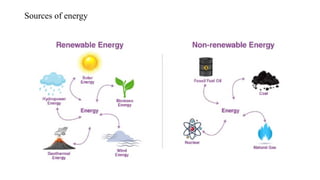
The document outlines the classification of energy sources into renewable and non-renewable categories. Renewable energy sources include solar, wind, tidal, hydraulic, geothermal, and biomass, while non-renewable sources consist of natural gas, coal, oil, and nuclear energy. Additionally, it describes various energy types such as gravitational, kinetic, mechanical, chemical, electrical, sound, and thermal energy, along with different types of power plants.