakite)
samadams AESK(beer)
tj
AESK(Monti07cello04)
…
Master key K
Store passwords
encrypted using K
…
authentication check:
AESK(guess) == users[userID].password
evans@virginia.edu
Engineering Crypto Applications
62](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day2-used-131016123610-phpapp01/75/Engineering-Cryptographic-Applications-Using-and-Misusing-Symmetric-Ciphers-63-2048.jpg)
![Encrypted Passwords Scheme
UserID
benf
Password
FAIL Master key K
AES (beer)
Store passwords
someone who gets
encrypted using K
AES (Monti07cello04)
password file and K
…
learns all passwords
AESK(flyakite)
samadams
tj
K
K
…
authentication check:
AESK(guess) == users[userID].password
evans@virginia.edu
Engineering Crypto Applications
63](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day2-used-131016123610-phpapp01/75/Engineering-Cryptographic-Applications-Using-and-Misusing-Symmetric-Ciphers-64-2048.jpg)
![Hashed Passwords Scheme
UserID
benf
Password
AESflyakite(0)
samadams AESbeer(0)
tj
AESMonti07cello04(0)
…
Store passwords
by using them as
key to encrypt 0
…
authentication check:
AESguess(0) == users[userID].password
evans@virginia.edu
Engineering Crypto Applications
64](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day2-used-131016123610-phpapp01/75/Engineering-Cryptographic-Applications-Using-and-Misusing-Symmetric-Ciphers-65-2048.jpg)
![Hashed Passwords Scheme
UserID
benf
Password
AESflyakite(K)
FAIL
samadams AESbeer(K)
tj
AESMonti07cello04(K)
…
…
Master key K
Store passwords
by using them to
encrypt K
authentication check:
AESguess(K) == users[userID].password
evans@virginia.edu
Engineering Crypto Applications
65](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day2-used-131016123610-phpapp01/75/Engineering-Cryptographic-Applications-Using-and-Misusing-Symmetric-Ciphers-66-2048.jpg)