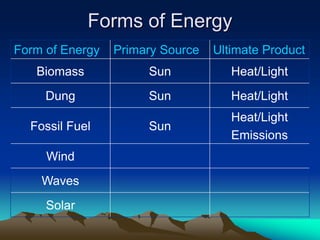
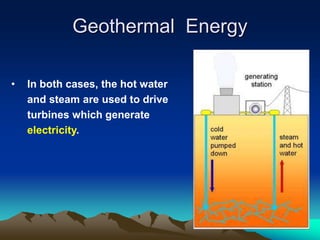
This document discusses different forms of energy, how they are transformed from one type to another, and their sources. It explains that the sun is the primary source of energy for many forms, either directly through solar power or indirectly through processes like photosynthesis. However, some forms of energy like geothermal, nuclear, and hydroelectric do not rely directly on the sun. Geothermal uses heat from the Earth's interior, nuclear harnesses energy from radioactive elements, and hydroelectric captures the kinetic energy of moving water.